Electromagnetic Radiation
TLDRIn this AP Physics essentials video, Mr. Andersen explores the concept of electromagnetic radiation, highlighting the discovery of infrared rays by William Herschel. He explains that visible light is just a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which ranges from low-energy radio waves with long wavelengths to high-energy gamma rays with short wavelengths. The video emphasizes the inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency, and how increasing frequency correlates with greater energy. It also touches on the potential dangers of high-energy radiation, such as gamma rays, which can ionize and damage cells. The summary aims to engage viewers with the fascinating and essential nature of electromagnetic radiation in our daily lives and the universe.
Takeaways
- 🌈 Newton's Experiment: Isaac Newton demonstrated that white light can be separated into its constituent colors using a prism.
- 🔍 Herschel's Discovery: William Herschel discovered infrared rays by finding a region of higher temperature beyond the red light, indicating the presence of invisible light that generates heat.
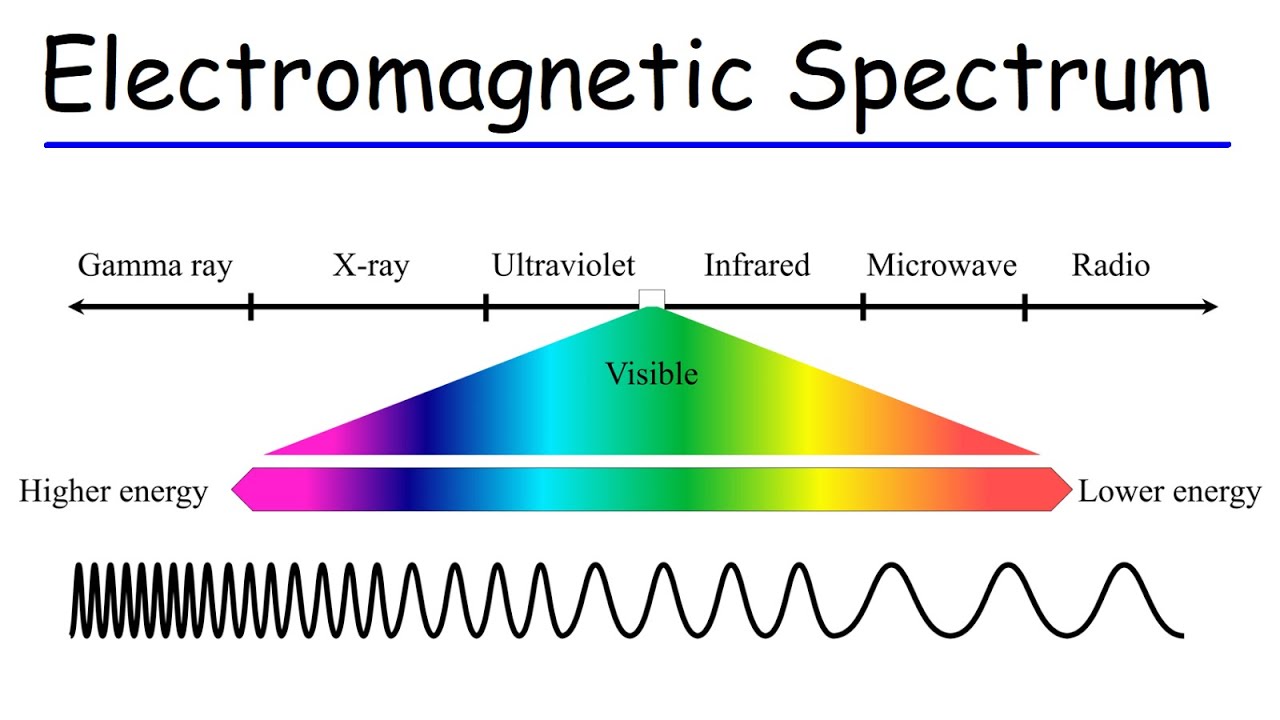
- 🌟 Electromagnetic Spectrum: The electromagnetic radiation spectrum includes a wide range of wavelengths, from very small to kilometers long.
- 🔗 Inverse Relationship: There is an inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency; as one increases, the other decreases.
- ⚡ Energy and Frequency: Higher frequency electromagnetic radiation carries more energy, which can be more damaging to cells.
- 👀 Visible Light: Humans can only see a small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum known as visible light.
- 🔥 Infrared Radiation: Infrared radiation is invisible to the human eye but can be felt as heat, and it has a longer wavelength than visible light.
- 🌌 Ultraviolet, Microwaves, and Radio Waves: Beyond visible light, there are ultraviolet light, microwaves, and radio waves, each with different wavelengths and applications.
- 📡 Radio Waves in Everyday Life: Radio waves are present in rooms, allowing us to receive radio and TV signals.
- ☢️ Danger of High-Energy Radiation: High-energy radiation like gamma rays can be harmful, causing damage to cells and even ionizing them.
- 📐 Wavelength and Frequency Comparison: Understanding the relationship between wavelength and frequency helps in making qualitative comparisons of electromagnetic radiation.
Q & A
What did Newton discover about white light when passed through a prism?
-Newton discovered that white light, when passed through a prism, breaks apart into its different colors.
What was William Herschel's experiment about in relation to light and temperature?
-William Herschel's experiment was to determine if there was a relationship between different colors of light and temperature by measuring the temperature of various colors of light with a thermometer.
What significant discovery did William Herschel make with his thermometer experiment?
-William Herschel discovered infrared rays, which are rays that we cannot see but generate a lot of heat.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency in electromagnetic radiation?
-In electromagnetic radiation, there is an inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency. As wavelength increases, frequency decreases, and vice versa.
How does the energy of electromagnetic waves vary with frequency and wavelength?
-The energy of electromagnetic waves increases with frequency and decreases with wavelength. Shorter wavelengths correspond to higher frequencies and more energy.
What part of the electromagnetic spectrum do we refer to as visible light?
-Visible light is a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes can detect, situated between infrared and ultraviolet.
What are the types of electromagnetic radiation listed in order from highest to lowest energy?
-The electromagnetic radiation types listed from highest to lowest energy are gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves.
What is the significance of the term 'electromagnetic radiation' in the context of the video?
-The term 'electromagnetic radiation' refers to the full spectrum of waves that propagate through space, including visible light, which is just a small part of the spectrum.
How do radio waves and gamma rays differ in terms of wavelength?
-Radio waves have much longer wavelengths, around the size of a building, while gamma rays have very short wavelengths, around the size of a nucleus.
What types of electromagnetic radiation can be found in a typical room, according to the video?
-In a typical room, you can find visible light, radio waves, and possibly microwaves.
Why are gamma rays more dangerous than radio waves?
-Gamma rays are more dangerous than radio waves because they have higher energy, which can damage or ionize cells, potentially causing harm to living organisms.
Outlines
🌈 Electromagnetic Radiation and Infrared Discovery
In this segment, Mr. Andersen introduces the topic of electromagnetic radiation, starting with the historical experiment by Newton who demonstrated the dispersion of white light into its constituent colors using a prism. The narrative then shifts to William Herschel's investigation into the relationship between light colors and temperature. Herschel used a thermometer to measure the heat emitted by different colors of light, including purple, blue, green, yellow, and red. Unexpectedly, he discovered that the area beyond red light, which we now know as infrared, was the hottest. This led to the understanding that electromagnetic radiation encompasses more than just visible light. The video script explains that the visible light spectrum is just a small part of the broader electromagnetic spectrum, which ranges from low-wavelength, high-frequency gamma rays to long-wavelength, low-frequency radio waves. The script also touches on the presence of various types of electromagnetic waves in the room, such as visible light, radio waves, and microwaves, and contrasts them with the potentially harmful gamma rays. The summary concludes with a discussion on the inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency and the energy carried by electromagnetic waves, highlighting the potential damage caused by high-energy waves like gamma rays.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electromagnetic Radiation
💡Visible Light
💡Infrared Rays
💡Spectrum
💡Wavelength
💡Frequency
💡Energy
💡Gamma Rays
💡X-rays
💡Ultraviolet
💡Microwaves
💡Radio Waves
Highlights
Newton's discovery that white light breaks into different colors when passed through a prism.
William Herschel's experiment to find the relationship between light colors and temperature.
Herschel's unexpected discovery of infrared rays beyond the visible spectrum.
Infrared rays are invisible but generate a lot of heat.
Electromagnetic radiation includes a wide range of wavelengths beyond visible light.
The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from low wavelengths to kilometers, with increasing frequency.
As frequency increases, so does the energy of electromagnetic waves.
High-energy electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, x-rays, and infrared.
Visible light is just a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Ultraviolet, microwaves, and radio waves are also part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radio waves can be used to pick up radio and TV signals.
Microwaves are present in the room, but hopefully not too many gamma rays.
Wavelength decreases as we move towards higher energy gamma rays.
Radio waves have wavelengths comparable to the size of a building, while gamma rays are nuclear-sized.
There is an inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency.
Higher frequency electromagnetic waves carry more energy.
Long wavelength, low frequency waves have less energy and are less harmful.
Short wavelength, high frequency waves can damage and ionize cells.
Learning to make qualitative comparisons based on wavelength and frequency of electromagnetic radiation.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
Electromagnetic Waves

Light waves, visible and invisible

Introduction To Light | Properties of Light | Introduction to Light | properties of light | letstute
Electromagnetic Spectrum - Basic Introduction

GCSE Physics - Electromagnetic Waves #64

The Electromagnetic Spectrum Song - by Emerson & Wong Yann (Singapore)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: