Neoliberal Policies, Globalization, & Trade [AP Human Geography Unit 7 Topic 6]
TLDRThis video from the Mr. Sin Channel delves into the intricacies of the global economy and international trade. It explores the impact of globalization, the benefits and challenges of participating in the world market, and the concept of comparative advantage. The script discusses trade indices, the role of organizations like the WTO and IMF, and the influence of neoliberal policies on economic growth. It also touches on the negative aspects of globalization, such as increased income inequality and the vulnerability of interconnected economies to crises.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Globalization has interconnected the world's economies, cultures, and nations through increased trade and interaction.
- 💼 Countries have opened their markets to global trade, increasing competition and consumer choice, and allowing for capital investments worldwide.
- 📈 Globalization has led to businesses accessing the global labor market, creating production and employment opportunities, but also contributing to income inequality.
- 🔄 Countries participate in the global economy to gain access to natural resources, improve efficiency, specialize, access new technologies, and strengthen political ties.
- 🔄 The Trade Complementary Index measures the likelihood of trade between countries based on the match between their export and import patterns.
- 💡 Comparative advantage is the concept where countries have a lower opportunity cost in producing a specific good or service, encouraging specialization and efficiency.
- 🛒 Neoliberal policies promote free trade and reduced government intervention, aiming for private ownership, free trade, and individual freedom over state control.
- 🏦 Organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) and International Monetary Fund (IMF) work to promote globalization and free trade for economic growth.
- 🏛 The European Union and MERCOSUR aim to integrate national economies into the international market for business and investment opportunities.
- 💰 OPEC's objective is to coordinate petroleum policies for stable oil prices, but it can also restrict competition and artificially inflate prices.
- 🔗 Neoliberal policies have led to the creation of free trade agreements like NAFTA and USMCA to promote economic growth and stability in specific regions.
Q & A
What is the impact of globalization on the global economy?
-Globalization has interconnected the world, increasing competition in the market, providing consumers with more choices, and creating new investment opportunities, economic opportunities, and access to the global labor market. However, it has also contributed to the rise in income inequality due to uneven distribution of economic benefits.
Why do countries participate in the global economy?
-Countries participate in the global economy to gain access to natural resources they may lack, improve efficiency and productivity, specialize more, access new technologies and ideas, and strengthen political relationships with other countries.
What is the trade complementary index, and how does it relate to global trade?
-The trade complementary index compares the export patterns of one country with the import patterns of another, indicating the likelihood of trade between them. A higher score suggests a more favorable trade relationship, with 100 meaning perfect match and 0 meaning no complementarity.
How does the complementary index affect trade between Chile and North America versus Latin America?
-According to the World Trade Organization data, Chile's imports are more complementary with North American countries than with those in Latin America, suggesting that it makes more economic sense for Chile to trade with North America despite the geographical proximity to Latin America.
What is comparative advantage and why is it important for countries in global trade?
-Comparative advantage refers to a country's ability to produce a specific good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another country. It is important because it allows countries to specialize in what they are good at, become more efficient, and trade with others to get goods and services they do not have a comparative advantage in.
How does specialization and trade based on comparative advantage benefit a country?
-Specialization and trade based on comparative advantage allow a country to become more efficient and productive in the goods and services it specializes in. This leads to increased production and the ability to acquire other goods and services through trade, ultimately benefiting the country more than if it tried to produce everything itself.
What is a tariff and how does it affect domestic and foreign goods?
-A tariff is a tax imposed by a government on imported goods and services. It aims to make foreign goods more expensive, encouraging consumers to buy domestically produced goods. Tariffs are paid by businesses but often passed onto consumers through higher product prices.
What are the arguments against tariffs and for free market competition?
-Critics argue that tariffs distort market prices and prevent efficient resource use. Economists like Milton Friedman and John Maynard Keynes believed in the benefits of free trade and market competition, which can lead to economic prosperity without government intervention.
What is neoliberalism and how does it relate to global trade policies?
-Neoliberalism is an economic policy characterized by reduced government intervention, promotion of free market capitalism, private ownership, free trade, and individual freedom. It encourages policies that support globalization and free trade, such as those of the World Trade Organization.
What role do international organizations like the World Trade Organization play in global trade?
-The World Trade Organization provides a forum for negotiating agreements aimed at reducing trade barriers and ensuring a level playing field for all countries. Its primary purpose is to open trade for the benefit of all, contributing to economic growth and development.
How do free trade agreements like NAFTA and USMCA impact the global economy?
-Free trade agreements like NAFTA and its successor USMCA promote free trade between member countries, aiming to stimulate economic growth and stability in the region. They create new spatial connections and economic interdependencies between countries and regions.
What are the potential negative impacts of neoliberal policies on the global economy?
-Neoliberal policies can prioritize the needs of wealthier corporations and states over developing regions, increasing economic inequality. Deregulation may lead to less accountability and unethical behavior, and competition with less developed areas can negatively impact workers in more advanced regions.
How can global crises, such as the 2008 financial collapse or COVID-19, affect the interconnected global economy?
-Global crises can have a ripple effect on the entire world economy. For example, the 2008 financial collapse in the U.S. impacted the global community for years, and COVID-19 caused a halt in the global economy, leading to shortages and broken supply chains.
What was the impact of the Ever Given blocking the Suez Canal on global trade?
-The blocking of the Suez Canal by the Ever Given in 2021 disrupted one of the world's busiest trade routes, costing an estimated $9.6 billion in trade per day, or $400 million per hour, highlighting the significance of global trade routes and their vulnerability to disruptions.
Outlines
🌏 Globalization and World Economy Overview
This paragraph introduces the concept of globalization and its impact on the world economy. It explains how countries have become more interconnected through trade, leading to increased market competition and consumer choice. The paragraph also touches on the benefits of capital investments and access to the global labor market, but notes the rise in income inequality due to uneven distribution of economic benefits. The reasons for countries participating in the global economy are outlined, including access to natural resources, improved efficiency, specialization, and political relationship strengthening. The complementary index and comparative advantage are introduced as key concepts influencing trade relationships between countries.
📈 Trade Policies and Economic Strategies
The second paragraph delves into the reasons countries engage in global trade, emphasizing the importance of specialization and comparative advantage for efficiency and productivity. It discusses government policies such as tariffs designed to protect domestic industries and reduce trade deficits, but also the arguments against such protectionist measures by economists like Milton Friedman. Neoliberalism is introduced as a policy promoting free trade and reduced government intervention, with organizations like the World Trade Organization and the International Monetary Fund working towards global economic growth. The paragraph also mentions other regional organizations and trade agreements like Mercosur, the European Union, and OPEC, each with different objectives and impacts on the global market.
🔄 Neoliberalism's Impact and Global Interdependence
The final paragraph examines the consequences of neoliberal policies on global trade networks and spatial connections, highlighting the creation of free trade agreements like NAFTA, which was replaced by USMCA. It discusses the criticisms of neoliberalism, including the prioritization of wealthier corporations and states over developing regions, leading to increased economic inequality. The paragraph also addresses the negative impacts of market deregulation and the vulnerability of developing nations in the global economy. It concludes with examples of how global crises, such as the 2008 financial collapse and the COVID-19 pandemic, affect the interconnected world, emphasizing the significance of supply chain disruptions and the ongoing efforts by international organizations to promote economic development and stability.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Globalization
💡Complementary Index
💡Comparative Advantage
💡Scarcity
💡Trade Deficit
💡Tariff
💡Neoliberalism
💡World Trade Organization (WTO)
💡International Monetary Fund (IMF)
💡European Union (EU)
💡Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
Highlights
Globalization has interconnected the world, impacting economies and cultures through increased trade and interaction.
Markets have opened up, increasing competition and consumer choice due to globalization.
Capital investments are being made worldwide, creating new economic opportunities in peripheral regions.
Global labor market access has led to new business production opportunities and worker benefits.
Rise in income inequality due to unequal distribution of economic benefits in the globalized world.
Countries participate in the global economy to gain access to natural resources, improve efficiency, and strengthen political ties.
Trade complementary index measures the likelihood of trade between countries based on export and import patterns.
Comparative advantage allows countries to specialize in goods or services they produce more efficiently.
Specialization and trade lead to increased efficiency and productivity for countries.
Tariffs are taxes on imported goods, aiming to promote domestic production but can distort market prices.
Neoliberalism promotes free trade and reduced government intervention in the economy.
World Trade Organization works to reduce trade barriers and ensure a level playing field for global trade.
IMF's missions include promoting international monetary cooperation and sustainable economic growth.
Organizations like Mercosur, EU, and OPEC promote regional integration and economic stability.
Free trade agreements like NAFTA and USMCA aim to increase economic growth and regional stability.
Neoliberal policies have led to increased global trade networks but also economic inequality and market instability.
Global crises, such as the 2008 financial collapse and COVID-19, have shown the interconnectedness and vulnerability of the global economy.
Supply chain disruptions, like the Suez Canal blockage, can have significant economic impacts globally.
The global economy's interconnectedness affects all levels of society, from local workers to national policies and international relations.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

ECONOMICS in the Global Age [AP World History Review, Unit 9 Topic 4] Period 6: 1900-Present

19. International Trade: Welfare and Policy

The Expansion of Silver Trade | Modern World History 13 of 30 | Study Hall

RESISTANCE to Globalization after 1900 [AP World History, Unit 9 Topic 7] Period 6: 1900-present
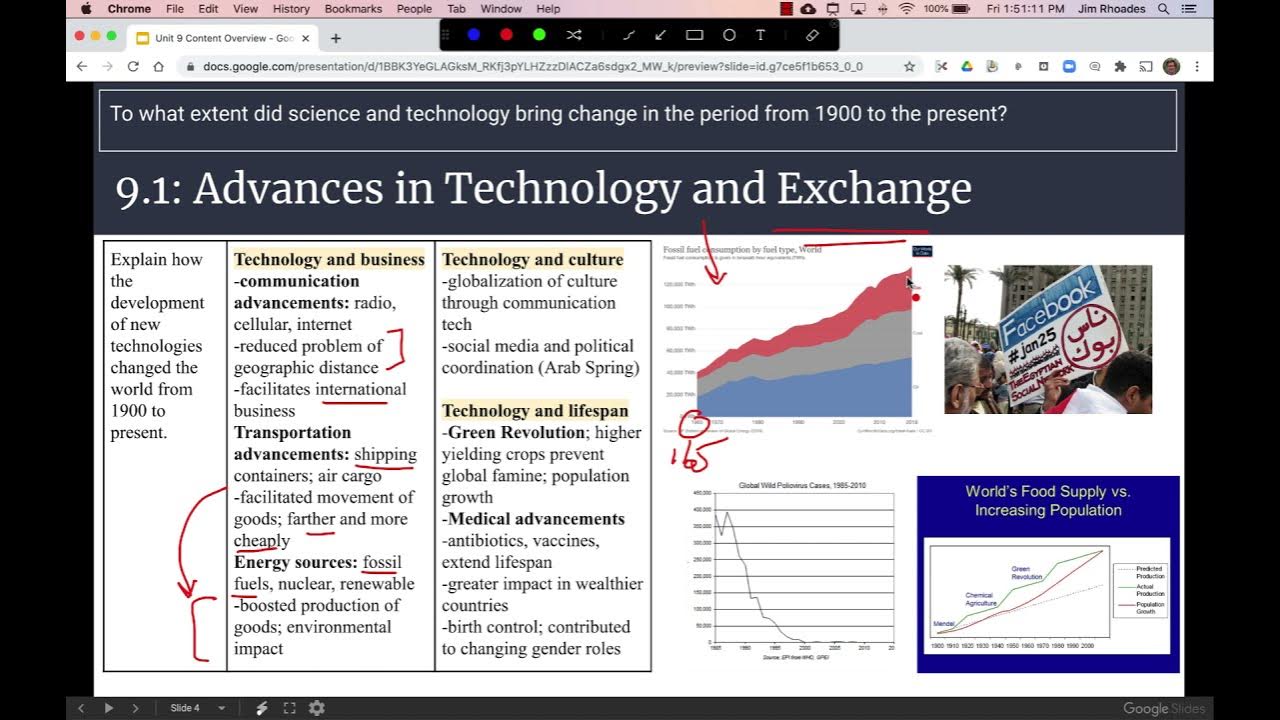
APWH Modern Unit 9 Overview

Challenges of Modern Agricultural Practices [AP Human Geography Unit 5 Topic 11]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: