Stratified Sampling Vs Cluster Sampling with Examples | Meaning and Comparison
TLDRThis video script discusses the key differences between stratified sampling and cluster sampling, two distinct probability sampling techniques. Stratified sampling is ideal for heterogeneous populations, subdividing them into homogeneous strata based on common characteristics, and then randomly selecting samples from each stratum. Cluster sampling, on the other hand, involves dividing the population into non-overlapping clusters and observing all elements within a randomly selected cluster. The script highlights that stratified sampling aims for accurate representation and homogeneity within strata, while cluster sampling focuses on cost reduction and efficiency. The differences in selection criteria, cost, convenience, and the treatment of homogeneity and heterogeneity are also explored, providing a comprehensive understanding of these sampling methods.
Takeaways
- 📊 Stratified sampling is used for heterogeneous populations where elements are classified into various strata based on common characteristics.
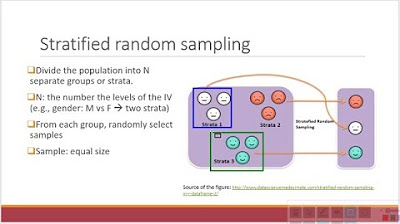
- 🔢 In stratified sampling, the population is subdivided into distinct and mutually exclusive subpopulations (strata), and samples are randomly selected from each stratum.
- 🎯 Each stratum in stratified sampling should be nearly homogeneous, and strata should contrast with each other to ensure accurate representation.
- 🌐 Cluster sampling is a probability sampling method for studying large populations, where the population is divided into non-overlapping subgroups (clusters).
- 🔍 In cluster sampling, a random sample of clusters is selected, and all elements within the chosen cluster are observed to gather information.
- 💡 The selection of clusters in cluster sampling is based on the ease of availability of requisite data and the diversity of the cluster's population.
- 📉 Stratified sampling aims for accurate representation of the population, while cluster sampling focuses on reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- 🌟 Cost and convenience favor cluster sampling as it is easier to obtain clusters and focus on a smaller part of the population, reducing overall costs.
- 🔄 The selection process in stratified sampling involves choosing items from each subgroup, whereas in cluster sampling, it involves selecting random subgroups and studying them as a whole.
- 🔄 In stratified sampling, the researcher decides the criteria for dividing strata, while in cluster sampling, it relies on natural divisions.
- 🔄 Stratified sampling seeks homogeneity within subgroups and heterogeneity between them, while cluster sampling aims for the opposite, seeking heterogeneity within clusters and homogeneity between them.
Q & A
What is stratified sampling?
-Stratified sampling is a sampling technique used when the population is heterogeneous, meaning it consists of different segments. In this method, the population is classified into various strata based on common characteristics, and then a sample is randomly selected from each stratum.
How is the population divided in stratified sampling?
-In stratified sampling, the population is divided into distinct and mutually exclusive subpopulations called strata, based on some common characteristics. Each stratum is expected to be nearly homogeneous, and the strata should contrast with each other.
What is the purpose of using stratification in sampling?
-The purpose of using stratification in sampling is to ensure that the sample is accurately representative of the population. By dividing the population into relatively homogeneous groups, the sampling process can better capture the diversity and characteristics of the entire population.
How does cluster sampling differ from stratified sampling?
-Cluster sampling is a method of probability sampling used for large populations where the entire population is divided into non-overlapping subgroups called clusters. Instead of selecting individual units, a random sample of clusters is drawn, and all elements within the selected cluster are observed. This contrasts with stratified sampling, where samples are selected from each stratum.
What are the advantages of cluster sampling over stratified sampling in terms of cost and convenience?
-Cluster sampling can be more cost-effective and convenient than stratified sampling because it focuses on entire groups (clusters) rather than individual units. This reduces the overall cost involved as it is easier to obtain clusters and gather data from them.
How are elements selected in stratified sampling?
-In stratified sampling, elements are selected randomly from each subgroup (stratum). This ensures that each stratum is represented in the sample, and the selection process is based on the predefined criteria for dividing the strata.
What is the selection criterion for clusters in cluster sampling?
-The selection criterion for clusters in cluster sampling is based on the ease of availability of requisite data. Each cluster should be highly diverse to represent all characteristics of the population and should not overlap with other clusters.
What is the main goal of stratified sampling in terms of homogeneity and heterogeneity?
-The main goal of stratified sampling is to achieve homogeneity within subgroups (strata) and heterogeneity between subgroups. This means that each stratum should be as similar as possible to the others in terms of the characteristics being studied.
How does the process of selecting clusters in cluster sampling work?
-In cluster sampling, clusters are first defined, and then a random sample of these clusters is selected. All elements within the chosen clusters are observed to gather information. This process ensures that each cluster is a mini representation of the entire population.
What is an example of stratified sampling?
-An example of stratified sampling is when a company wants to launch a student laptop. The company might divide the student population into three age-based groups (12-15 years, 15-18 years, and 18-21 years) and then randomly select students from each group to form a representative sample.
How can one find more information on stratified and cluster sampling?
-For more detailed information on stratified and cluster sampling, including their definitions and comparisons, one can visit the official website keydifferences.com, which provides comprehensive resources on these sampling techniques.
Outlines
📊 Introduction to Stratified and Cluster Sampling
This paragraph introduces the topic of stratified and cluster sampling, explaining that stratified sampling is used for heterogeneous populations where elements are classified into strata based on common characteristics. The process involves subdividing the population into distinct strata and then randomly selecting samples from each. An example is given where a company divides the student population into age groups for a student laptop launch. Cluster sampling, on the other hand, is used for large populations and involves dividing the entire population into non-overlapping subgroups called clusters. A random sample of clusters is then observed to gather information, with each cluster being a mini representation of the entire population.
🔍 Differences and Applications of Stratified and Cluster Sampling
This paragraph delves into the differences between stratified and cluster sampling. Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subgroups (strata) and selecting samples from each, aiming for accurate representation and proper sampling. Cluster sampling, in contrast, focuses on reducing costs and improving efficiency by selecting entire groups (clusters) at random. The paragraph also discusses the selection of elements, with stratified sampling choosing items randomly from each subgroup and cluster sampling selecting entire clusters. The division of the population and the homogeneity or heterogeneity within and between the subgroups or clusters are also highlighted, emphasizing the researcher's objectives in each sampling method.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Stratified Sampling
💡Cluster Sampling
💡Heterogeneity
💡Homogeneity
💡Random Sampling
💡Strata
💡Clusters
💡Sampling Techniques
💡Accuracy
💡Cost and Convenience
💡Elementary Units
Highlights
Stratified sampling is used for heterogeneous populations where elements are classified into various strata.
In stratified sampling, each stratum is nearly homogeneous and contrasts with other strata.
The population is subdivided into distinct and mutually exclusive subpopulations or strata based on common characteristics.
Simple random sampling technique is used to select the sample within each stratum in stratified sampling.
Stratified sampling combines individual stratum samples to obtain an overall sample for analysis.
Cluster sampling is a method of probability sampling used for large populations, dividing them into non-overlapping subgroups called clusters.
In cluster sampling, a random sample of clusters is drawn, and all elements of the selected cluster are observed.
Each cluster in cluster sampling is a mini representation of the entire population, containing a wide range of elements.
The selection criterion in cluster sampling is based on the ease of availability of requisite data.
Stratified sampling aims at accurate sampling with properly represented populations, while cluster sampling aims at reducing cost and improving efficiency.
Cluster sampling is more cost-effective and convenient compared to stratified sampling.
In stratified sampling, items are randomly chosen from each subgroup, whereas in cluster sampling, entire groups or clusters are selected randomly.
Stratified sampling strives for homogeneity within subgroups and heterogeneity between subgroups.
Cluster sampling, on the other hand, seeks heterogeneity within subgroups and homogeneity between different clusters.
The researcher defines the population and divides it into clusters, ensuring high diversity and no overlapping in cluster sampling.
An example of stratified sampling is a company launching a student laptop by dividing the student population into age groups.
An example of cluster sampling involves selecting a number of schools as clusters and studying the students within the selected schools.
For further study on the topic, the official website keydifferences.com provides detailed comparisons of stratified and cluster sampling.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Statistics Lecture 1.5: Sampling Techniques. How to Develop a Random Sample

Sampling Methods 101: Probability & Non-Probability Sampling Explained Simply

Probability and Non-Probability Sampling in Research Methods
Research Methods 1: Sampling Techniques

Sampling: Simple Random, Convenience, systematic, cluster, stratified - Statistics Help

4.2 Probability Sampling Techniques
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: