RESISTANCE to Globalization after 1900 [AP World History, Unit 9 Topic 7] Period 6: 1900-present
TLDRThis video explores the varied responses to globalization from 1900 to the present, highlighting the discontent and resistance it has sparked. It discusses the 1999 Battle of Seattle, which brought global attention to economic inequality, and the creation of the World Social Forum in 2001. The video also addresses protests against the IMF and World Bank, environmental concerns, threats to national sovereignty, and human rights abuses linked to globalization. It contrasts the benefits enjoyed by the global north with the costs borne by the global south, and examines China's approach to managing social media to prevent the spread of dissenting ideas.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Globalization has had varied responses since 1900, with both positive and negative impacts on different regions.
- 📈 The global north generally benefited more from globalization in terms of prosperity and cultural influence.
- 🔄 In the 1970s, nations of the global south sought corrections to the international economic order, but their demands were largely unheeded.
- 🏙️ The Battle of Seattle in 1999 brought global inequality to the world's attention and led to the creation of the World Social Forum in 2001.
- 🛑 Critics of the WTO argue that it has lowered labor standards and contributed to environmental degradation, among other issues.
- 🌍 Protests against the IMF and World Bank started in the late 1980s, with a significant demonstration in West Berlin in 1988.
- 🌳 Environmental concerns are a major complaint against globalization, with increased shipping of goods contributing to carbon emissions and climate change.
- 🏛️ National sovereignty is seen as threatened by globalization, exemplified by Brexit as a response to perceived constraints from the EU.
- 💰 Human rights abuses are linked to some trade agreements, with child labor and low wages being significant concerns.
- 📱 Social media's role in globalization is contentious, with China shutting down Western platforms like Facebook and Twitter and introducing its own controlled platform, Weibo.
- 🚫 Resistance to globalization stems from a variety of concerns, including economic disparity, environmental impact, national sovereignty, and human rights abuses.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The main focus of the video is to explain the various responses to increasing globalization from 1900 to the present.
How did the process of globalization affect social, political, and economic realities during the 20th and 21st centuries?
-The process of globalization affected social, political, and economic realities by impacting nearly every corner of the known world, with the global north benefiting most in terms of prosperity and cultural influence.
What was the outcome of the nations of the global south demanding correctives to the international economic order in the 1970s?
-The wealthy nations of the world did not take significant action in response to the demands, and nothing really ever came of it.
What event brought global inequality to the world's attention in 1999?
-The protest movement known as the Battle of Seattle brought global inequality to the world's attention in 1999.
Why was the World Trade Organization (WTO) a target for anti-globalization sentiments?
-The WTO was a target for anti-globalization sentiments because critics believed it lowered labor standards, caused environmental degradation, violated human rights, and prevented developing nations from protecting themselves against Western interests.
What was the World Social Forum, and what was its purpose?
-The World Social Forum was created in 2001 as a response to globalization, embodying the ideals of anti-globalizationists and working to create a more equitable world.
How did protests against the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank evolve over time?
-Protests against the IMF and the World Bank started in 1988 with a visual protest in West Berlin and expanded by 2001 to include protests across the world in 23 nations, mostly poorer ones who felt they were being slighted by the system.
What is one environmental complaint against globalization?
-One environmental complaint against globalization is the unsustainable strain it puts on the environment, such as releasing more carbon dioxide through shipping goods worldwide, which accelerates climate change.
How did the concept of national sovereignty become a point of resistance against globalization?
-National sovereignty became a point of resistance as some countries, like Britain with Brexit, saw globalization and international partnerships as constraints on their ability to make political and economic decisions in their own best interests.
What was China's response to the perceived threat of Western social media platforms?
-China responded by shutting down sites like Facebook and Twitter, which they believed were responsible for creating unrest, and introduced their own platform called Weibo, which allowed for social media use without the 'danger' of Western ideas.
Outlines
🌐 Introduction to Resistance to Globalization
This paragraph introduces the topic of resistance to globalization, a movement that emerged in response to the cultural and economic homogenization brought about by globalization. It sets the stage for the video by acknowledging that not everyone is in favor of a globalized world and hints at the various forms this resistance takes, from political movements to social protests. The paragraph also briefly mentions the historical context of globalization within the AP World History curriculum, specifically unit 9, and teases the upcoming exploration of the causes and effects of this resistance from 1900 to the present day.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Globalization
💡Resistance to Globalization
💡Battle of Seattle
💡World Trade Organization (WTO)
💡World Social Forum
💡International Monetary Fund (IMF)
💡Environmental Degradation
💡National Sovereignty
💡Human Rights Abuses
💡Social Media
Highlights
Exploring the various responses to increasing globalization from 1900 to the present.
Globalization's impact on social, political, and economic realities worldwide.
The global north benefiting more from globalization in terms of prosperity and cultural influence.
The demand for correctives to the international economic order by the global south in the 1970s.
The Battle of Seattle in 1999 bringing global inequality to the world's attention.
The World Trade Organization (WTO) as a target for anti-globalization sentiments.
The creation of the World Social Forum in 2001 embodying anti-globalization ideals.
Protests against the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank for favoring richer countries.
The expansion of protests against the IMF and World Bank to 23 nations by 2001.
The environmental strains caused by globalization, such as increased carbon dioxide emissions and climate change.
The perceived threat to national sovereignty due to globalization, exemplified by Brexit.
The association of globalization with human rights abuses, like child labor and low wages.
China's approach to resisting western social media platforms by shutting them down and introducing its own platform, Weibo.
The Chinese government's filtering of information on Weibo to prevent the spread of western ideas.
The mixed blessings of globalization, bringing economic and social benefits to some but not to all.
The rise of resistance movements against globalization due to its uneven distribution of benefits.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
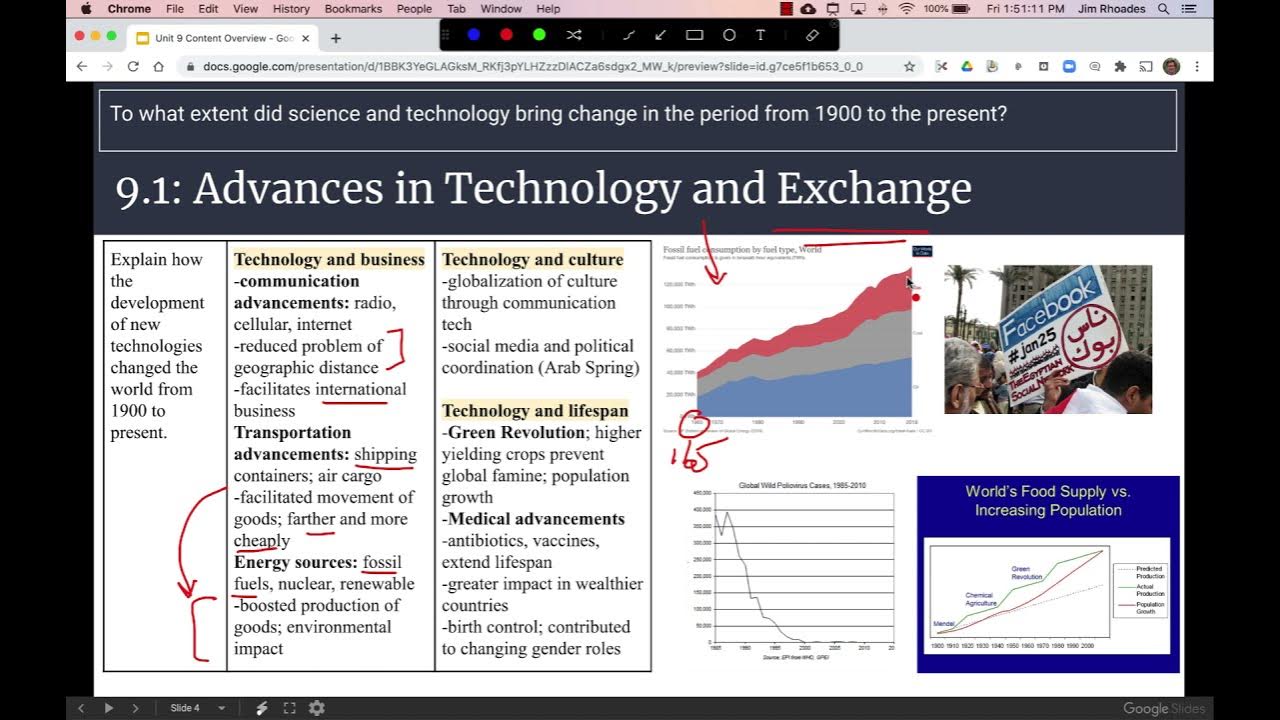
APWH Modern Unit 9 Overview

Neoliberal Policies, Globalization, & Trade [AP Human Geography Unit 7 Topic 6]

Globalized CULTURE After 1900 [AP World History Review, Unit 9 Topic 6] Period 6: 1900-Present

ECONOMICS in the Global Age [AP World History Review, Unit 9 Topic 4] Period 6: 1900-Present

AP World History (WHAP) Unit 6 Introduction: Consequences of Industrialization 1750-1900

The Next Global Superpower Isn't Who You Think | Ian Bremmer | TED
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: