Markets, Efficiency, and Price Signals: Crash Course Economics #19
TLDRThis Crash Course Economics video discusses the differences between free market and centrally planned economies. It explains that central planning can be inefficient at meeting consumer demands. Free markets use price signals to indicate what producers should make and distribute based on what consumers want. The video analyzes concepts like predatory pricing and price gouging, noting that some view market-driven pricing as unjust, though economically it can be more efficient. It concludes that consumers have power to drive change through their spending and by supporting socially conscious companies.
Takeaways
- 😀 Central planning can provide full employment but often fails to efficiently allocate resources or meet consumer preferences
- 👍 Price signals in free markets indicate what producers should make and distribute goods efficiently
- 💡 Free markets incentivize efficiency and meeting consumer demand better than central planning
- 🤔 Government regulations and interventions aim to address market failures and improve social welfare
- 😠 Critics see price gouging and predatory pricing as examples of market cruelty and greed
- 😇 But markets and altruism can coexist - conscious consumerism promotes social goals
- 🛍 Ultimately consumers collectively choose priorities and influence markets through spending
- 💸 Capitalism crowdsources society's wants and needs through price signals
- 🚨 If we want change, we must demand and support more ethical business practices
- ❤️ Purchasing power brings opportunity and responsibility to promote social good
Q & A
What are the main economic systems discussed in the video?
-The video discusses free market economies and centrally planned economies as the main economic systems.
What are some disadvantages of centrally planned economies mentioned?
-Centrally planned economies often result in shortages of consumer goods, such as soap, sugar, and electronics, due to a focus on heavy equipment and military hardware.
How do competitive markets differ from centrally planned economies in meeting consumer needs?
-Competitive markets have been more successful at providing most of the things people want because they are driven by supply and demand, unlike centrally planned economies where government agencies decide what gets produced.
What are the two types of efficiency discussed, and how do they differ?
-The two types of efficiency discussed are productive efficiency, which is about producing goods at the lowest possible cost, and allocative efficiency, which ensures that the goods produced are what consumers actually want.
How do price signals function in a free market economy?
-Price signals in a free market economy indicate what consumers want by showing high demand through higher prices, prompting producers to make more of those goods.
What argument did economist Joel Waldfogel make against gift giving?
-Joel Waldfogel argued that gift giving is inefficient because it may result in people receiving items they do not value, suggesting that cash would be a more efficient gift.
What role does government regulation play in the United States economy according to the video?
-The video suggests that while the United States is often seen as a free market economy, it is heavily regulated, with government control in areas like national defense and public education, to improve social welfare.
How is price gouging viewed, and what are the arguments for and against anti-price gouging laws?
-Price gouging is controversial; some see it as exploiting consumers during emergencies, while others argue that allowing prices to rise can encourage the supply of essential goods. Anti-price gouging laws are said to potentially worsen the problem by discouraging supply.
What is predatory pricing, and how has it been treated in legal contexts in the US and Germany?
-Predatory pricing involves selling goods at a loss to eliminate competition. In the US, courts have been skeptical of predatory pricing claims, but in Germany, Walmart was ordered to raise prices due to such accusations.
How does the video portray the relationship between capitalism and social responsibility?
-The video suggests that capitalism and social responsibility can coexist, urging consumers to support companies that aim to improve the world and make purchases that have a positive impact.
Outlines
😃 Introducing the video and key topics
Adriene and Jacob introduce themselves and the Crash Course Economics video. They state they will discuss differences between free market and centrally planned economies, price signals, and concepts like price gouging and predatory pricing.
😟 Challenges of central planning
Adriene explains that central planning has some benefits like guaranteed employment, but hasn't worked well in practice. Consumers in the Soviet Union faced shortages of consumer goods because the focus was on production of heavy equipment and military hardware. Countries have moved away from large-scale central planning.
😀 Benefits of free markets and price signals
Jacob discusses two types of efficiency that free markets tend to achieve better than central planning: productive efficiency (lowest cost production) and allocative efficiency (producing what consumers want). Price signals help producers understand what consumers want. Free markets incentivize producers to avoid waste and meet consumer demand.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Free market
💡Central planning
💡Efficiency
💡Price signals
💡Invisible hand
💡Public economics
💡Price gouging
💡Predatory pricing
💡Corporate greed
💡Crowdfunding
Highlights
The talk discusses using AI to understand protein folding, which could help develop new proteins and drugs.
DeepMind's AlphaFold system made a huge leap in predicting protein structures accurately.
Understanding protein folding can help identify causes and treatments for diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
AlphaFold works by taking amino acid sequences and using neural networks to predict the 3D structure.
The system was trained on 170,000 protein structures from an open database called the Protein Data Bank.
AlphaFold exceeded human experts in the latest Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction contest.
The breakthrough illustrates how AI can accelerate scientific progress better than trial-and-error experiments.
AlphaFold's predictions will be made freely available through open databases for scientists worldwide to use.
Structural biology has been revolutionized - we can now model most proteins accurately with AI.
The next steps are using these models to design new proteins and enzymes from scratch.
AI-designed proteins could lead to new medicines, biomaterials, clean energy sources, and more.
Exciting commercial applications are emerging, like designing proteins to capture CO2 or break down plastics.
But risks need to be managed, as protein engineering has potential for misuse if not handled responsibly.
Overall, this technology represents an incredible breakthrough that will accelerate discoveries across biology.
The speaker concludes that AI will continue to transform science in ways we can't yet imagine.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Monopolies and Anti-Competitive Markets: Crash Course Economics #25

Price Controls, Subsidies, and the Risks of Good Intentions: Crash Course Economics #20

What is Consumers Surplus and Producer Surplus?
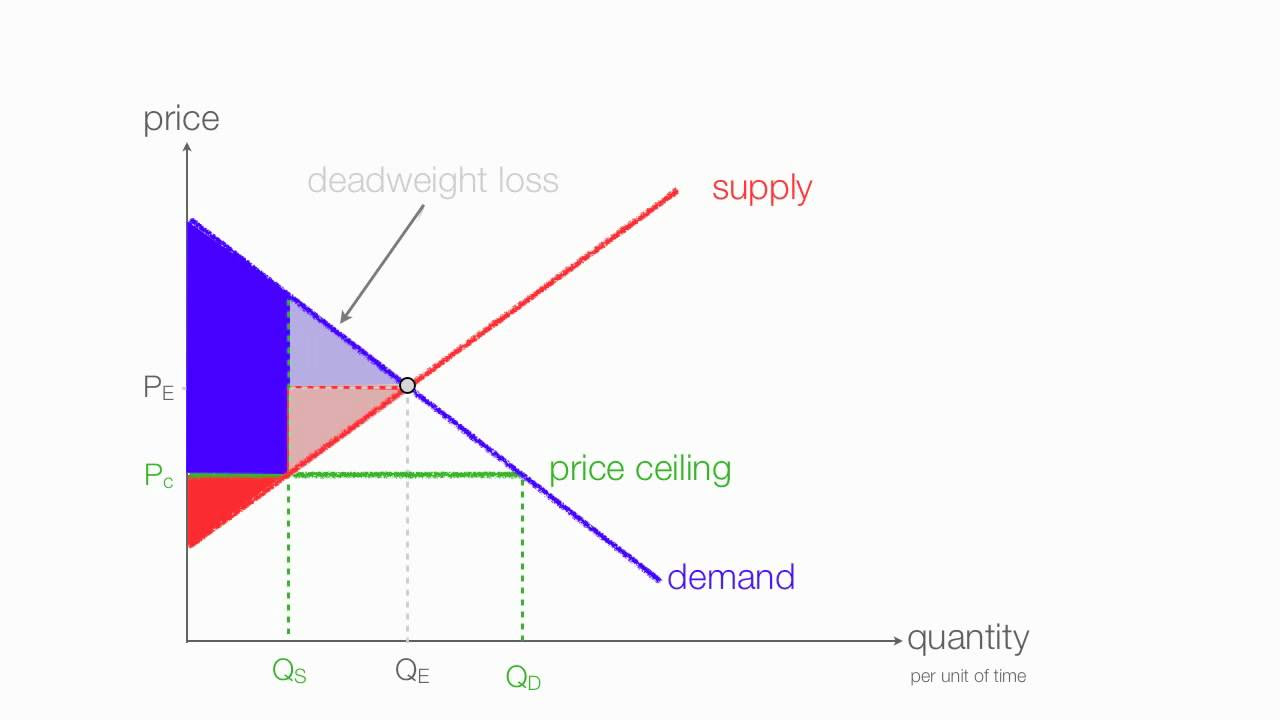
How to calculate changes in consumer and producer surplus with price and floor ceilings.

Consumer Surplus and Producer Surplus
Y1 8) Consumer and Producer Surplus
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: