ECONOMICS in the Global Age [AP World History Review, Unit 9 Topic 4] Period 6: 1900-Present
TLDRThis video explores the economic shifts from 1900 to the present, focusing on the spread of free market economics post-Cold War, the emergence of knowledge economies fueled by advancements in communication and IT, and the growth of transnational free trade organizations and multinational corporations. It discusses examples like the US, UK, Chile, China, Finland, and Japan, and highlights the impact of globalization on manufacturing and the global economy.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The global economy from 1900 to the present has seen significant shifts, with three main movements: the spread of free market economics, the rise of knowledge economies, and the growth of transnational free trade organizations and multinational corporations.
- 💡 Free market economics proliferated after the end of the Cold War and the collapse of the Soviet Union, leading to economic liberalization worldwide.
- 🚀 The U.S. and U.K. under Reagan and Thatcher played key roles in promoting free market economies globally.
- 🇨🇱 Chile's economy transitioned from state control to free market under Augusto Pinochet, with the help of the 'Chicago Boys' economists.
- 🇨🇳 China's economic policies shifted towards more free market approaches under Deng Xiaoping, leading to increased economic freedoms and a desire for broader liberties.
- 📚 The rise of knowledge economies was driven by advancements in communication and information technology towards the end of the 20th century.
- 🇫🇮 Finland and Japan are examples of countries that successfully transitioned into knowledge economies through investments in technology and education.
- 🏭 The manufacturing sector has largely moved to Asia and Latin America, where labor is cheaper, impacting the global distribution of manufacturing jobs.
- 🌍 Transnational free trade organizations like NAFTA and ASEAN have facilitated trade between nations by reducing tariffs and other barriers.
- 🕊️ The World Trade Organization (WTO) aims to reduce trade barriers globally, with 164 member nations representing over 95% of global trade.
- 🏢 Multinational corporations have become major players in the global economy, employing knowledge workers in one country and manufacturing and selling goods in others.
Q & A
What were the three main movements in the global economy from 1900 to the present discussed in the video?
-The three main movements are the proliferation of free market economics, the rise of knowledge economies, and the rise of transnational free trade organizations and multinational corporations.
How did the end of the Cold War influence the spread of free market economics?
-The end of the Cold War accelerated the spread of free market economics as former Soviet bloc countries in Eastern Europe transitioned from communism to free-market economies and democratic governments.
What role did Mikhail Gorbachev's perestroika reforms play in the Soviet Union's economy?
-Mikhail Gorbachev's perestroika reforms introduced some limited free market economics in the Soviet Union before its collapse, which was later accelerated after the USSR was dismantled.
Which countries were notable for encouraging the growth of free market economies after the Cold War?
-The United States under President Ronald Reagan and Great Britain under Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher were notable for encouraging the growth of free market economies worldwide.
How did the Chicago Boys contribute to Chile's economic transformation?
-The Chicago Boys, a group of economists from the University of Chicago, addressed Chile's economic problems by implementing free market reforms, privatizing state-run businesses, and tackling rampant inflation under Augusto Pinochet's regime.
What economic changes did Deng Xiaoping introduce in China?
-Deng Xiaoping relaxed some of China's communist economic policies by allowing peasants to lease land and sell their crops at market, permitting private ownership of some businesses, and moving towards a more open economy.
What is a knowledge economy and how does it differ from a traditional economy?
-A knowledge economy is one that depends on the quality and quantity of information available, which can be monetized as a commodity. It contrasts with traditional economies where workers are involved in manufacturing physical goods, whereas in a knowledge economy, workers are more focused on intellectual and informational roles.
How did Finland transition into a knowledge economy?
-Finland transitioned into a knowledge economy by heavily investing in communication technology and education, which allowed them to secure a significant share of the world's cell phone and software development markets.
What impact did the rise of knowledge economies have on the global manufacturing sector?
-The rise of knowledge economies led to a decrease in manufacturing work in nations where knowledge work increased. Manufacturing jobs were outsourced to countries in Asia and Latin America where labor was cheaper, resulting in a global shift in the manufacturing industry.
What is the purpose of a transnational free trade organization?
-The purpose of a transnational free trade organization is to eliminate barriers to exchange between nations, such as tariffs, in order to facilitate trade and promote economic integration and growth.
How does the World Trade Organization (WTO) contribute to the globalization of the world's economy?
-The WTO contributes to the globalization of the world's economy by having member nations represent over 95% of global trade and working to reduce barriers to trade in the form of tariffs, quotas, and other restrictions, thus promoting the free flow of goods, services, and intellectual property.
What are the key characteristics of a multinational corporation?
-A multinational corporation is an entity incorporated in one country but manufactures and sells goods in other countries, employing knowledge workers in their home country and selling products on a global market.
Outlines
🌐 Global Economy Shifts and Free Market Expansion
This paragraph discusses the significant changes in the global economy from 1900 to the present, focusing on the spread of free market economics. The end of the Cold War and the collapse of the Soviet Union accelerated economic liberalization, with former Soviet bloc countries and nations in the non-aligned movement adopting free-market economies. Examples include the United States and the United Kingdom under Reagan and Thatcher, Chile under Pinochet with the influence of the 'Chicago Boys', and China's economic reforms under Deng Xiaoping. These shifts laid the groundwork for the spread of economic freedom and the desire for broader political freedoms.
💡 Rise of Knowledge Economies and Manufacturing Decline
The paragraph highlights the emergence of knowledge economies, which are based on the availability and monetization of information. This shift was fueled by advancements in communication and information technology towards the end of the 20th century. Workers in knowledge economies focus on intellectual tasks rather than manufacturing. Examples provided include Finland's investment in communication technology and education, leading to success in the cell phone and software markets, and Japan's transition from a manufacturing-based economy to a leader in banking, finance, and information technology. The paragraph also addresses the decline in manufacturing jobs in knowledge-work-intense countries, with these jobs often moving to Asia and Latin America where labor costs are lower.
🌍 Growth of Transnational Organizations and Multinational Corporations
This section examines the rise of transnational free trade organizations and multinational corporations. Transnational free trade organizations are agreements between nations that reduce trade barriers, such as tariffs. Examples include NAFTA, which allowed for tariff-free trade between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico, and ASEAN, which has fostered integration and growth among Southeast Asian nations. The World Trade Organization (WTO) is also mentioned as a global free trade agreement with a wide membership. Multinational corporations are entities that operate in multiple countries, employing knowledge workers and manufacturing goods for sale globally. Nestlé and Mahindra & Mahindra are cited as examples. The paragraph concludes by reflecting on the profound changes in the world economy due to globalization since 1900.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Globalization
💡Free Market Economics
💡Knowledge Economy
💡Transnational Free Trade Organizations
💡Multinational Corporations
💡Economic Liberalization
💡Perestroika
Highlights
Explaining the continuities and changes in the global economy from 1900 to the present.
The proliferation of free market economics post-Cold War and collapse of the Soviet Union.
Mikhail Gorbachev's introduction to limited free market economics through perestroika reforms.
The shift of Eastern European nations from communism to free-market economies.
The encouragement of free market economies by leaders like Ronald Reagan and Margaret Thatcher.
The economic transformation in Chile under Augusto Pinochet, influenced by the Chicago Boys.
The unpopularity of Chile's economic reforms due to Pinochet's authoritarian enforcement.
China's economic liberalization under Deng Xiaoping, allowing private ownership and market freedoms.
The rise of knowledge economies, defined by the reliance on information and its monetization.
Finland's investment in communication technology and education, leading to a significant presence in global markets.
Japan's transition from a manufacturing-based economy to a leader in the knowledge economy.
The shift of the world's manufacturing sector to Asia and Latin America due to lower labor costs.
The emergence of transnational free trade organizations, such as NAFTA and ASEAN.
The World Trade Organization (WTO) facilitating global trade by reducing tariffs and quotas.
The rise of multinational corporations, defined as entities operating in multiple countries.
Nestlé as an example of a multinational corporation, sourcing and selling globally.
The significant changes in the world economy after 1900 due to globalization.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
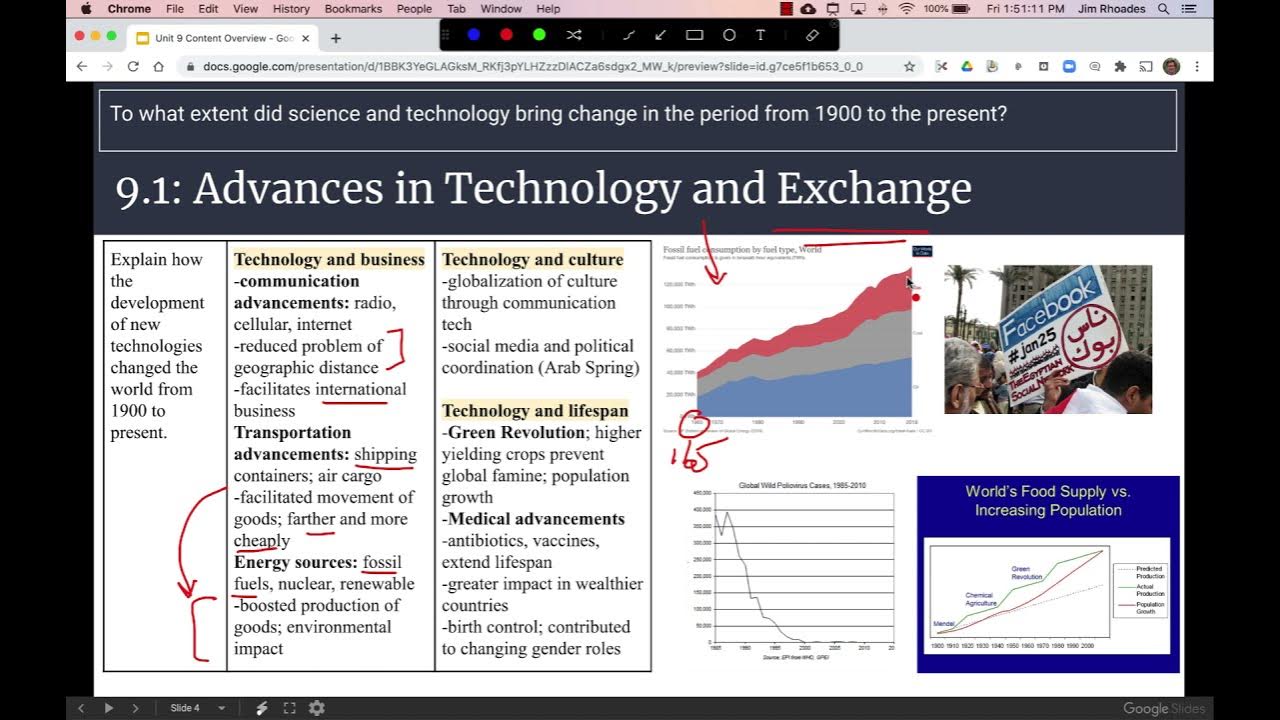
APWH Modern Unit 9 Overview

Neoliberal Policies, Globalization, & Trade [AP Human Geography Unit 7 Topic 6]

AP World History (WHAP) Unit 9 Part 3: International Cooperation

The Economics of the Industrial Revolution [AP World History Review—Unit 5 Topic 7]

AP World History (WHAP) Unit 9 Part 2: Economic Transformation (20th c.)

Globalized CULTURE After 1900 [AP World History Review, Unit 9 Topic 6] Period 6: 1900-Present
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: