Force and Motion | Science for Kids
TLDRIn this educational video, we explore the fundamentals of force and motion in an interactive manner. Starting with the basics, we define force as a push or pull that can change an object's movement or direction, using everyday actions like opening a door as examples. We then delve into motion, illustrated by rolling a ball, and introduce the concept of gravity through dropping objects of varying weights. The video further explains friction, showcasing its effects by rubbing hands together. We cover Newton's first law of motion, the role of mass in movement, and the effects of air resistance. Concluding with fun facts and practical demonstrations, this video makes learning about physics engaging and accessible, encouraging viewers to observe these phenomena in their everyday lives.
Takeaways
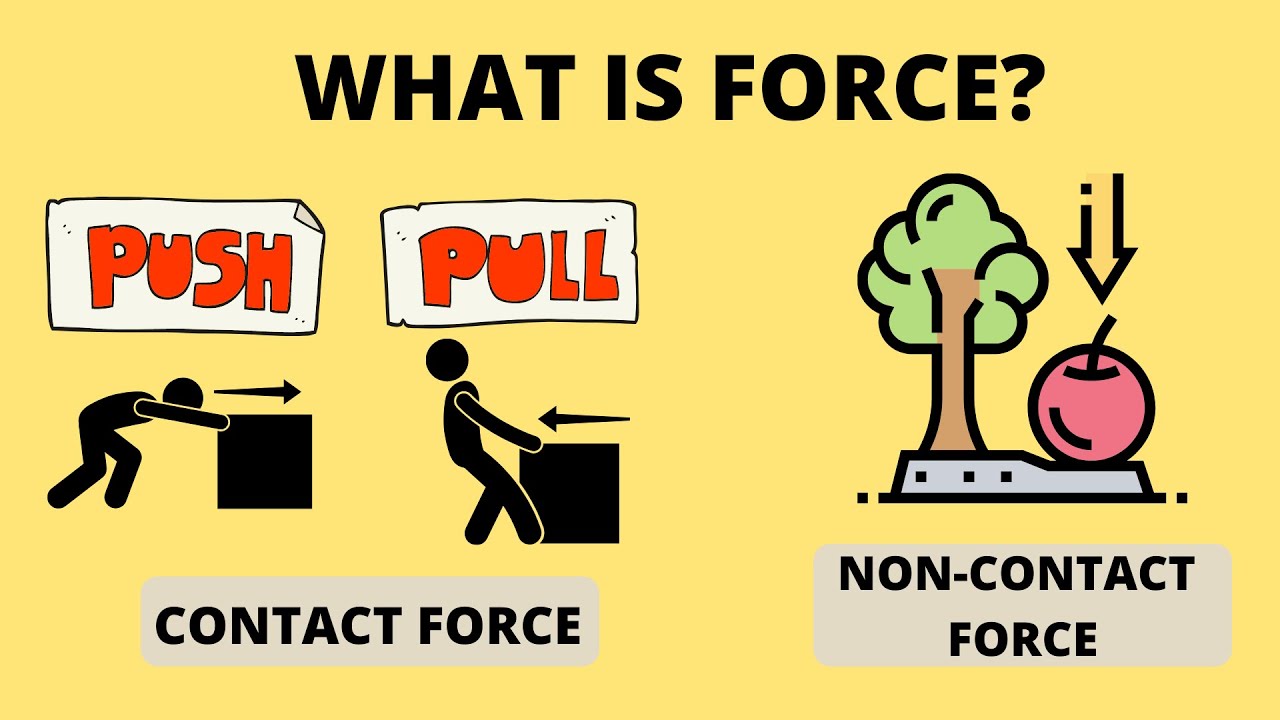
- 💪 Force is described as a push or pull that can cause objects to move or change direction.
- 🚶♂️ Motion is defined as the movement of an object from one place to another.
- ⏱️ Speed is calculated using the formula distance divided by time, illustrating how quickly an object moves over a certain distance.
- 🌍 Gravity is the force that attracts objects towards the center of the Earth, demonstrated by dropping objects from a height to observe their fall.
- 🤲 Friction is the resistance encountered when two surfaces slide against each other, observable by the heat generated when rubbing hands together.
- 🔧 Newton's first law of motion states that an object will remain in motion or at rest until acted upon by an external force.
- ⚖️ The amount of force needed to move an object is dependent on its mass, with heavier objects requiring more force.
- 🌬️ Air resistance is a form of friction that slows down objects moving through the air, such as parachutes or skydivers.
- 🚲 Forward motion on a bike or scooter is achieved by pushing against the pedals, with friction eventually bringing the vehicle to a stop when pedaling ceases.
- 🎾 Throwing a ball involves applying force to it; the harder you throw, the faster it moves, demonstrating the relationship between force and motion.
Q & A
What is force?
-Force is a push or a pull that can cause an object to move or change its direction.
Can you provide an everyday example of applying force?
-Opening and closing a door is an example of applying force. This includes twisting the doorknob and then pulling or pushing the door to open or close it.
What is motion?
-Motion is the movement of an object from one place to another.
How can motion be observed with a simple experiment?
-Rolling a ball across the floor is a simple way to observe motion. Watching how it moves helps understand the concept.
What is gravity?
-Gravity is the force that pulls objects towards the center of the Earth.
How can gravity be observed?
-Dropping objects of different weights from a height and observing how they fall is a great way to observe gravity.
What is friction?
-Friction is the force that opposes motion when two surfaces rub against each other.
How can friction be experienced in a simple way?
-Rubbing your hands together allows you to feel the heat generated by friction, thus experiencing friction.
What does Newton's first law of motion state?
-Newton's first law of motion states that an object in motion will stay in motion and an object at rest will stay at rest, unless acted upon by an outside force.
How does the amount of force needed to move an object relate to its mass?
-The heavier an object is, the more force is needed to move it. This relationship indicates that mass and force are directly related.
Outlines
🌟 Introduction to Force and Motion
This video introduces the concepts of force and motion in a simple and engaging manner. It begins by explaining what force is, illustrating it as a push or pull that can change an object's movement or direction, with the act of opening and closing a door serving as a practical example. The video then transitions to motion, defined as the movement of an object from one place to another, using the rolling of a ball as a demonstration. Speed is briefly touched upon, suggesting viewers time themselves over a distance and calculate speed using the formula distance/time. Gravity is introduced as the force that pulls objects toward Earth's center, with a suggestion to observe this by dropping objects of varying weights. Friction is described as a force that opposes motion between two surfaces, with an experiment of rubbing hands together to feel heat from friction. The video wraps up with fun facts about force and motion, highlighting how force can affect an object's speed, direction, and shape, and mentioning Newton's first law of motion. It concludes with examples of friction, gravity, air resistance, and the role of force in activities like biking and throwing a ball, emphasizing the measure of force in Newtons and the concept of kinetic energy.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Force
💡Motion
💡Gravity
💡Friction
💡Newton's First Law of Motion
💡Mass
💡Air Resistance
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Speed
💡Newton
Highlights
Introduction to force and motion
Definition of force as a push or pull
Example of force using a door
Definition of motion and its observation
Demonstration of motion with a rolling ball
Introduction to speed and its calculation
Explanation of gravity
Gravity observation through dropping objects
Understanding friction
Friction demonstration by rubbing hands
Fun facts about force and motion
Explanation of Newton's first law of motion
The role of mass in moving objects
Examples of friction in daily life
Discussion on gravity's role on Earth and in space
Air resistance and its effects on motion
How forces affect biking or scootering
Impact of throwing force on a ball's motion
Measurement of force in Newtons
Relationship between speed, kinetic energy, and motion
Conclusion and invitation to subscribe
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: