What Distinguishes Compounds from Molecules?
TLDRThe video script delves into the fundamental concepts of chemistry, explaining the differences between atoms, molecules, and compounds. It describes atoms as the smallest units of elements, with noble gases being monoatomic. Molecules, on the other hand, are formed by two or more atoms chemically combined, and can be diatomic like H2 or polyatomic like O3. Compounds are molecules composed of different elements, such as water (H2O), and exhibit unique properties distinct from their constituent elements. The script also touches on the classification of elements into metals and nonmetals, the formation of ionic and covalent compounds, and the process of naming and representing compounds with chemical formulas.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Atoms are the fundamental units of elements and cannot be broken down further.
- 🔬 Noble gases like helium, neon, and argon exist as individual atoms and are known as monoatomic elements.
- 🤝 Molecules are formed when two or more atoms chemically combine, resulting in diatomic or polyatomic structures.
- 🌬️ Diatomic molecules consist of two atoms bonded together, such as H2 in the case of hydrogen molecules.
- 🌐 Polyatomic molecules are composed of three or more atoms, like the ozone molecule O3 made of three oxygen atoms.
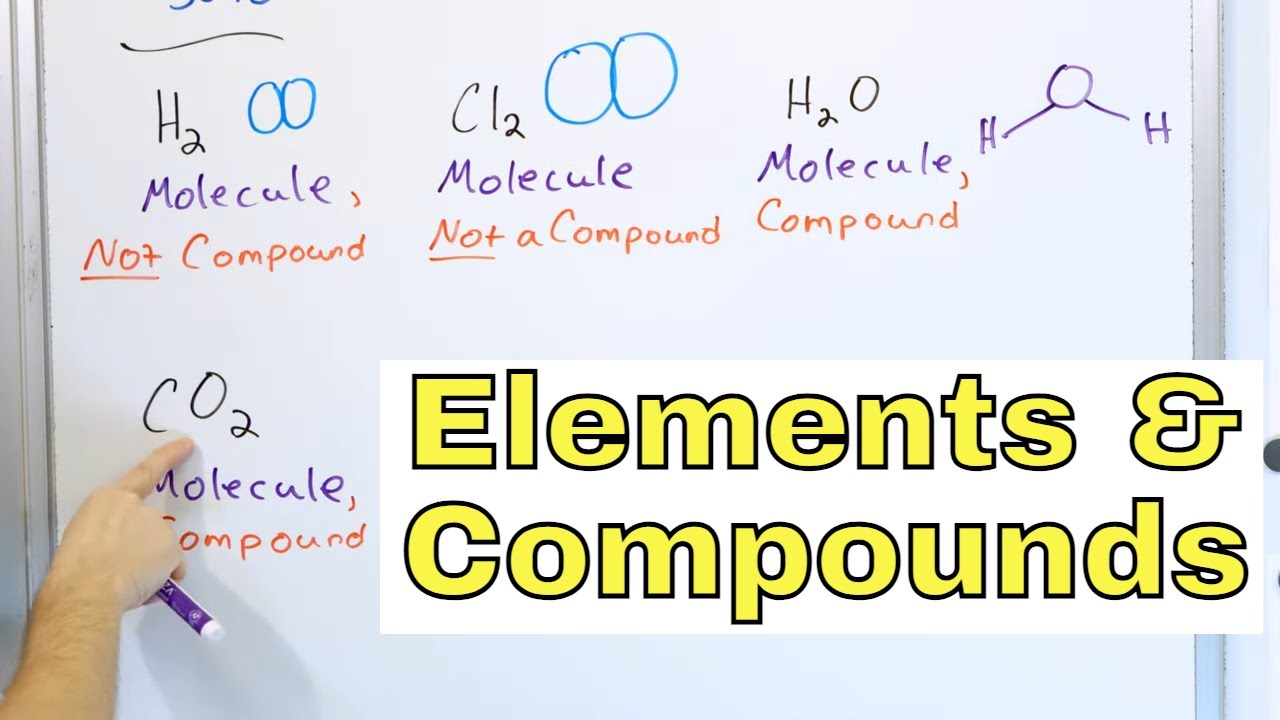
- 🧪 Compounds are molecules formed by two or more different elements chemically bonded together.
- 🏗️ The composition of a compound can be identified on the periodic table as either metal or nonmetal elements.
- 🔌 Ionic compounds are formed when metal elements combine with nonmetal elements, while molecular or covalent compounds are formed between nonmetallic elements.
- 🌈 Compounds have distinct properties that are different from the elements that constitute them, such as magnesium oxide being a white solid unlike its constituent elements.
- 📜 Naming compounds involves combining the names of the elements in a specific manner, like carbon dioxide (CO2) or sodium chloride (NaCl).
- 📊 A chemical formula represents the types and ratios of atoms in a compound, as seen in H2O where 'H' stands for hydrogen and 'O' for oxygen with their respective quantities.
Q & A
What are the smallest parts of an element called?
-The smallest parts of an element are called atoms.
What is the fundamental unit of an element?
-The fundamental unit of an element is an atom, which consists of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Which gases are known as noble gases and why?
-Noble gases include helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. They are called noble gases because they exist as individual atoms and are generally unreactive with other elements.
What is a molecule and how is it different from an atom?
-A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that form the smallest identifiable unit into which a pure substance can be divided and still retain the same chemical properties. Unlike atoms, which can exist alone (as in the case of noble gases), molecules are always made up of more than one atom.
What are diatomic and polyatomic molecules, and give examples of each?
-Diatomic molecules are those formed by the combination of two atoms. An example is a hydrogen molecule (H2), formed by two hydrogen atoms. Polyatomic molecules are formed by the combination of three or more atoms. An example is an ozone molecule (O3), formed by three oxygen atoms.
What is a compound and how does it differ from a molecule?
-A compound is also a type of molecule, but it specifically consists of two or more different elements that are chemically bonded together. For example, water (H2O) is a compound made by chemically joining an oxygen atom with two hydrogen atoms.
What is the significance of the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in water?
-The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in water is 2:1. This ratio is crucial because changing it results in a different compound with different properties.
How are elements classified on the periodic table in relation to compounds?
-Elements on the periodic table can be classified as metals and nonmetals. The right side of the line on the periodic table represents nonmetals, while the left side (except for hydrogen) represents metals. The presence of metal elements in a compound typically results in an ionic compound, while compounds formed only between nonmetallic elements are called molecular or covalent compounds.
How do the properties of a compound differ from the properties of the elements that form it?
-A compound has different properties from the elements that form it. For example, magnesium (a metal) and oxygen (a gas) combine to form magnesium oxide, which has different properties from both magnesium and oxygen. Magnesium is a silvery solid, oxygen is a colorless gas, but magnesium oxide is a white solid.
How are compounds named?
-Compounds are named based on the elements that compose them and their proportions. For instance, carbon and oxygen combine to form carbon dioxide, sodium and chlorine form sodium chloride, and zinc and oxygen form zinc oxide.
What information does a chemical formula provide about a compound?
-A chemical formula indicates the types of elements present in a compound and the ratio of different atoms. For example, in H2O, 'H' stands for hydrogen and 'O' stands for oxygen, while the number '2' indicates that there are two hydrogen atoms present. The absence of a number next to oxygen implies there is one oxygen atom.
Outlines
🌟 Understanding Atoms, Molecules, and Compounds
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concepts of atoms, molecules, and compounds. Atoms are the smallest units of elements, with each element consisting of a single type of atom. Noble gases like helium, neon, and argon are examples of monoatomic elements. Molecules, on the other hand, are formed by two or more atoms chemically combined, and can be diatomic (like H2) or polyatomic (like O3). Compounds are molecules made up of different elements, such as water (H2O), which is a combination of hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a 2:1 ratio. The composition of compounds can be analyzed through the periodic table, distinguishing between metal and nonmetal elements. Compounds exhibit unique properties that differ from the elements they are composed of, as demonstrated by the example of magnesium oxide, which has distinct properties from both magnesium and oxygen. The paragraph also touches on the naming and chemical formula representation of compounds.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Elements
💡Atoms
💡Molecules
💡Compounds
💡Diatomic
💡Polyatomic
💡Ionic Compounds
💡Molecular or Covalent Compounds
💡Chemical Formula
💡Properties of Compounds
💡Naming Compounds
Highlights
Atoms are the fundamental units of elements and cannot be broken down further.
Each element contains only one type of atom, forming the basic building blocks of matter.
Noble gases like helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon exist as individual atoms, known as monoatomic elements.
Molecules are formed by two or more atoms chemically combined, unlike single-atom elements.
Diatomic molecules consist of two atoms bonded together, such as hydrogen molecules (H2).
Polyatomic molecules are composed of three or more atoms, like ozone molecules (O3) made of three oxygen atoms.
Compounds are molecules formed by two or more different elements chemically bonded together.
Water is a compound formed by the chemical combination of oxygen and hydrogen atoms in a 2:1 ratio.
The properties of a compound are different from the elements that make it up, such as magnesium oxide being a white solid unlike its constituent elements.
Metal and nonmetal elements on the periodic table can be classified to understand the type of compounds they form.
Ionic compounds are formed when metal elements combine with nonmetal elements.
Molecular or covalent compounds are formed between nonmetal elements.
Naming compounds involves combining the names of the elements in a specific manner, like carbon dioxide (CO2).
A chemical formula represents the types and ratios of atoms in a compound, such as H2O indicating two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
The study of atoms, molecules, and compounds is crucial for understanding the composition and properties of matter.
The distinction between monoatomic, diatomic, and polyatomic molecules is essential for grasping chemical structures and reactions.
The concept of compounds reveals how elements can combine in specific ratios to form substances with unique properties.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Elements, Atoms, Molecules, Ions, Ionic and Molecular Compounds, Cations vs Anions, Chemistry

Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Intro to Elements, Compounds, & the Periodic Table - [1-1-3]

What is the difference between an Atom, Element, Molecule and Compound?

BTEC Applied Science: Unit 1 Chemistry Elements
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: