What is Acceleration?
TLDRThis video script delves into the concept of acceleration, clarifying common misconceptions by differentiating between high speed and the physics definition of acceleration as the change in velocity. It outlines three methods to accelerate a car: using the accelerator, applying brakes (negative acceleration), and steering (changing direction). The script further explains how to measure acceleration, introduces the formula, and distinguishes between uniform and non-uniform acceleration, emphasizing that a body under acceleration is in non-uniform motion. The content is engaging, informative, and encourages audience interaction.
Takeaways
- 🚗 Acceleration in physics refers to the change in velocity, not necessarily an increase in speed.
- 🔽 There are three ways to accelerate a car: using the accelerator, applying the brakes (negative acceleration or retardation), and changing direction with the steering wheel.
- 📈 The formula for acceleration is the change in velocity (∆V) divided by the time taken (T), expressed as a = (Vf - Vi) / T, where Vf is the final velocity and Vi is the initial velocity.
- 📊 Velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (speed) and direction. Changes in either result in acceleration.
- 🔄 When an object's velocity is constant, there is no acceleration. Acceleration occurs when there is a change in speed or direction.
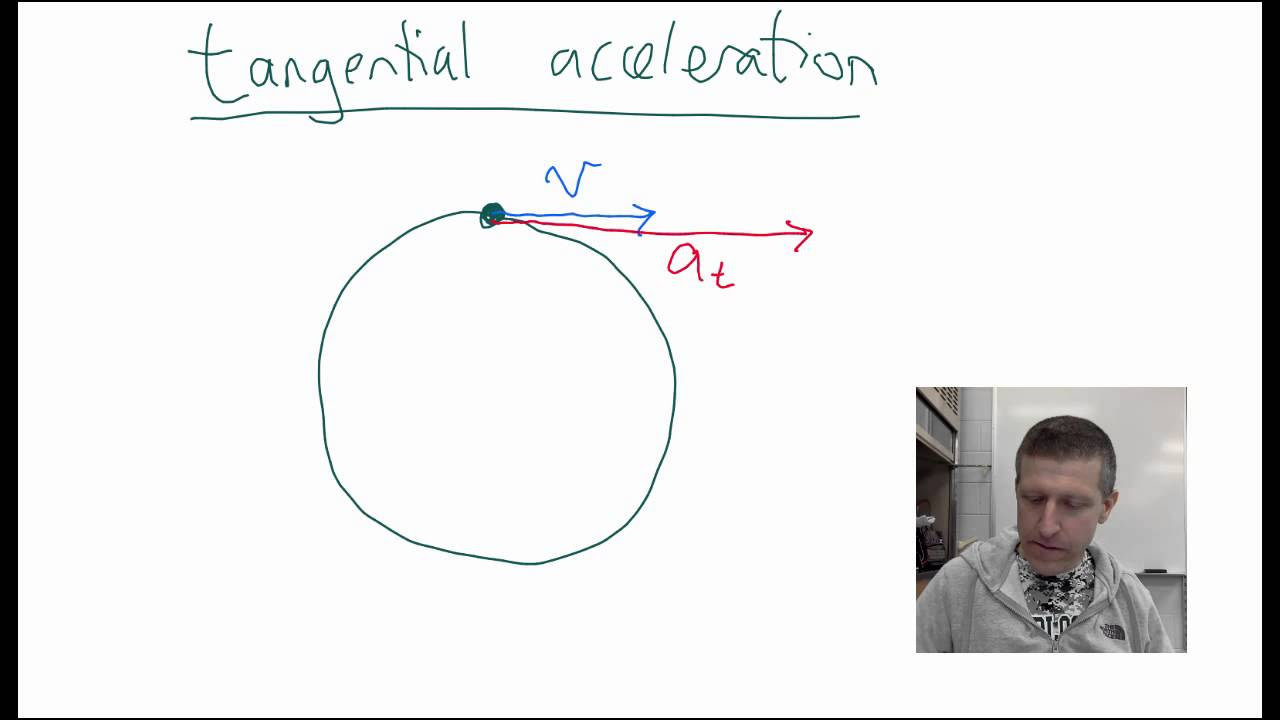
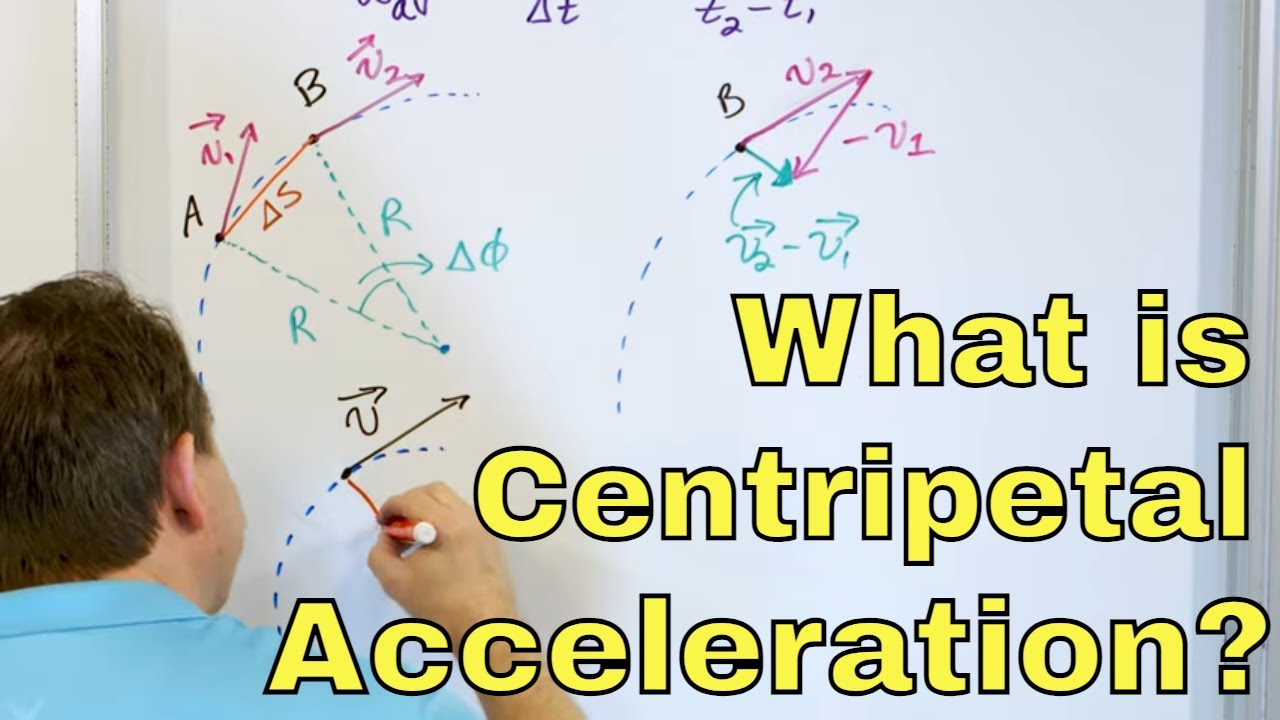
- 🎾 Examples of acceleration include a car increasing speed, a ball thrown upwards slowing down due to gravity (retardation), and a ball moving in a circular path at a constant speed.
- 🌐 The acceleration due to gravity is a uniform acceleration that affects all objects near the Earth's surface, approximately 9.8 m/s².
- 🚀 Uniform acceleration occurs when the rate of change of velocity is constant over time, such as an object falling under gravity's influence.
- 🛣 Non-uniform acceleration happens when the rate of change of velocity is not constant, as in the case of a car accelerating with varying force.
- 🔧 Force is the cause of acceleration. Different forces, like engine power or Earth's gravity, can cause an object to accelerate or decelerate.
- 📝 The unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s²), indicating the change in meters per second over one second.
Q & A
What is the correct definition of acceleration in physics?
-Acceleration is the change in velocity over time, which can involve increasing or decreasing speed or changing the direction of motion.
How does pressing the accelerator pedal affect a car's velocity?
-Pressing the accelerator pedal increases the car's speed, which means it increases the magnitude of the car's velocity.
What is the term for when acceleration results in a decrease in speed?
-When acceleration causes a decrease in speed, it is referred to as retardation or negative acceleration.
How can changing the direction of a car's motion be considered acceleration?
-Changing the direction of a car's motion is considered acceleration because it involves a change in the velocity, even if the speed remains constant.
What is the formula for calculating acceleration?
-The formula for calculating acceleration is a = (V - U) / T, where 'a' is the acceleration, 'V' is the final velocity, 'U' is the initial velocity, and 'T' is the time taken for the change in velocity.
What is the unit of acceleration?
-The unit of acceleration is meters per second squared (m/s^2).
Is a car under constant acceleration in uniform motion or non-uniform motion?
-A car under constant acceleration is in non-uniform motion because the velocity is changing over time.
What causes a ball to accelerate when it is dropped?
-A ball accelerates when it is dropped due to the force of Earth's gravity pulling it downwards.
What type of acceleration is experienced by a ball falling under the influence of gravity?
-A ball falling under the influence of gravity experiences uniform acceleration because the acceleration due to gravity is constant.
How can you determine if an object's motion is uniform or non-uniform?
-An object's motion is uniform if it maintains a constant velocity. If the velocity changes over time, either in magnitude or direction, the motion is non-uniform.
What are the three ways to change a car's velocity as discussed in the script?
-The three ways to change a car's velocity are by using the accelerator to increase speed, applying the brakes to decrease speed, and using the steering wheel to change the direction of motion.
Outlines
🚗 Understanding Acceleration
This paragraph introduces the concept of acceleration in physics, clarifying that it does not simply mean moving at high speeds but rather refers to the change in velocity. The speaker explains that there are three ways to accelerate a car: by using the accelerator to increase speed, applying the brakes to decrease speed, and steering to change direction. The paragraph emphasizes that acceleration is a vector quantity, involving both speed and direction, and provides examples to illustrate instances of acceleration and deceleration.
📐 Measuring and Examples of Acceleration
The second paragraph delves into how acceleration is measured, defining it as the rate of change of velocity over time. It presents the formula for calculating acceleration and applies it to various examples, including a car's motion and a ball's motion. The speaker distinguishes between uniform circular motion and non-uniform motion, and between uniform and non-uniform acceleration. The paragraph also touches on the concept of gravity and its role in acceleration, specifically the acceleration due to gravity.
🔢 Calculation and Forces Behind Acceleration
This paragraph focuses on the calculation of acceleration, using a car example to demonstrate how to apply the formula in practical scenarios. It highlights the difference between uniform acceleration, where the rate of change of velocity is constant, and non-uniform acceleration, where the rate varies over time. The speaker also introduces the concept that force causes acceleration, mentioning the force of the engine in a car or the force of gravity and brakes as examples. The paragraph concludes with an invitation for viewers to engage with the content by attempting questions related to the topic.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Acceleration
💡Velocity
💡Retardation
💡Steering Wheel
💡Brakes
💡Speedometer
💡Uniform Circular Motion
💡Formula of Acceleration
💡Uniform Acceleration
💡Non-Uniform Acceleration
Highlights
Acceleration in physics is defined as the change of speed or more precisely, change of velocity.
Acceleration does not necessarily mean going at a high speed; it can also involve a decrease in speed or change in direction.
There are three ways to accelerate a car: using the accelerator pedal, applying the brakes, and turning the steering wheel to change direction.
When the car's speed increases by pressing the accelerator, it is a positive acceleration.
Pressing the brakes to decrease the car's speed is also a form of acceleration known as retardation or negative acceleration.
Using the steering wheel to change the car's direction at a constant speed results in acceleration due to the change in velocity's direction.
Examples of acceleration include a car going at a constant speed in a straight line, dropping a pebble into water, catching a ball, throwing a ball up, and a ball going around in a circle at a constant speed.
Acceleration is measured as the change of velocity divided by time, and its unit is meter per second squared (m/s^2).
The formula for acceleration is given by a = (V - u) / T, where a is acceleration, V is final velocity, u is initial velocity, and T is time.
When a body is under acceleration, it is in non-uniform motion because its velocity is changing.
Uniform acceleration occurs when the acceleration is constant, such as in the case of a ball falling due to Earth's gravity.
Non-uniform acceleration happens when the acceleration changes over time, like when a car accelerates with varying increases in velocity.
Force causes acceleration, and examples include the force of an engine on a car, Earth's gravity, or the force of brakes causing retardation.
The video provides a comprehensive understanding of the concept of acceleration and its various applications in real-life scenarios.
The content is engaging and informative, encouraging viewers to participate by answering questions and sharing their thoughts in the comments section.
The video concludes with a call to action for viewers to like, comment, share, and subscribe to the channel for more educational content.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: