Basic Electricity - Resistance and Ohm's law
TLDRThis video delves into the concepts of electrical resistance and Ohm's law, essential for understanding how to protect LED circuits with resistors. It explains the role of resistors in controlling current flow and converting kinetic energy to heat. The script simplifies the complex behavior of electrons and atoms, introduces the unit of resistance (ohms), and demonstrates using a multimeter to measure resistance. It also covers the color coding of resistors and how to apply Ohm's law (V=IR) to calculate the appropriate resistor value for an LED circuit. The video emphasizes the linear relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in simple resistors and provides a practical example of calculating and applying a 330-ohm resistor in a 9-volt LED circuit. It concludes with a caution about exceeding recommended voltage levels and a teaser for the next topic: electrical power.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Understanding electrical resistance is crucial for managing current flow in circuits, especially when working with LEDs.
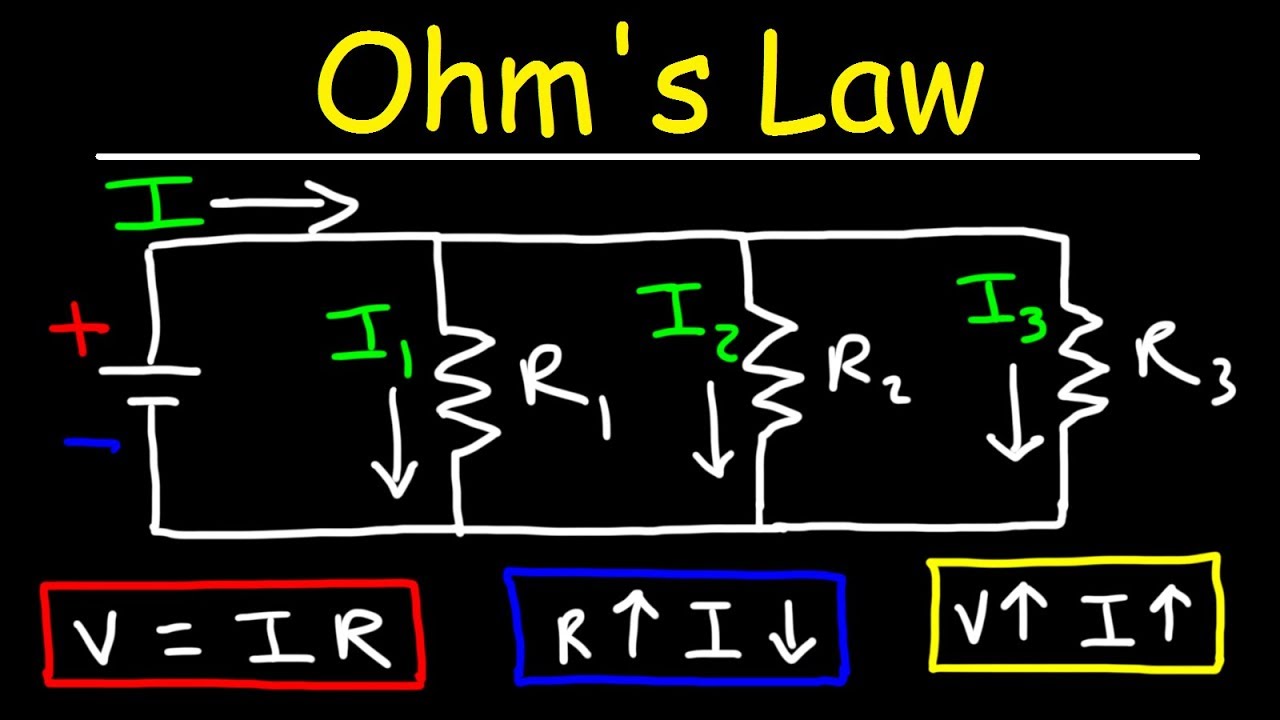
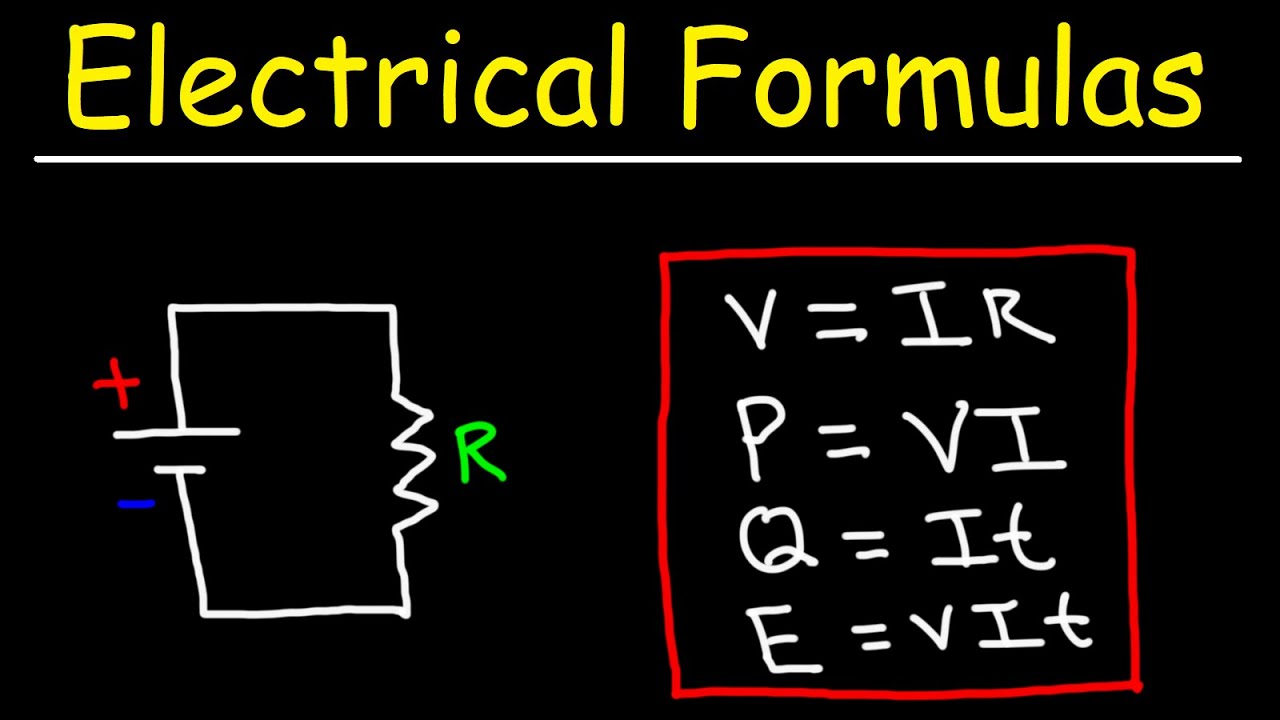
- ⚡️ Ohm's Law (V=I×R) is a fundamental principle that relates voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit.
- 🔌 Resistors can be used to limit current in a circuit, preventing components like LEDs from blowing up due to excessive current.
- 🔩 Different types of resistors exist, from basic hobbyist resistors to surface mount and large power supply resistors.
- 💡 The resistance in a material is due to atomic vibrations and the lack of suitable atomic arrangements for electron flow.
- 📏 Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω), with lower values indicating better conductors and higher values indicating poor conductors.
- 🎨 Resistors are often color-coded, allowing for quick identification of their resistance values using a resistor color code chart.
- 🔍 A multimeter is a tool that can measure resistance and is essential for working with electronics.
- 🔋 For a simple LED circuit, the resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's Law to ensure a safe current flow.
- 🚫 Not all electronic components obey Ohm's Law, and exceeding recommended voltage levels can lead to component failure.
- 🌡️ High resistance values can lead to excessive heat generation, which is a topic explored in the study of electrical power.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a resistor in a circuit?
-The primary function of a resistor is to limit the flow of electrical current in a circuit, preventing components from drawing too much current and potentially getting damaged.
How does a resistor work to control the flow of electrons?
-A resistor works by introducing resistance to the flow of electrons. As electrons move through the resistor material, they collide with atoms, which converts some of their kinetic energy into heat, thus resisting the flow and controlling the current.
What is Ohm's Law and how is it expressed mathematically?
-Ohm's Law is a fundamental principle that defines the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) in an electrical circuit. It is mathematically expressed as V = I × R, which can be rearranged to solve for any of the variables given the other two.
What does the color coding on resistors represent?
-The color coding on resistors represents their resistance value. Each color corresponds to a specific number or multiplier, and the combination of these colors allows one to determine the resistance value of the resistor.
How can you measure the resistance of a component?
-You can measure the resistance of a component using a multimeter, which is a versatile tool capable of measuring various electrical properties, including resistance.
What is the significance of the tolerance value indicated by the resistor's color code?
-The tolerance value indicates the maximum amount by which the actual resistance can vary from the specified value. A 5% tolerance, for example, means the resistor could be 5% higher or lower than its rated value, which is typically sufficient for most home electronics projects.
How does the forward voltage of an LED affect the calculation of the required resistor value?
-The forward voltage of an LED is the voltage drop across the LED when it is operating. This value is subtracted from the total supply voltage to determine the voltage across the resistor, which is then used in Ohm's Law to calculate the necessary resistance to limit the current to the desired level.
What happens if the resistor value is too high in a circuit?
-If the resistor value is too high, less current will flow through the circuit. In the case of an LED circuit, this could result in the LED being too dim or not lighting up at all.
What is the limitation of using Ohm's Law for calculating resistor values in certain circuits?
-Ohm's Law assumes a linear relationship between voltage and current, which holds true for pure resistive components. However, in circuits with non-ohmic components, such as LEDs at high voltages, the relationship becomes more complex, and other factors like power and heat dissipation must be considered.
Why is it important to consider the polarity when connecting an LED and a resistor in a circuit?
-While the polarity is not important for resistors, it is crucial for LEDs. LEDs are polarized components with an anode (positive) and a cathode (negative), and they will only light up when connected correctly with the anode towards the higher voltage.
What should one do to further understand the concepts discussed in the script?
-To further understand the concepts discussed, one should watch additional tutorials on the topics, such as the mentioned LED tutorial and the one on multimeters, and explore resources like Ohmnilabs for more insights into electronics and robotics.
Outlines
🔌 Introduction to Electrical Resistance and Ohm's Law
This paragraph introduces the concept of electrical resistance and the importance of resistors in controlling the flow of current in a circuit, specifically in LED circuits. It discusses the role of voltage as a pushing force and shares an example of an LED being damaged due to excessive current. The paragraph explains the basic functioning of resistors, how they convert kinetic energy from electrons into heat, and the variability in resistance across different materials. It also touches on the simplification of atomic and subatomic behavior in this context. The measurement of resistance in ohms and the use of a multimeter for this purpose are also covered. The paragraph concludes with an introduction to the color coding system of resistors and the use of resistor color calculators for determining resistance values.
🔋 Applying Ohm's Law in Simple LED Circuits
This paragraph delves into the practical application of Ohm's Law in simple LED circuits. It explains how to calculate the appropriate resistor value to limit the current flowing through an LED, ensuring its safe operation. The concept of linear relationships in Ohm's Law is discussed, along with the consequences of exceeding recommended voltage levels. The paragraph provides a step-by-step guide on setting up a circuit with a 9-volt battery, selecting the correct resistor value based on the LED's forward voltage and maximum current, and the importance of polarity in LED connections. It also highlights the limitations of Ohm's Law when dealing with higher voltages and introduces the concept of electrical power, which will be explored in a subsequent video. The paragraph ends with a cautionary note about the dangers of high voltage and a mention of Ohmnilabs, a company that creates robots.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electrical Resistance
💡Ohm's Law
💡Resistor
💡LED Circuit
💡Voltage
💡Current
💡Color Code
💡Tolerance
💡Forward Voltage
💡Linear Relationship
💡Power Supply
Highlights
The video discusses electrical resistance, Ohm's law, and the selection of resistors for LED circuits.
Voltage can act as a pushing force in electrical circuits, but it needs to be controlled to prevent damage to components like LEDs.
Resistors are used to limit the flow of electrical current in a controlled manner, preventing components from blowing up due to excessive current.
Different types of resistors exist, from basic ones used in hobbyist circuits to tiny surface mount resistors found in devices like phones, and large ones for power supply.
The resistance in a material like copper wire is due to the vibration of atoms and the occasional collision of electrons with these atoms.
Resistance can also arise from the arrangement of atoms in a material and the availability of free electrons for current flow.
Nearly all materials have some resistance to electrical current, with metals typically having the least resistance.
Resistance is measured in ohms, with 1 ohm being very low resistance and 1 megaohm being very high.
A multimeter is a tool used to measure resistance and other electrical properties.
Resistors are color-coded, with a specific pattern that translates to a resistance value, such as red, violet, brown, and gold representing 270 ohms.
Ohm's law, V=I*R, is a fundamental principle relating voltage, current, and resistance, and can be rearranged to solve for any of the variables.
By applying Ohm's law, one can calculate the necessary resistance to limit current in a circuit, such as for an LED.
The relationship between voltage and current is linear for pure resistors, meaning that doubling the voltage doubles the current.
In a simple LED circuit, the resistor's role is to limit current, and the LED's forward voltage is a key factor in these calculations.
The video provides a practical example of calculating and using a resistor to protect an LED from excessive current.
The video also touches on the limitations of Ohm's law and hints at the concept of electrical power, which will be explored in a future video.
Ohmnilabs, a company that makes robots, is mentioned as an example of practical applications of electrical principles.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: