Quantum Physics For Babies Book Read Aloud For Babies & Children
TLDRIn 'Quantum Physics for Babies' by Chris Ferrie, the concept of quantum physics is introduced to young minds in a playful and accessible manner. The video begins with the illustration of a ball possessing energy, contrasting it with a ball that has zero energy. It then delves into the atomic structure, explaining that all balls are composed of atoms, which include neutrons, protons, and electrons. The narrative highlights the quantized nature of electron energy levels, where electrons can only exist in specific energy states and cannot be found in between. The video creatively demonstrates that electrons can absorb energy to move to a higher energy level and release energy to descend to a lower one. This energy exchange is quantized, with each unit of energy change being referred to as a 'quantum.' The script concludes by humorously bestowing the title of 'quantum physicist' upon the viewer, encouraging a sense of curiosity and achievement. The video is part of the 'a.m. p.m. story time,' which is suitable for any time of the day, whether for waking up, snacking, or bedtime, inviting viewers to join and enjoy a book-filled experience.
Takeaways
- 🏀 This is a ball: The script begins with a simple introduction to a ball, which serves as a starting point for the discussion on energy.
- ⚡ Ball has energy: It is mentioned that the ball possesses energy, setting the stage for the concept of energy in quantum physics.
- 🔋 Zero energy state: The concept of a ball with zero energy is introduced, which is a fundamental idea in quantum mechanics.
- ⚛️ Atoms composition: The script explains that all balls are made of atoms, which are composed of neutrons, protons, and electrons.
- ⚡️ Electron energy states: Electrons can exist in different energy states, which are represented by their position relative to the nucleus.
- 🚫 Quantum uncertainty: It is stated that an electron cannot exist in between these energy states, highlighting the discrete nature of quantum physics.
- 🔵 Maximum and minimum energy: The script distinguishes between an electron with the most energy (green) and one with the least, illustrating energy levels.
- 🔢 Energy quantization: The energy that electrons possess is quantized, meaning it comes in specific, discrete amounts.
- ⬆️ Energy absorption: Electrons can absorb energy to move to a higher energy state, which is depicted as 'jumping up'.
- ⬇️ Energy release: Conversely, electrons must release energy to fall to a lower energy state, symbolized by 'falling down'.
- 💫 Quantum of energy: The amount of energy an electron exchanges during these transitions is referred to as a 'quantum'.
- 👨🔬 Becoming a quantum physicist: The script humorously suggests that by understanding these concepts, the reader has become a quantum physicist.
- 📚 Enjoyable learning: The closing remark encourages readers to enjoy books and learning at any time of the day, emphasizing the accessibility of knowledge.
Q & A
What does the book 'Quantum Physics for Babies' by Chris Ferrie aim to teach?
-The book aims to introduce the fundamental concepts of quantum physics to a very young audience in a simple and engaging way.
What is the significance of a ball in the context of the book?
-The ball is used as an analogy to explain the concept of energy on a basic level, emphasizing that all balls (or objects) have energy.
What are the three basic particles that make up an atom?
-The three basic particles that make up an atom are neutrons, protons, and electrons.
How does the script describe the behavior of electrons in an atom?
-The script describes that electrons can be in certain locations but not in between those locations, highlighting the quantized nature of their energy levels.
What is the term used to describe the discrete amount of energy that an electron can take or give?
-The term used is 'quantum,' which refers to the smallest possible discrete amount of energy an electron can exchange.
Why does the script mention that an electron cannot be in certain positions within an atom?
-This is referring to the quantum mechanical principle that electrons exist in specific energy levels or orbitals and cannot be found in between these quantized states.
What is the concept of energy quantization as explained in the book?
-Energy quantization refers to the idea that energy exists in discrete amounts or levels, rather than being continuous. An electron can only have specific, quantized energy levels.
How does the book use the concept of a 'quantum' to simplify the idea of energy exchange for babies?
-The book uses the term 'quantum' to describe the smallest packet of energy that an electron can absorb or emit, making the concept more digestible for young children.
What is the final message conveyed to the reader after explaining the concept of a quantum?
-The final message is that the reader, despite being very young, has now grasped the basics of quantum physics and can be considered a 'quantum physicist.'
What is the purpose of the 'a.m p.m story time' mentioned at the end of the transcript?
-The 'a.m p.m story time' is an invitation for readers to join and enjoy a book at any time of the day, whether it's in the morning, noon, or bedtime.
Why is music included in the transcript?
-The music is likely used to make the reading more engaging and entertaining for the young audience, enhancing their learning experience.
How does the book attempt to make complex scientific concepts accessible to babies?
-The book uses simple language, analogies, and repetitive structures to break down complex concepts like energy, atoms, and quantum physics into understandable parts for babies.
Outlines
📚 Introducing Quantum Physics to Babies
The first paragraph introduces the concept of quantum physics in a child-friendly manner through the book 'Quantum Physics for Babies' by Chris Ferrie. It explains that all objects, including a ball, are made up of atoms which consist of neutrons, protons, and electrons. The paragraph emphasizes the idea that electrons can exist in different energy states but cannot have zero energy. It also introduces the concept of quantization, where electrons can absorb or release energy in discrete amounts known as quanta. The educational content is wrapped up with an encouraging note, inviting the audience to embrace the title of 'quantum physicist'.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡quantum physics
💡energy
💡atoms
💡neutrons
💡protons
💡electrons
💡energy levels
💡quantized
💡quantum
💡energy absorption and release
💡story time
Highlights
This is a ball, this ball has energy
This ball has zero energy
All balls are made of atoms, neutrons, and protons
An electron can be here, or here, or here
An electron cannot be here no not right there or here
All electrons have energy
This electron in the green has the most energy
This electron has the least energy
There are no electrons with zero energy
This energy is quantized
An electron can take energy to jump up
It must give energy to fall down
This amount of energy is a quantum
Now you are a quantum physicist
Thanks for joining us guys and remember that a.m p.m story time is for any time of the day
Whether you're just waking up, noon time snacking or bedtime is happening, stop by and enjoy a book with us
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
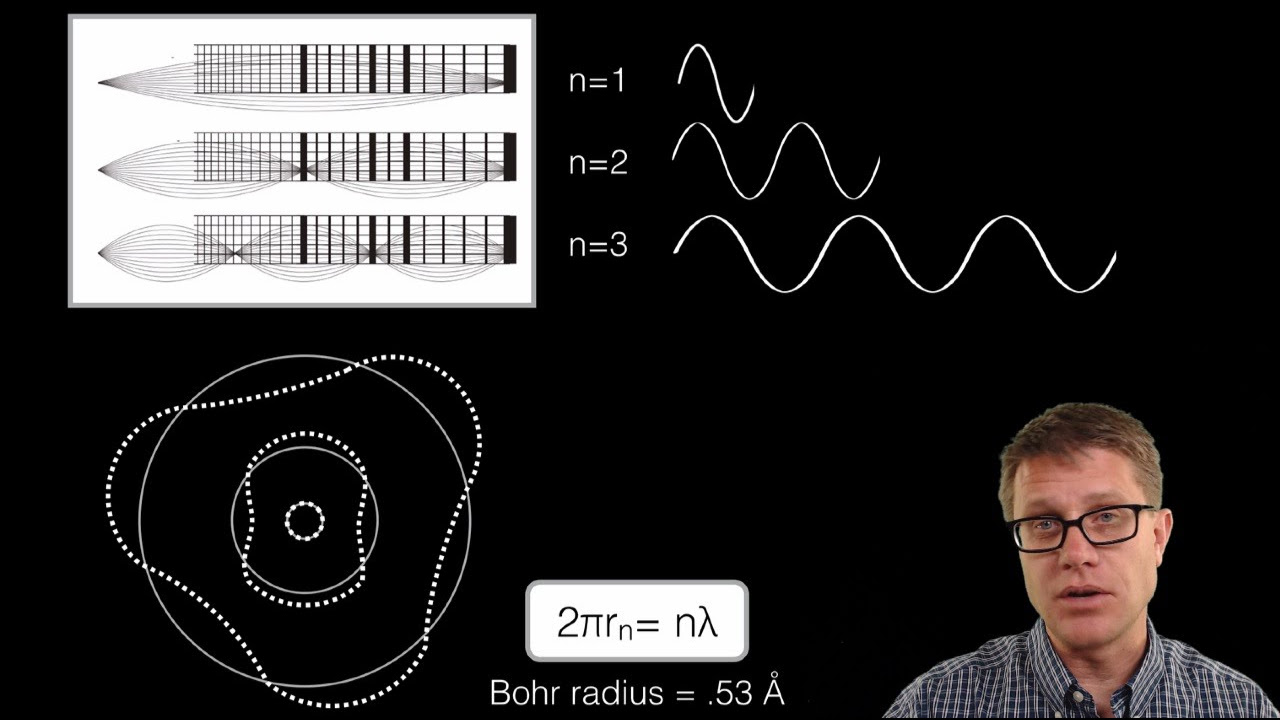
Wave Model of an Electron

Bohr's Atomic Model
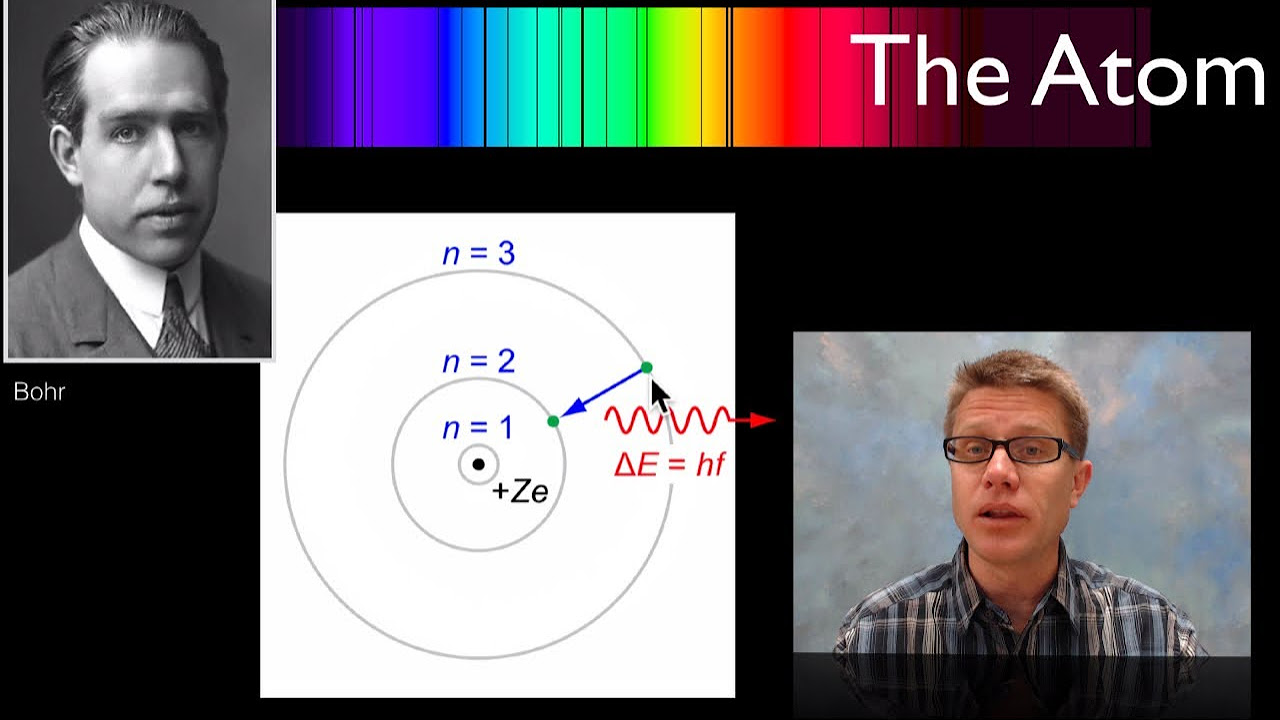
The Bohr Atom
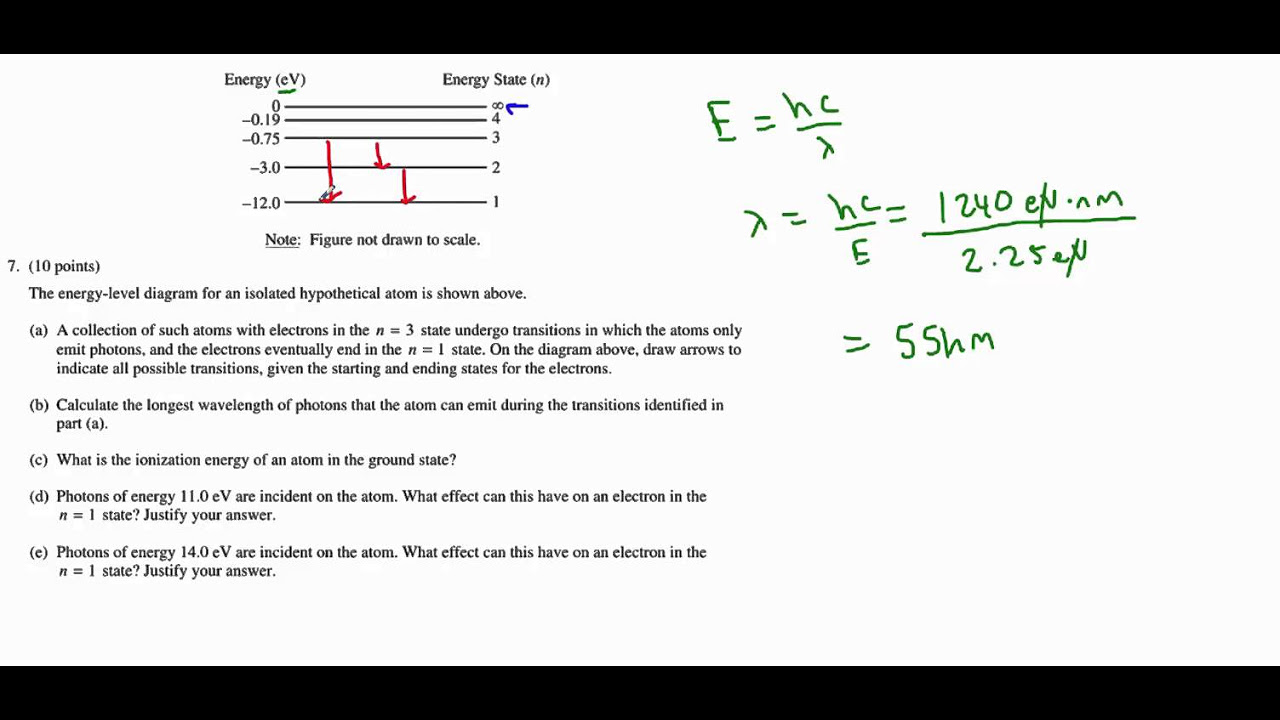
AP Physics B 2013 Question 7 - Modern Physics - Energy Levels
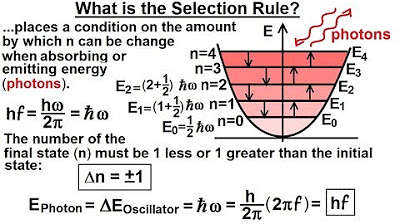
Physics - Ch 66 Ch 4 Quantum Mechanics: Schrodinger Eqn (44 of 92) What is the Selective Rule?
Physics - Ch 66 Ch 4 Quantum Mechanics: Schrodinger Eqn (39 of 92) What is the Quantum Oscillator?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: