Acceleration | Physics
TLDRThis educational video by Teach Talk introduces the concept of acceleration in physics, explaining it with relatable examples like a bike's components and their functions. It defines acceleration as the rate of change in velocity of an object and outlines three ways to change acceleration: by altering speed, decelerating, or changing direction. The video also presents a formula to calculate average acceleration and solves a sample problem involving a car coming to a stop. It concludes with a quiz to reinforce the concept, encouraging viewers to engage and learn about acceleration in a fun and accessible manner.
Takeaways
- 📚 The channel 'Teach Talk' focuses on making learning fun and easy, covering topics in general science, biology, chemistry, physics, and earth science.
- 🔔 Viewers are encouraged to subscribe and click the notification bell for updates on new videos.
- 🚲 Acceleration is likened to a bike, which has three main parts: pedals for acceleration, brakes for deceleration, and handlebars for changing direction.
- 📈 In physics, acceleration is defined as the rate of change in velocity of an object per unit of time.
- ⏩ Acceleration can occur by increasing speed, decreasing speed, or changing direction, even at constant speed.
- 🧮 The formula for average acceleration is given as the change in velocity over elapsed time, or 'a = (v_f - v_i) / t'.
- 🔍 Example problems in the video demonstrate how to calculate acceleration, including cases with initial velocity not equal to zero.
- 🚗 A negative acceleration indicates a decrease in speed, as shown in the example of a car coming to a stop.
- ✅ Two practice problems on acceleration are solved in the video, testing understanding of the concept.
- 👩🏫 The episode concludes with a call to action, encouraging viewers to subscribe, like, and share the video, and to participate by commenting their scores on the problems.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the concept of acceleration in physics, including its definition and examples of how it can change.
How is acceleration defined in physics?
-Acceleration is defined as the rate of change in velocity of a moving object per unit of time.
What are the three ways to change acceleration according to the video?
-The three ways to change acceleration are by increasing speed while traveling in a straight line, decreasing speed while traveling in a straight line, and changing direction even while traveling at a constant speed.
What is the formula used to calculate average acceleration?
-The formula used to calculate average acceleration is a = (change in velocity) / elapsed time, which can also be written as a = (v_f - v_i) / t, where v_f is the final velocity, v_i is the initial velocity, and t is the time.
How is the change in velocity calculated?
-The change in velocity is calculated by finding the difference between the final velocity (v_f) and the initial velocity (v_i), which is expressed as Δv = v_f - v_i.
What is the significance of the negative sign in the acceleration value?
-The negative sign in the acceleration value indicates that the object is slowing down or decreasing its speed.
In the sample problem, how does the car demonstrate negative acceleration?
-In the sample problem, the car demonstrates negative acceleration as it comes to a stop, slowing from 25 meters per second to 0 meters per second in 2.8 seconds, resulting in an acceleration of -8.93 meters per second squared.
How can you convert units to find the acceleration in the second problem?
-To find the acceleration, you need to convert the velocity from kilometers per hour to meters per second before applying the formula. In this case, 90 kilometers per hour is approximately 25 meters per second.
What is the final velocity when an object comes to a stop?
-When an object comes to a stop, its final velocity is 0 meters per second.
How can you find the time it takes for an object to stop given its acceleration and initial velocity?
-You can find the time it takes for an object to stop by rearranging the acceleration formula to solve for time: t = (v_f - v_i) / a. By substituting the given values, you can calculate the time required to stop the object.
Outlines
🚴 Introduction to Acceleration and Bike Analogy
This paragraph introduces the concept of acceleration in physics by using a relatable analogy of a bike. It explains that a bike has three main parts: pedals for acceleration, brakes for deceleration, and handlebar grip for changing direction. The paragraph then defines acceleration as the rate of change in velocity of an object per unit of time. It outlines three ways to change acceleration: by increasing speed, decreasing speed, or changing direction, even at a constant speed. The paragraph also presents the formula for calculating average acceleration (Δv/Δt or (v_f - v_i)/t) and provides an example of a car accelerating and decelerating to illustrate the concept.
📚 Solving for Acceleration with a Sample Problem
This paragraph focuses on solving for acceleration using a sample problem. It involves a car that comes to a stop, slowing down from 25 meters per second in 2.8 seconds. The paragraph explains how to use the given initial velocity, final velocity, and time to calculate the car's acceleration using the formula for acceleration. The solution process is detailed, showing the steps to arrive at the acceleration value of -8.93 meters per second squared, indicating the car's deceleration.
🏎️ Acceleration Quiz and Recap
This paragraph presents a quiz to test understanding of the concept of acceleration. It includes two problems: one where a car travels at 90 kilometers per hour from rest, and another where a driver needs to stop a chimney traveling at 50 meters per second with a negative acceleration of 0.5 meters per second squared. The paragraph provides the formulas and calculations needed to solve these problems, emphasizing the application of the concept of acceleration. It also recaps the main points from the video, including the definition of acceleration, the three ways an object can accelerate, and the formula to calculate it. The paragraph concludes with an invitation for viewers to share their scores and a reminder to subscribe, like, and share the video for collective learning.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Acceleration
💡Velocity
💡Bike Mechanics
💡Formula
💡Sample Problem
💡Deceleration
💡Direction Change
💡Initial Velocity
💡Final Velocity
💡Time Interval
💡Educational Content
Highlights
Introduction to Teacher Chain's 'Teach Talk' channel emphasizing learning as fun and easy.
Encouragement for first-time viewers to subscribe and activate notifications for upcoming videos.
Welcome to the episode focused on acceleration within the context of physics, targeted from grade 7 to grade 12 students.
Analogy of a bike to explain acceleration, highlighting its parts like pedals, brakes, and handlebar grip.
Definition of acceleration in physics as the rate of change in velocity per unit time.
Explanation of three ways to change acceleration: increasing speed, decreasing speed, and changing direction.
Introduction to the formula for calculating average acceleration.
Clarification on calculating change in velocity and the importance of understanding initial velocity in problems.
Example of a car's acceleration from start to gaining constant acceleration and then to stop with negative acceleration.
Step-by-step solution to a sample problem calculating the acceleration of a car coming to a stop.
Quick recap of the video's main points on acceleration, including definition, ways to accelerate, and formula application.
Introduction to quiz time for viewers to test their understanding of acceleration with two problems.
Solution to the first quiz problem regarding a car's acceleration over three hours from rest.
Solution to the second quiz problem on calculating the time it takes for a vehicle to come to a complete stop given its acceleration.
Invitation for viewers to share their quiz scores in the comment section.
Closing remarks encouraging viewers to subscribe, like, and share the video for collaborative learning.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

MELC-Based Science 7 Lesson || Describing Motion || Acceleration

What is Acceleration?
Calculus - Position Average Velocity Acceleration - Distance & Displacement - Derivatives & Limits
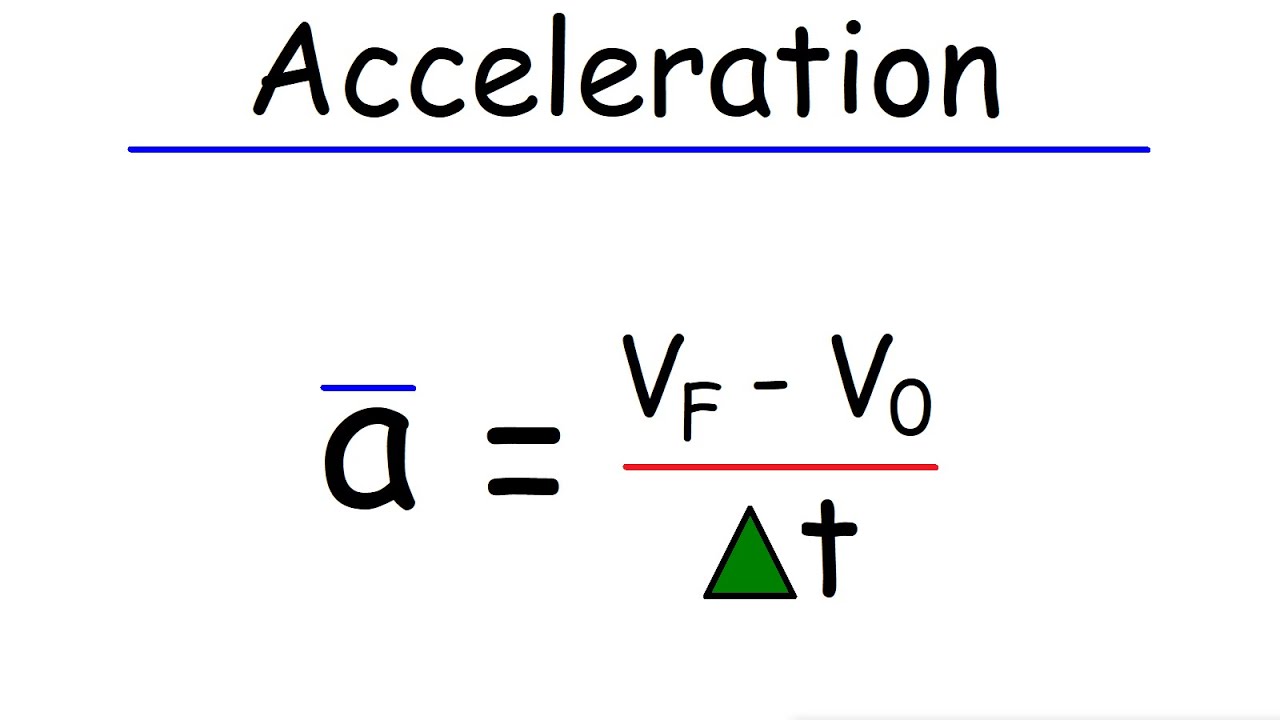
Average Acceleration and Instantaneous Acceleration

GCSE Physics Revision "Acceleration"
Uniform Circular Motion - IB Physics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: