Chapter 04 - World History, Vol. 1 - OpenStax (Audiobook)
TLDRThis comprehensive audiobook transcript delves into the rich tapestry of ancient Near Eastern history, spanning from the dawn of the Iron Age around 1200 BCE to the rise of the Persian Empire under Darius the Great. It explores the Assyrian Empire's military conquests, the geopolitical dynamics of the ancient Near East, and the cultural heritage shared by various city-states. The narrative traverses the establishment of the Babylonian Kingdom by Hammurabi, the Hittites' rise and fall, and the Late Bronze Age collapse that reshaped the region. It also highlights the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian Empires' dominance, the intricate world of diplomacy and trade, and the daily life and social structure of these ancient civilizations. The text further examines the Egyptian New Kingdom's era of expansion and cultural achievements, the impact of the Hyksos on Egyptian society, and the New Kingdom Pharaohs' monumental building projects and military campaigns. The Persian Empire's administrative innovations, the development of Zoroastrianism, and its influence on Judean, Christian, and Islamic traditions are also discussed. The Hebrew's unique monotheistic faith and their history, from the patriarch Abraham to the Babylonian exile and the Persian period, are explored, emphasizing the evolution of Judaism and its adaptation to urban life. This audiobook is an invaluable resource for learners, providing a gateway to the past through the Los Angeles Harbor College Foundation and available on various platforms.
Takeaways
- 📚 The Assyrians were known for their highly trained armies and efficient state organization, which allowed them to create one of the largest empires the Near East had seen by the Iron Age.
- 🏰 The city of Babylon rose to power under Hammurabi in the 18th century BCE, establishing a new Mesopotamian Empire that stretched from the Euphrates River to the Persian Gulf.
- 🌐 The Hittites, an Indo-European speaking group, expanded from Anatolia into Syria and Mesopotamia, eventually engaging in a major conflict with Egypt at the Battle of Kadesh.
- 🔍 The Neo-Assyrian Empire is distinguished from the Old and Middle Assyrian Empires and is known for its calculated frightfulness and use of forced deportation to subdue rebellions.
- ⚔️ The Neo-Babylonian Empire, under King Nebuchadnezzar II, gained control over Mesopotamia, Syria, and Phoenician ports, and was known for its military campaigns against Egypt.
- 🤝 Diplomacy in ancient Mesopotamia was complex, with alliances, marriages, ambassadorial exchanges, and spy networks all playing a role in maintaining relationships between kingdoms.
- 🛣️ The Assyrians and other empires maintained extensive road networks to facilitate trade and the movement of armies, which was essential for the flow of goods and resources.
- 🏛️ The social structure of the ancient Near East was hierarchical, with distinct classes such as nobles, commoners, and the enslaved, each with different legal statuses and rights.
- 🎭 The New Kingdom of Egypt represents the height of Egyptian power, with Pharaohs like Amenhotep I, Queen Hatshepsut, and Ramesses II expanding Egypt's influence and constructing monumental architecture.
- 🔥 Akhenaten's shift to monotheistic worship of the Aten was a significant religious transformation in Egypt, though it was later reversed after his death.
- 📜 The Hebrew Bible, or Old Testament, provides a detailed history of the Hebrew people, their faith, and their interactions with the Near East, but its historical accuracy is a subject of scholarly debate.
Q & A
What significant role did the Assyrian Empire play in the ancient Near East?
-The Assyrian Empire, known for its highly trained armies and efficient state organization, expanded significantly out of northern Mesopotamia during the Iron Age around 1,200 BCE. They established one of the largest empires in the Near East at the time, relying on ruthless military tactics and a network of royal roads to maintain and manage their empire.
How did the Assyrians manage to maintain control over their vast empire?
-The Assyrians maintained control over their empire through a combination of ruthless military tactics, efficient state organization, and a wide network of royal roads that facilitated rapid communication and troop movement across the empire.
What impact did the Assyrian conquests have on the Kingdom of Israel?
-The Assyrians conquered the Kingdom of Israel in the 8th Century BCE, which was one of the significant conquests that expanded their empire. This event was crucial as it demonstrated the military might of the Assyrians and their influence over the region.
What technological and organizational innovations were introduced during the chaos of ancient Near Eastern conflicts?
-The chaos and rivalry in the ancient Near East led to significant innovations, particularly in military technology. These included advancements in weaponry and the organization of armies, which were crucial for the various empires to maintain and expand their territories.
Who was Sargon of Akkad, and what was his significance in Mesopotamian history?
-Sargon of Akkad, ruling around 2300 BCE, built the first empire in Mesopotamia, known as the Akkadian Empire. His model of imperial expansion and administration set a precedent followed by successive regional powers, marking a new era in Near Eastern history.
What were the major contributions of Hammurabi to the Mesopotamian civilization?
-Hammurabi is best known for his law code, one of the oldest deciphered writings of significant length in the world. During his reign in the 18th century BCE, he also transformed Babylon into a major power center of Mesopotamia, significantly expanding its territory and influence.
What led to the decline of the Neo-Assyrian Empire?
-The decline of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in the late 7th Century BCE was due to internal strife, administrative problems, and the rising powers of Babylonia and Media. These factors culminated in military defeats and loss of territories, leading to the empire's downfall.
How did the Babylonians and Medes react to the weakening of the Neo-Assyrian Empire?
-The Babylonians and Medes took advantage of the weakening Neo-Assyrian Empire by forming an alliance and launching attacks that eventually led to the fall of Assyria. In 612 BCE, they captured and destroyed the Assyrian capital of Nineveh, marking the end of the empire.
What role did the Hittites play in the history of the Near East?
-The Hittites emerged as a significant power in Anatolia around 1650 BCE and expanded their influence into Syria and other parts of the Near East. They are known for their military might, including their use of chariots, and their conflicts with Egypt, notably the Battle of Kadesh in 1274 BCE.
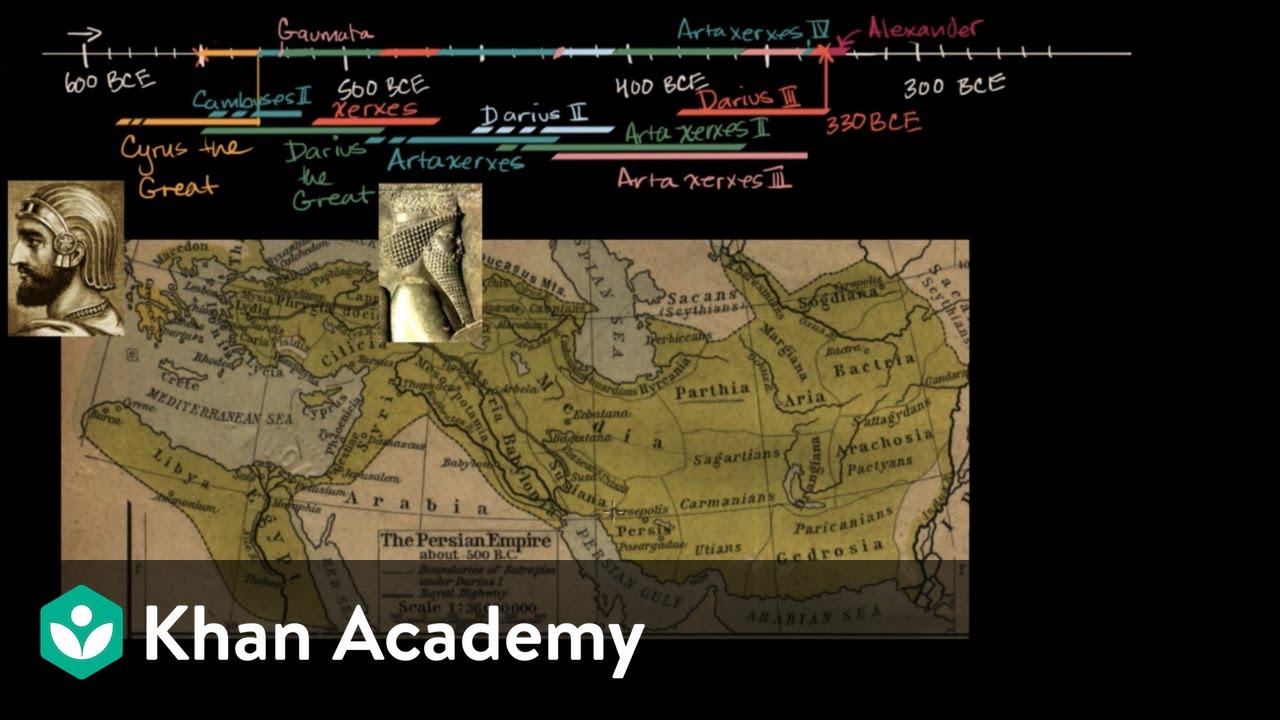
Describe the Persian Empire's method of administration and communication.
-The Persian Empire, under leaders like Darius the Great, developed an efficient administrative system divided into satrapies, each governed by a satrap. They maintained control and communication across the vast empire through a network of Royal Roads and a system of mounted couriers, enabling rapid transmission of messages and orders.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to World History and the Ancient Near East
The script introduces an open-source textbook and audiobook on world history, focusing on the period from the dawn of civilization to 1500 CE. It promotes the availability of courses at Los Angeles Harbor College and mentions the importance of studying the ancient Near East, which saw the rise and fall of numerous empires, including the Assyrians, known for their military prowess and significant regional legacy. The Assyrians' conquests, including the Kingdom of Israel and Egypt, as well as their use of military tactics and infrastructure like the Royal Roads, are highlighted. The text also emphasizes the interconnectedness of the region's history, shaped by common cultural heritages and periods of rivalry and conflict.
🏺 The Rise and Fall of Ancient Mesopotamian Empires
This paragraph delves into the history of Mesopotamia, discussing the rise of powerful city-states and empires, such as those of Sargon of Akkad and Hammurabi's Babylonian Kingdom. It outlines the political, military, and social structures that allowed these civilizations to thrive and expand. The narrative also touches on the fall of these empires, including the invasion of the Hittites and the subsequent decline of the Hittite Empire, which was once a dominant power in the Near East. The paragraph underscores the significance of diplomacy, trade, and military strategy in the complex geopolitical landscape of the ancient Near East.
🛣️ The Assyrian Empire and Its Legacy
The focus shifts to the Neo-Assyrian Empire, detailing its resurgence under Ashurnasirpal II and its rise to dominance in the Near East. The paragraph highlights the empire's military innovations, including the use of specialized troops and advanced weaponry, which allowed it to conquer vast territories. The narrative also discusses the empire's eventual downfall due to the combined forces of Babylonia and Media, leading to the division of its territories. The lasting impact of the Assyrian military strategies and statecraft on the region is emphasized.
🎓 Diplomatic Relations and Trade in Ancient Mesopotamia
This section explores the diplomatic strategies and trade networks of the Mesopotamian city-states, kingdoms, and empires. It discusses the importance of alliances, marriages, and diplomatic emissaries in maintaining peace and fostering cooperation. The role of gift-giving, ambassadors, and spies in international relations is also examined. Additionally, the paragraph covers the significance of trade for acquiring essential resources and the efforts made by empires to secure and maintain trade routes.
🏛️ Daily Life, Family, and Religion in Ancient Near East
The paragraph provides insights into the daily life, social structure, and religious practices of the ancient Near East civilizations. It describes the social hierarchy, ranging from nobles to the enslaved, and the legal distinctions that existed among these classes. The family structure, living conditions, and the role of religion in everyday life are also detailed. The narrative highlights the polytheistic religious systems, the importance of temples and priesthoods, and the influence of religious beliefs on culture and law.
🏺 The Assyrian Social Hierarchy and Military Organization
This section delves into the social hierarchy of the Assyrian Empire, from the enslaved to the king, who was considered a viceroy of the gods. It outlines the professional classes, including skilled workers and merchants, and the importance of the military in Assyrian society. The paragraph also discusses the Assyrian king's role in religious and military affairs, the significance of divination, and the empire's use of calculated frightfulness and forced deportation to maintain control.
🌞 The Hittite and Egyptian Interactions
The script contrasts the Hittite society, which was primarily rural and practiced chattel slavery, with the more urbanized societies of the Near East. It highlights the Hittites' religious practices and the importance of the king as the high priest. The paragraph then transitions to the New Kingdom period of Egypt, discussing the expulsion of the Hyksos and the subsequent expansionist conquests that made Egypt a superpower of its time. The narrative also touches on the innovations and cultural exchanges that occurred during this period.
🏰 The New Kingdom Pharaohs and Their Architectural Legacy
This section focuses on the New Kingdom period in Egypt, marked by the reign of powerful pharaohs who expanded Egypt's territories and built impressive architectural wonders. It details the military campaigns, religious innovations, and construction projects undertaken by pharaohs such as Ahmose, Amenhotep I, Hatshepsut, Akhenaten, and Ramesses II. The narrative also explores the religious reforms of Akhenaten and the subsequent return to traditional worship under Tutankhamun and the Ramesside kings.
📜 The End of the New Kingdom and the Persian Conquest
The final paragraph discusses the decline of the New Kingdom due to internal and external pressures, including the rise of the Assyrian Empire and the migration of the Sea Peoples. It outlines the rise of Persia under Cyrus the Great and the subsequent conquest of Mesopotamia, Syria, Canaan, and Egypt, leading to the establishment of the largest empire in the Near East at the time. The paragraph concludes with the death of Cyrus and the ascension of his son, Cambyses II, marking the transition to the Achaemenid Persian Empire.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Assyrian Empire
💡Hammurabi
💡Hittite Empire
💡Neo-Assyrian Empire
💡Late Bronze Age Collapse
💡Zoroastrianism
💡Persian Empire
💡Hebrews
💡Mesopotamia
💡Royal Roads
💡Babylonian Exile
Highlights
The Iron Age in the Near East began around 1,200 BCE with the rise of the Assyrian Empire, which expanded from northern Mesopotamia and became the largest empire the region had seen to date.
Archaeological finds and textual documentation, including the Bible, have helped historians piece together the history of the Assyrian state.
The Assyrians' military tactics, efficient state organization, and Royal Roads contributed to their ability to hold a vast empire together.
The Assyrians conquered the Kingdom of Israel in the 8th century BCE and added Egypt to their lands in the 7th century BCE.
The Hittites, an Indo-European speaking group from Anatolia, rose to power in the 1600s BCE and had a significant impact on the political landscape of the Near East.
The Hittite Empire's battle with Egypt in the 1200s BCE, known as the Battle of Kadesh, led to one of the earliest recorded peace treaties in history.
The Neo-Assyrian Empire emerged after the decline of the Hittite Empire and became dominant in the Near East through a combination of military conquest and diplomacy.
The Neo-Babylonian Empire, under King Nebuchadnezzar II, expanded its control after the fall of the Assyrian Empire, engaging in wars to weaken Egypt's power.
Diplomatic relationships in Mesopotamia were maintained through alliances, marriages, ambassadorial exchanges, and the giving of gifts between kingdoms.
Long-distance trade was vital for the Mesopotamian city-states, with resources like stone, timber, and metal ores being scarce and procured from distant locations.
The social structure of the Babylonians during the Old Babylonian period included nobles, commoners, and the enslaved, each with different legal statuses and rights.
The Neo-Assyrian military was a highly trained, professional standing army that employed specialized groups and technology, making it the most modern and efficient in the ancient world.
The Egyptian New Kingdom (1550-1069 BCE) marked the height of Egyptian power and influence, with Pharaohs like Ramesses II expanding Egypt's reach and engaging in significant building campaigns.
The Amarna Period, under Pharaoh Akhenaten, was a unique era where Egypt shifted to a monotheistic religion centered around the sun god Aten, before reverting back to traditional religious practices.
The Persian Empire, under Cyrus the Great and Darius I, became the largest empire in the Near East, with an efficient administration system and respect for local traditions that facilitated its vast territorial control.
The Hebrew Bible, or Old Testament, provides a history of the Hebrew people, their religious development, and the formation of Judaism, which has influenced Christianity and Islam.
The development of monotheism among the Hebrews was a gradual process, with archaeological evidence suggesting a mix of polytheistic and monotheistic practices coexisted for some time.
The Babylonian exile was a period of cultural and religious revival for the Judeans, during which the core of the Hebrew Bible was edited and assembled, shaping the foundations of Judaism.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Cyrus the Great establishes the Achaemenid Empire | World History | Khan Academy

History of Every ANCIENT Empire, i guess...

Chapter 09 - World History, Vol. 1 - OpenStax (Audiobook)

Chapter 06 - World History, Vol. 1 - OpenStax (Audiobook)

Ancient Mesopotamia | Early Civilizations | World History | Khan Academy

Overview of ancient Persia | World History | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: