Statistics Lecture 1.5: Sampling Techniques. How to Develop a Random Sample
TLDRThe transcript discusses various types of data and sampling methods in统计学. It differentiates between qualitative and quantitative data, and focuses on the importance of random sampling in experiments and observations. The speaker explains the concepts of random sample, simple random sample, and introduces four common sampling techniques: convenience, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling. The differences between these methods are highlighted, emphasizing the need for representative and random selection to minimize sampling error and ensure accurate statistical analysis.
Takeaways
- 📚 The distinction between qualitative and quantitative data was discussed, highlighting the importance of understanding these types for data analysis.
- 🔍 The concept of 'random' in data collection was explored, emphasizing its necessity for unbiased sampling.
- 🧠 A clear definition of 'random' was provided: every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected in the sample.
- ⚖️ The difference between an 'observation' and an 'experiment' was clarified, with the key point being whether the subjects are being modified or not.
- 💊 Examples of observational studies include polling and counting specific traits without intervention, while experimental studies involve applying treatments and observing effects.
- 🎯 Simple random sampling was defined and distinguished from convenience sampling, emphasizing the equal chance of selection for all members of a population.
- 🔢 Systematic sampling was introduced as a method where every nth member of a numbered population is selected starting from a randomly chosen point.
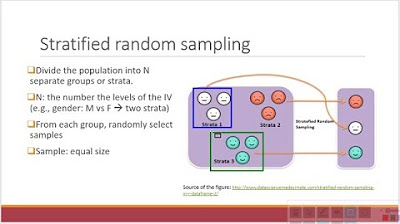
- 🌁 Stratified sampling was explained as a method to ensure representation from different subgroups within a population, based on specific characteristics.
- 🔮 Cluster sampling involves dividing the population into clusters, regardless of characteristics, and then randomly selecting entire clusters for data collection.
- 🚫 Two types of errors in sampling were mentioned: non-sampling error (due to mistakes in data collection or processing) and sampling error (due to natural variation between the sample and the population).
Q & A
What are the two main types of data mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of data mentioned in the script are qualitative and quantitative data.
What is the main focus of section 1.5 in the script?
-The main focus of section 1.5 is the design of experiments and understanding the concept of random data collection.
What is the difference between an observation and an experiment in the context of the script?
-In the context of the script, an observation involves measuring specific traits without modifying the subjects, whereas an experiment involves applying some treatment to the subjects and then observing the effects.
How is a simple random sample defined in the script?
-A simple random sample is defined as a sample where every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
What are the two types of errors that can occur during sampling as mentioned in the script?
-The two types of errors that can occur during sampling are non-sampling error, which is due to mistakes like writing down wrong information or math errors, and sampling error, which is the difference in characteristics between the sample and the population due to the random chance of selection.
What is the main issue with convenience sampling as discussed in the script?
-The main issue with convenience sampling is that it is not truly random, as it involves using results that are easy to get, which can lead to a biased and unrepresentative sample.
How does systematic sampling ensure randomness in the script?
-Systematic sampling ensures randomness by putting the population in order, starting at a random spot on the list, and then selecting every nth individual after the starting point.
What is the purpose of stratified sampling as explained in the script?
-The purpose of stratified sampling is to make sure that every subgroup within the population is represented in the sample by breaking the population into subgroups based on a specific characteristic and then taking a random sample from each subgroup.
How does cluster sampling differ from stratified sampling?
-Cluster sampling differs from stratified sampling in that it does not group individuals by any characteristic but instead divides the population into clusters, regardless of any characteristic, and then randomly selects a certain number of clusters, sampling the entire cluster.
Why is it important to understand the difference between random and simple random sampling?
-Understanding the difference between random and simple random sampling is important because it ensures that every individual and every group of the same size in the population has an equal chance of being selected, which is crucial for obtaining a representative sample and reducing sampling error.
What is the significance of the placebo effect mentioned in the script?
-The significance of the placebo effect mentioned in the script is to illustrate the psychological impact of belief in a treatment, showing that the mind can create effects similar to those of the actual treatment, even when the subject is given an inactive substance like a sugar pill.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Vocabulary and Data Types
This paragraph introduces the discussion on vocabulary related to data types, specifically qualitative and quantitative data. It also sets the stage for a review of these concepts and introduces the topic of random data collection, which is crucial for the subsequent discussion on experiments and observations.
🧠 Understanding Experiments vs. Observations
This section delves into the distinction between experiments and observations. It explains that while observations involve measuring specific traits without modifying the subjects, experiments involve applying treatments and observing the effects on subjects. The paragraph emphasizes the importance of understanding this difference in the context of data collection and scientific studies.
🎯 Defining 'Random' in Data Collection
The speaker clarifies the concept of 'random' in the context of data collection. It explains that 'random' means every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The paragraph also introduces the idea of a simple random sample and provides an analogy of selecting names from a hat to illustrate the concept.
🔢 Types of Sampling Methods
This paragraph discusses various sampling methods, starting with the non-random convenience sample and moving on to systematic sampling. It explains how systematic sampling involves selecting every nth individual from a list after choosing a random starting point, ensuring a more representative sample than convenience sampling.
🌁 Stratified Sampling for Subgroup Representation
The speaker introduces stratified sampling, a method that ensures representation from different subgroups within the population. This method is particularly useful when researchers want to ensure that certain characteristics or strata are included in the sample. The paragraph explains how the population is divided into subgroups first and then a random sample is taken from each subgroup.
📏 Cluster Sampling: Grouping for Convenience
Cluster sampling is explained as a method where the population is divided into clusters, not based on characteristics, but for convenience in data collection. The speaker describes how random clusters are selected, and all individuals within those clusters are included in the sample. This method differs from stratified sampling in that it does not focus on characteristics of subgroups.
🚨 Addressing Sampling Errors
The final paragraph addresses two types of errors that can occur during sampling: non-sampling errors, which result from mistakes in data collection or processing, and sampling errors, which are the differences between the sample and the population due to the random nature of sampling. The speaker emphasizes the inevitability of sampling error and the importance of being aware of both types of errors.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Data Types
💡Randomness
💡Experiments vs. Observations
💡Sampling Techniques
💡Random Sample
💡Simple Random Sample
💡Stratified Sampling
💡Cluster Sampling
💡Sampling Error
💡Non-Sampling Error
💡Frequency Distributions
Highlights
Discussion on types of data, including qualitative and quantitative.
Review of material from previous class, focusing on vocabulary and concepts.
Introduction to section 1.5 and the importance of understanding experimental design.
Explanation of the concept of 'random' in data collection and its significance.
Definition and distinction between observations and experiments.
Examples of observational studies, such as polling and its non-intrusive nature.
Description of experimental studies, including drug tests and the use of control groups.
Clarification on the difference between modifying and non-modifying subjects in studies.
Discussion on the concept of random sampling and its importance in data collection.
Definition of a simple random sample and how it ensures equal selection chance.
Explanation of convenience sampling and its limitations in randomness.
Description of systematic sampling and its method of selection.
Introduction to stratified sampling and its focus on subgroup representation.
Clarification on the difference between stratified and cluster sampling.
Explanation of cluster sampling and its random selection of groups.
Discussion on the two types of errors in sampling: non-sampling error and sampling error.
Completion of chapter one and transition to chapter two, indicating a progression in the course material.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

4.2 Probability Sampling Techniques
Sampling: Sampling & its Types | Simple Random, Convenience, Systematic, Cluster, Stratified
Research Methods 1: Sampling Techniques

Sampling: Simple Random, Convenience, systematic, cluster, stratified - Statistics Help

Probability and Non-Probability Sampling in Research Methods
What Are The Types Of Sampling Techniques In Statistics - Random, Stratified, Cluster, Systematic
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: