Empirical Research - Qualitative vs. Quantitative
TLDREmpirical research is a method of gaining or testing knowledge about reality through experience and observation. It is divided into two main types: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative research focuses on developing hypotheses by collecting soft data through interviews or observations, which are open-ended and flexible. Quantitative research, on the other hand, aims to test these hypotheses using hard data obtained from structured methods like surveys or experiments. The research process in qualitative studies is circular and less structured, allowing for loops and flexibility, while quantitative research follows a linear, well-structured process. Qualitative research often involves a small sample size for in-depth analysis, whereas quantitative research uses a large sample size for generalizing findings. This video script provides a comprehensive understanding of empirical research, its goals, and the differences between its qualitative and quantitative approaches.
Takeaways
- 📚 **Empirical Research Definition**: Empirical research involves gaining or testing knowledge about reality through experience or observation.
- 🎯 **Goal of Empirical Research**: The goal is to collect or test experiences about reality, which is divided into qualitative and quantitative research.
- 👥 **Qualitative Research Focus**: It is used to develop hypotheses, often through interviews or observations, and is well-suited for unknown research fields.
- 📊 **Quantitative Research Focus**: It is used to test hypotheses with measurable data, often through surveys or experiments, and is suited for well-known research areas.
- 🧐 **Data Collection in Qualitative Research**: Involves soft data like text, images, or videos, gathered through open-ended methods like interviews.
- 📈 **Data Collection in Quantitative Research**: Involves hard or numerical data, gathered through standardized methods like surveys, which can be statistically analyzed.
- ⚙️ **Research Process in Qualitative Research**: It is circular and flexible, allowing for loops and returns to previous steps.
- 🔍 **Research Process in Quantitative Research**: It is linear with a structured process and clearly defined steps, with less flexibility to return to previous steps.
- 🔑 **Hypothesis Development**: In qualitative research, hypotheses are developed based on collected data, whereas in quantitative research, hypotheses are tested.
- 🧐 **Sample Size in Qualitative Research**: Tends to be small, with an open size that can be adjusted during the study.
- 📏 **Sample Size in Quantitative Research**: Tends to be large, with a predetermined size before the study begins, aiming for generalization.
- 🔑 **Selection of Research Participants**: In qualitative research, a few individuals are studied in-depth, while in quantitative research, a larger sample is used for broader generalization.
Q & A
What does the term 'empirical' derive from and what does it mean?
-The term 'empirical' comes from the Greek word 'empiria', which means experience or observation. Empirical knowledge is thus seen as knowledge based on experiment or observation.
What is the primary goal of empirical research?
-The primary goal of empirical research is to collect or test knowledge about reality, which is typically done through qualitative or quantitative methods.
How does qualitative research contribute to empirical research?
-Qualitative research contributes to empirical research by developing hypotheses based on experiences or observations. It is particularly useful for exploring unknown fields of research where new ideas and hypotheses can be formulated.
What is the role of quantitative research in empirical studies?
-Quantitative research plays a role in empirical studies by testing the hypotheses that have been developed, often using numerical data and statistical methods to determine the validity of these hypotheses.
How does the data collection process differ between qualitative and quantitative research?
-In qualitative research, data is collected in an open format using methods like interviews or observations, resulting in soft data such as text, images, or videos. In contrast, quantitative research collects data in a standardized format, often through surveys or experiments, resulting in hard or numerical data that can be statistically analyzed.
What is the typical research process like in qualitative research?
-The research process in qualitative research is circular, less structured, and allows for flexibility and loops, enabling researchers to return to previous steps as needed.
How is the research process structured in quantitative research?
-The research process in quantitative research is linear, with a well-structured process featuring clearly defined steps. It generally does not allow for loops or returns to previous steps.
What is the difference in sample size between qualitative and quantitative research?
-Qualitative research typically involves a small sample size, focusing on a few individuals to gain an in-depth understanding. Quantitative research, on the other hand, aims for a larger sample size to make generalized statements about a population.
How does the selection of research participants differ between the two types of research?
-In qualitative research, the selection tends to be purposive with a focus on a small, specific group of individuals. In quantitative research, the selection aims to be representative of a larger population, often using random sampling techniques.
What are the key differences between qualitative and quantitative research in terms of hypothesis development and testing?
-Qualitative research is more about developing hypotheses through the exploration of experiences and observations. Quantitative research focuses on testing these hypotheses using collected data and statistical analysis.
How can the results of qualitative research inform the direction of quantitative research?
-The observations and experiences gathered through qualitative research can lead to the formulation of hypotheses. These hypotheses can then be structured and tested within a quantitative research framework to validate or refute them using numerical data.
What is the significance of the structured questionnaire in quantitative research?
-A structured questionnaire in quantitative research ensures that data is collected in a standardized manner, allowing for the use of statistical methods to identify patterns, correlations, and to test hypotheses effectively.
Outlines
📚 Empirical Research: Understanding and Types
This paragraph introduces the concept of Empirical research, which is derived from the Greek word 'empiria', meaning experience or observation. Empirical knowledge is experimental knowledge, and the goal of Empirical research is to collect or test knowledge about reality. The paragraph distinguishes between two main areas of Empirical research: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative research focuses on collecting experiences, while quantitative research tests these experiences. The paragraph also provides an example of how one might approach a research question about how people in Vienna deal with inflation, first qualitatively through interviews and then quantitatively by testing a hypothesis with a standardized questionnaire. The difference between qualitative and quantitative research is further explored, with qualitative research being more suited for developing new hypotheses in unknown fields and quantitative research for testing these hypotheses in well-known areas with existing literature.
🔍 Data Collection and Research Process in Empirical Research
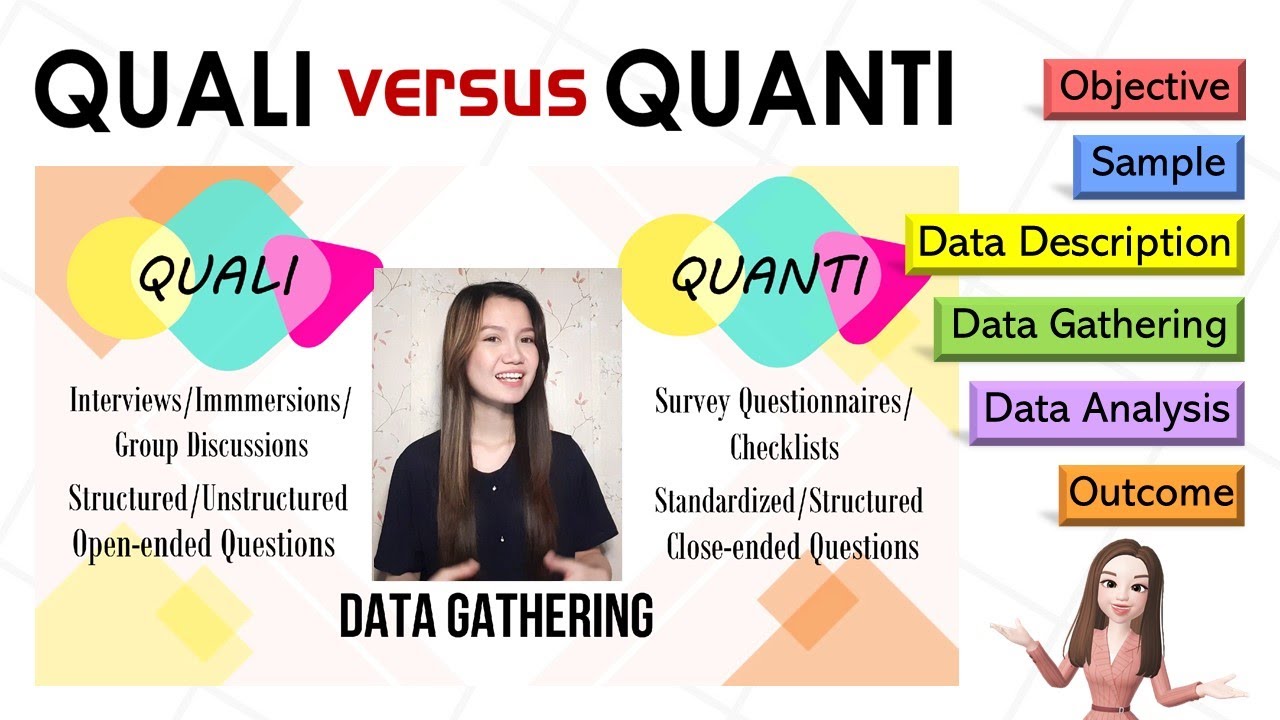
This paragraph delves into the specifics of data collection in qualitative and quantitative research. In qualitative research, data is collected in an open format, often through interviews or observations, resulting in 'soft data' such as text, images, or videos. The process is described as circular, allowing for flexibility and the possibility to return to previous steps. In contrast, quantitative research uses 'hard data' or numerical data, collected through surveys or experiments, and analyzed using statistical methods. The research process in quantitative research is linear and structured, with clearly defined steps and less flexibility to revisit earlier stages. The paragraph also discusses the difference in sample size, with qualitative research typically involving a small, in-depth sample and quantitative research aiming for a larger, generalized sample. The sample size in qualitative research can be adjusted during the study, while in quantitative research, it is determined before the study begins.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Empirical research
💡Qualitative research
💡Quantitative research
💡Hypothesis
💡Data collection
💡Soft Data
💡Hard Data
💡Research process
💡Sample size
💡Literature review
💡Statistical methods
Highlights
Empirical research is derived from the Greek 'empiria', meaning experience or observation.
The goal of empirical research is to collect or test knowledge about reality through qualitative or quantitative methods.
Qualitative research is typically used to develop hypotheses, while quantitative research is used to test them.
An example of qualitative research is conducting interviews with people in Vienna to understand how they deal with increased inflation.
A hypothesis derived from qualitative research can then be tested using quantitative methods, such as a standardized questionnaire.
Quantitative research is suited for well-known research areas with existing literature, while qualitative research is ideal for unexplored fields.
In qualitative research, data is collected in an open format, such as through interviews or observations, resulting in soft data like text, images, or videos.
Quantitative research involves collecting hard data or numerical data through surveys or experiments, which can be analyzed statistically.
The research process in qualitative research is circular and flexible, allowing for loops and returns to previous steps.
In contrast, quantitative research follows a linear process with well-structured, clearly defined steps.
Qualitative research often involves a small sample size with in-depth study of each individual subject.
Quantitative research typically uses a large sample size to make generalized statements about a population.
The sample size in a qualitative study can be adjusted during the study, whereas in a quantitative study, it is determined before the study begins.
Qualitative research is often exploratory, seeking to develop new ideas and hypotheses based on collected data.
Quantitative research requires a prior literature review to formulate hypotheses that will be tested with collected data.
The difference in data collection is exemplified by the use of open-ended questions in qualitative research versus standardized, structured questions in quantitative research.
The video concludes with a summary of the differences between qualitative and quantitative research, emphasizing the unique applications and processes of each method.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Qualitative and Quantitative Research
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1 - Qualitative and Quantitative Research - EP.5 (Research Simplified)

PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1 - Research Approaches - EP.7 (Research Simplified)

Qualitative vs Quantitative vs Mixed Methods Research: How To Choose Research Methodology

Research Design: Choosing a Type of Research Design | Scribbr 🎓

Quantitative Research vs Qualitative Research (Practical Research 2)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: