MELC-Based Science 7 Lesson || Describing Motion || Acceleration
TLDRThe video script introduces the concept of acceleration, explaining it as the rate of change in an object's speed or velocity. It clarifies that acceleration occurs when there is a change in speed, direction, or both, and distinguishes between positive acceleration and deceleration. The script provides a formula for calculating acceleration and illustrates it with examples, such as a car accelerating from rest and a cyclist changing speed. The examples demonstrate how to apply the formula to find average acceleration in different scenarios, emphasizing the physical interpretation of the results, including the significance of negative acceleration values.
Takeaways
- 📚 Acceleration is the rate of change in speed or velocity of an object, providing insight into how quickly an object speeds up or slows down.
- 🚀 An object is considered to be accelerating if its speed, direction, or both change over time.
- 📈 The three conditions for acceleration are: change in speed, change in direction, or both.
- 🚴♂️ An example of speed change is a cyclist reducing their speed from 60 km/h to 40 km/h.
- 🔄 An example of direction change is an object moving first north, then south at a constant speed.
- 🔽 Positive acceleration refers to an increase in speed or velocity, while deceleration is a decrease.
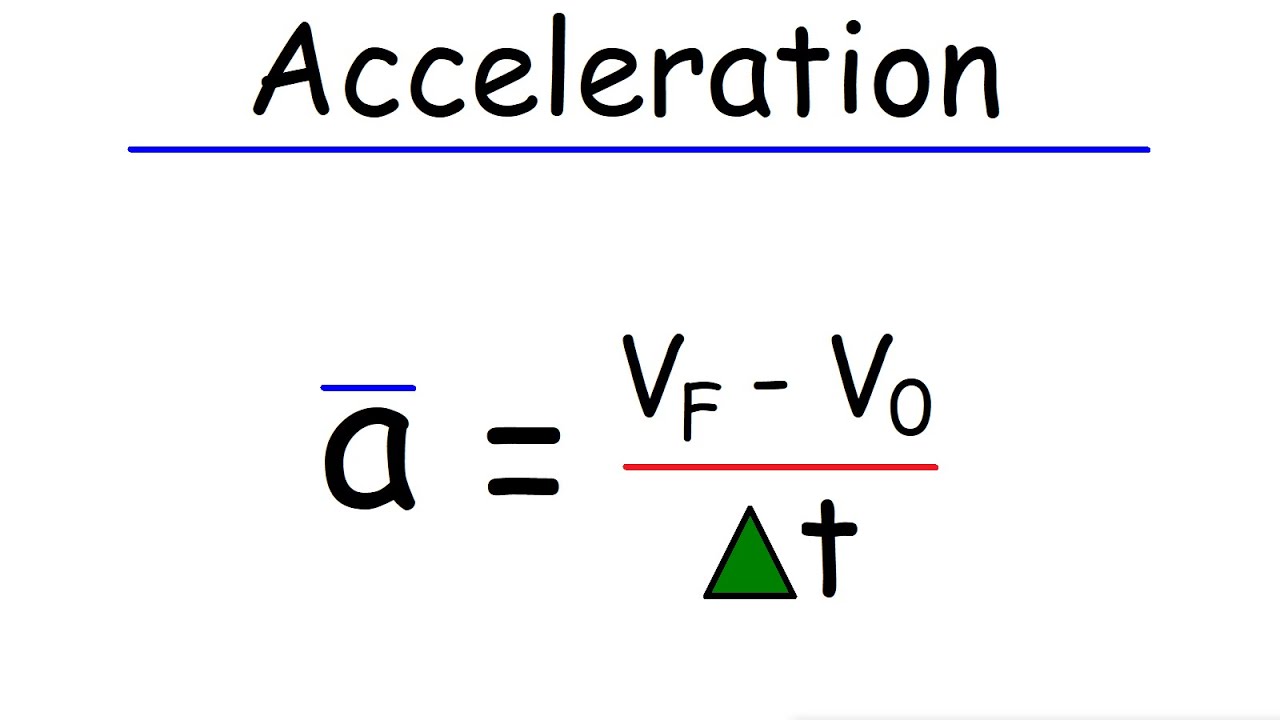
- 📝 The formula for calculating acceleration is: acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time.
- 🚗 In a given problem, a car accelerates from rest to 24 m/s in 6 seconds, resulting in an average acceleration of 4 m/s².
- 🚴♂️ Another example involves a cyclist who decelerates, with an acceleration of negative four kilometers per hour square, when changing speed from 60 km/h to 40 km/h over five hours.
- 🌐 Acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²) and indicates the change in velocity over time.
- 📊 Understanding acceleration is crucial for describing the motion of an object in terms of distance, speed, and velocity.
Q & A
What is the main topic of this video?
-The main topic of this video is the concept of acceleration and how it relates to the motion of an object.
What are the three essential kinematic quantities discussed in the video?
-The three essential kinematic quantities discussed in the video are distance or displacement, speed or velocity, and acceleration.
How can an object be considered as accelerating?
-An object is considered as accelerating if it changes its speed, direction, or both. This can be exemplified by a cyclist slowing down, a dog changing its running direction, or a man running in opposite directions with different speeds.
What is the definition of positive acceleration?
-Positive acceleration refers to an increase in speed or velocity of an object.
What is the term used for a decrease in speed or velocity?
-A decrease in speed or velocity is referred to as deceleration.
How is acceleration calculated?
-Acceleration is calculated using the formula: acceleration equals the change in velocity divided by time, or acceleration equals the final velocity minus the initial velocity divided by time. The unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s^2).
What is the average acceleration of a car that accelerates from rest to 24 m/s in 6 seconds?
-The average acceleration of the car is 4 meters per second squared (4 m/s^2), using the formula: (24 m/s - 0 m/s) / 6 s = 4 m/s^2.
What was the acceleration of a cyclist who changed speed from 60 km/h to 40 km/h in 5 hours?
-The cyclist's acceleration was negative four kilometers per hour squared (negative 4 km/h^2), indicating deceleration.
What does the negative sign in acceleration indicate?
-The negative sign in acceleration indicates that the object is decelerating, or slowing down.
Why is it important to distinguish between speed and velocity when discussing motion?
-It is important to distinguish between speed and velocity because speed is a scalar quantity that refers to 'how fast an object is moving,' while velocity is a vector quantity that refers to 'the rate at which an object changes its position.' Understanding this distinction helps in accurately analyzing and describing the motion of objects.
How does the concept of acceleration relate to Newton's second law of motion?
-Acceleration is directly related to Newton's second law of motion, which states that the net force acting on an object is equal to the product of the object's mass and its acceleration (F_net = m * a). This law helps us understand how forces cause changes in an object's motion.
What is the significance of understanding acceleration in physics?
-Understanding acceleration is crucial in physics as it allows us to predict and analyze the motion of objects under various conditions, which is essential in fields such as mechanics, aerospace engineering, and even sports science.
Outlines
🚀 Introduction to Acceleration
This paragraph introduces the concept of acceleration, emphasizing its importance in understanding an object's motion. It explains that objects do not always move at a constant speed or velocity and may change their speed or direction, or both. Acceleration is defined as the rate of change in speed or velocity, providing insight into how quickly an object speeds up or slows down. The paragraph outlines the conditions under which an object is considered to be accelerating: a change in speed, a change in direction, or both. It also introduces the terms 'positive acceleration' for an increase in speed and 'deceleration' for a decrease in speed. The formula for calculating acceleration is presented, and a problem-solving example is provided to illustrate the concept.
📉 Negative Acceleration in Cyclist's Speed Change
This paragraph focuses on a specific example of acceleration, highlighting the case of a cyclist who decelerates from 60 kilometers per hour to 40 kilometers per hour over a period of five hours. The summary emphasizes the negative sign in the calculated acceleration value, indicating a decrease in speed. The concept of negative acceleration is directly related to deceleration, as previously defined. The example serves to reinforce the understanding of how acceleration, whether positive or negative, can be calculated and applied to real-world scenarios.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Acceleration
💡Displacement
💡Speed
💡Velocity
💡Deceleration
💡Final Velocity
💡Initial Velocity
💡Time
💡Meter per Second Squared (m/s^2)
💡Positive Acceleration
💡Formula
Highlights
The lesson focuses on understanding acceleration and its impact on the motion of an object.
Objects do not always move at a constant speed or velocity; they can change in speed or direction.
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change in speed or velocity of an object.
An object is considered to be accelerating if its speed or direction changes.
Three conditions for acceleration are: changing speed, changing direction, or both.
Positive acceleration refers to an increase in speed or velocity.
Deceleration is the term used for a decrease in speed or velocity.
The formula for calculating acceleration is the change in velocity divided by time.
The SI unit for acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s^2).
A car's average acceleration can be calculated using the given initial velocity, final velocity, and time.
In the example, the car's average acceleration is 4 meters per second squared.
A cyclist's acceleration can be negative, indicating deceleration.
The negative sign in acceleration denotes a decrease in speed, as illustrated by the cyclist example.
Understanding acceleration is crucial for describing the motion of an object in terms of distance, speed, and direction.
The lesson provides practical applications of acceleration through real-world examples.
The concept of acceleration applies to both linear and multi-dimensional motion.
The lesson emphasizes the importance of accurately calculating acceleration for a comprehensive understanding of motion.
The video aims to enhance learners' ability to describe and analyze the motion of objects.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Calculus - Position Average Velocity Acceleration - Distance & Displacement - Derivatives & Limits

Physics - What is Acceleration | Motion | Velocity | Infinity Learn NEET

Acceleration | Physics

What is Acceleration?
Average Acceleration and Instantaneous Acceleration

What is Speed, Velocity & Acceleration? | Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: