What is Resistance? An Explanation
TLDRThis video offers a foundational understanding of resistance, a key concept in circuit analysis. It explains resistance as the hindrance to the flow of charge, highlighting its inverse relationship with current, as per Ohm's law (V=IR). The video simplifies the concept by discussing how altering resistance affects current flow and introduces the symbol and unit for resistance (R and ohms, symbolized by the Greek letter Omega). The goal is to provide viewers with a clear grasp of the role resistance plays in electronic circuits.
Takeaways
- 📚 Resistance is a fundamental concept in understanding circuits, particularly when dealing with capacitors and resistors.
- 🌟 The symbol for resistance is 'R', and it is a measure of the hindrance to the flow of electric charge.
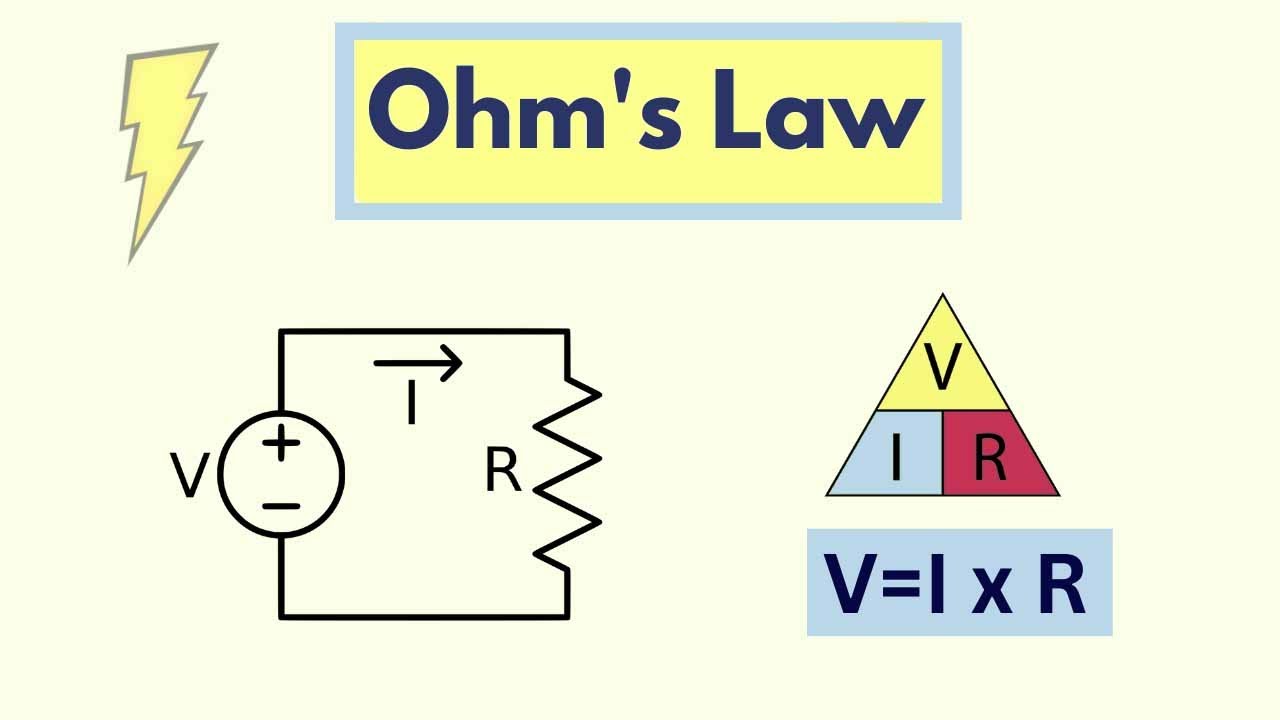
- ⚖️ Ohm's law (V=IR) relates voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R), where voltage is the product of current and resistance.
- 🔄 Resistance and current are inversely proportional; as resistance increases, current decreases, and vice versa.
- 🔧 The unit of resistance is the ohm, which is symbolized by the Greek letter Omega (Ω).
- 📝 Resistance can be expressed as a numerical value followed by the ohm unit, for example, '500 ohms' or '500Ω'.
- 💡 Understanding the meaning behind the calculations is crucial, not just getting the right answer.
- 📊 The capacitor equation (Q=CV) is another important relationship in circuits, where Q represents charge, C is capacitance, and V is voltage.
- 🔧 Resistance affects the flow of electrons, which is the basis of its function in a circuit.
- 🎓 Gaining a conceptual understanding of resistance is essential for working with circuits effectively.
- 👍 The video aims to provide a helpful starting point for grasping the concept of resistance and its impact on current.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is to provide a general understanding of resistance, its concept, symbols, units, and how it relates to other components in electrical circuits.
How does the speaker describe resistance?
-The speaker describes resistance as the hindrance to the flow of charge, and as the ratio of voltage to electric current flowing through a resistor.
What is the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance according to Ohm's law?
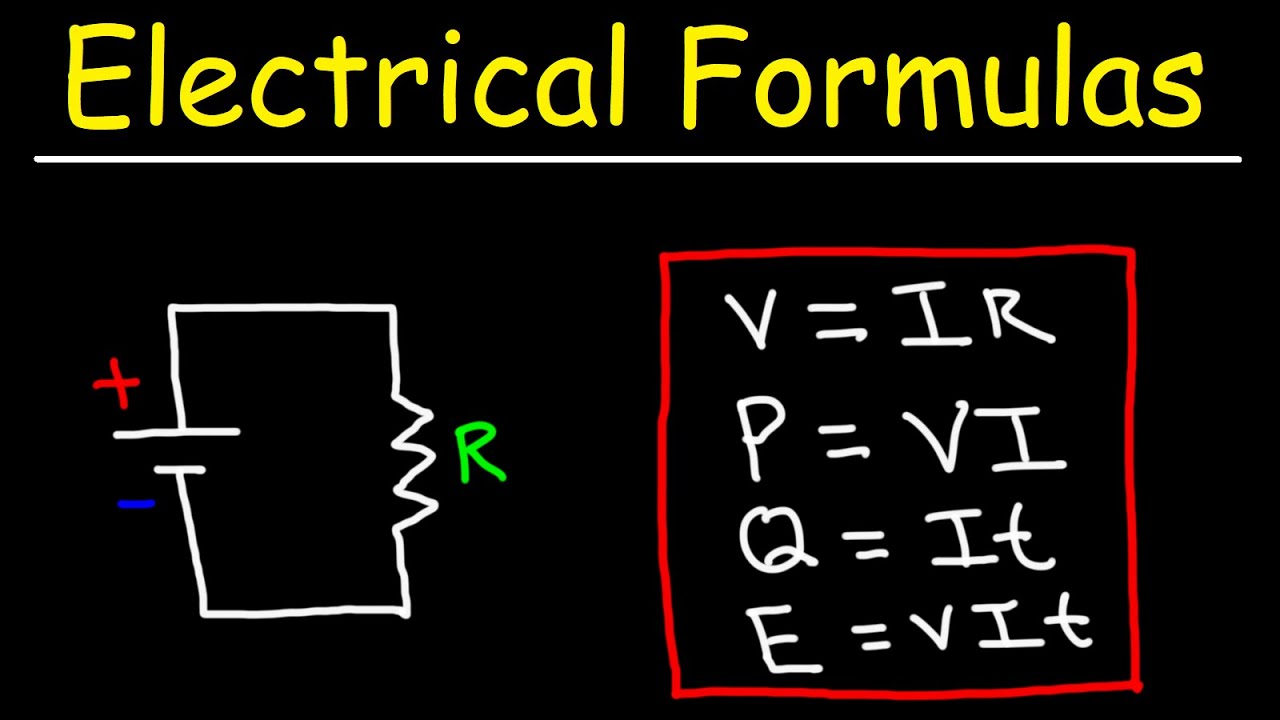
-According to Ohm's law, voltage (V) is equal to the product of current (I) and resistance (R), or V = I * R.
How do changes in resistance affect the current in a circuit?
-If the voltage is kept constant, an increase in resistance will result in a decrease in current, and a decrease in resistance will result in an increase in current, indicating an inversely proportional relationship between resistance and current.
What is the unit of resistance and how is it symbolized?
-The unit of resistance is the ohm, which is symbolized by the Greek letter Omega (Ω).
What is the significance of the inverse relationship between resistance and current?
-The inverse relationship signifies that resistors are used to control the flow of electrons in a circuit. By increasing resistance, the flow of charge (current) is reduced, and vice versa.
How can resistance be expressed in a formula?
-Resistance can be expressed in a formula as R = V / I, where R is resistance, V is voltage, and I is current.
What is the role of resistors in a circuit?
-Resistors are used to resist the flow of electrons, thereby controlling the amount of current that flows through a circuit.
What are the other components mentioned in the script that are related to resistance?
-The other components mentioned in the script related to resistance are capacitors, and the concepts of current, voltage, capacitance, and charge.
How can one conceptualize the effect of resistance on current?
-One can conceptualize the effect of resistance on current by considering that increasing resistance decreases current and decreasing resistance increases current, due to their inversely proportional relationship.
What is the significance of understanding the meaning behind Ohm's law calculations?
-Understanding the meaning behind Ohm's law calculations is significant as it helps in comprehending the physical behavior of electrical circuits, rather than just getting the right answers without knowing their implications.
Outlines
📘 Introduction to Resistance
This paragraph introduces the concept of resistance in the context of electrical circuits, explaining its role alongside other key terms such as current, voltage, capacitance, and charge. The speaker aims to provide a general understanding of resistance, its symbols, units, and abbreviations, and how these relate to Ohm's law and the capacitor equation. The main point is that resistance is the hindrance to the flow of charge, and it inversely affects the current, with an increase in resistance leading to a decrease in current and vice versa. The unit of resistance is the ohm, symbolized by the Greek letter Omega (Ω).
🚀 Wrapping Up the Discussion
The speaker concludes the discussion on resistance by summarizing the key points covered in the video. They reiterate that resistance is the opposition to the flow of electrons in a circuit and that it is inversely proportional to current. The speaker also emphasizes the importance of understanding the meaning behind the calculations and the fundamental concepts of Ohm's law and the role of resistance in electrical circuits. The video ends with a call to action for viewers to engage by liking or commenting if they found the content helpful, and a teaser for the next video.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Resistance
💡Conceptual Background
💡Symbols and Units
💡Ohm's Law
💡Capacitors and Resistors
💡Current
💡Voltage
💡Capacitance
💡Charge
💡Inversely Proportional
💡Greek Letter Omega (Ω)
Highlights
The video provides a general conceptual background on resistance.
Resistance is discussed in relation to other circuit terms such as current, voltage, capacitance, and charge.
Ohm's law (V=IR) is introduced as a fundamental principle in understanding resistance.
The video emphasizes the importance of understanding the meaning behind calculations, not just the answers.
A definition of resistance is provided as the hindrance to the flow of charge.
Resistance is also defined as the ratio of voltage to current.
The relationship between resistance and current is explained as being inversely proportional.
The concept of resistors is explained as components that resist the flow of electrons.
The symbol for resistance is R, which is used in Ohm's law calculations.
The unit for resistance is the ohm, symbolized by the Greek letter Omega.
The video clarifies how resistance is expressed in problems, using the formula R = 500 ohms.
The abbreviation for ohm is represented by the Greek letter Omega, not the letter 'O'.
The video aims to give viewers a good starting point for understanding the concept of resistance.
The impact of resistance on the flow of current is reiterated as the primary focus of the video.
The video concludes with an encouragement for viewers to engage by liking or commenting.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: