Elements, Atoms, Molecules, Ions, Ionic and Molecular Compounds, Cations vs Anions, Chemistry
TLDRThe video script offers a detailed explanation of the fundamental differences between atoms and molecules, and further delves into the concepts of pure elements and compounds. It clarifies that atoms are single units of matter, while molecules are made up of two or more atoms bonded together. The script also distinguishes between pure elements, which consist of a single type of atom, and compounds, which are composed of different types of atoms. It introduces the viewer to the classification of compounds into ionic and covalent, explaining that ionic compounds result from the transfer of electrons between a metal and a nonmetal, whereas covalent compounds involve the sharing of electrons between nonmetals. The script also highlights exceptions to these classifications, such as ammonium chloride, which despite being composed of nonmetals, is considered an ionic compound due to the presence of ions. The explanation is enriched with examples like helium, hydrogen gas, water (H2O), oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2), neon, and fluorine, to illustrate the concepts discussed.
Takeaways
- 🌐 **Atoms vs. Molecules**: An atom is the smallest unit of an element, while a molecule is a group of two or more atoms bonded together.
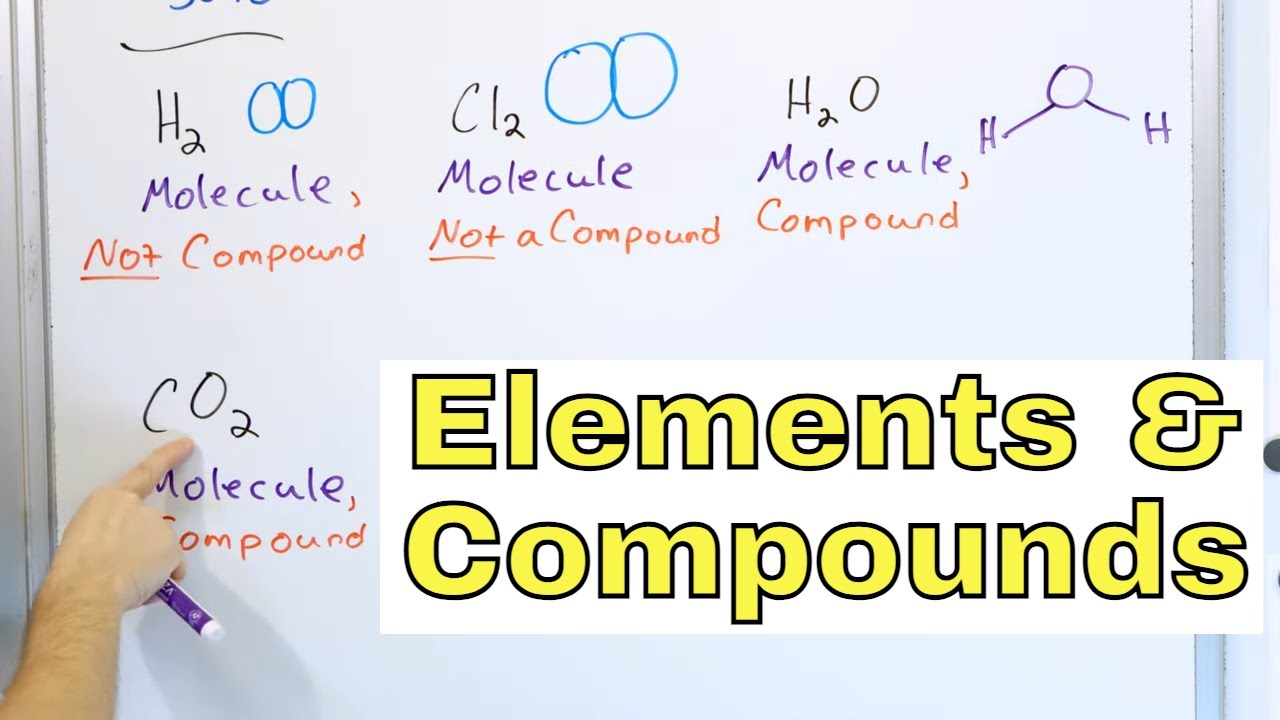
- 🌟 **Helium and Hydrogen**: Helium is composed of individual atoms, and hydrogen gas (H2) is composed of molecules, each containing two hydrogen atoms.
- 💧 **Water (H2O)**: Water is a molecule made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, and it is not a pure element but a compound.
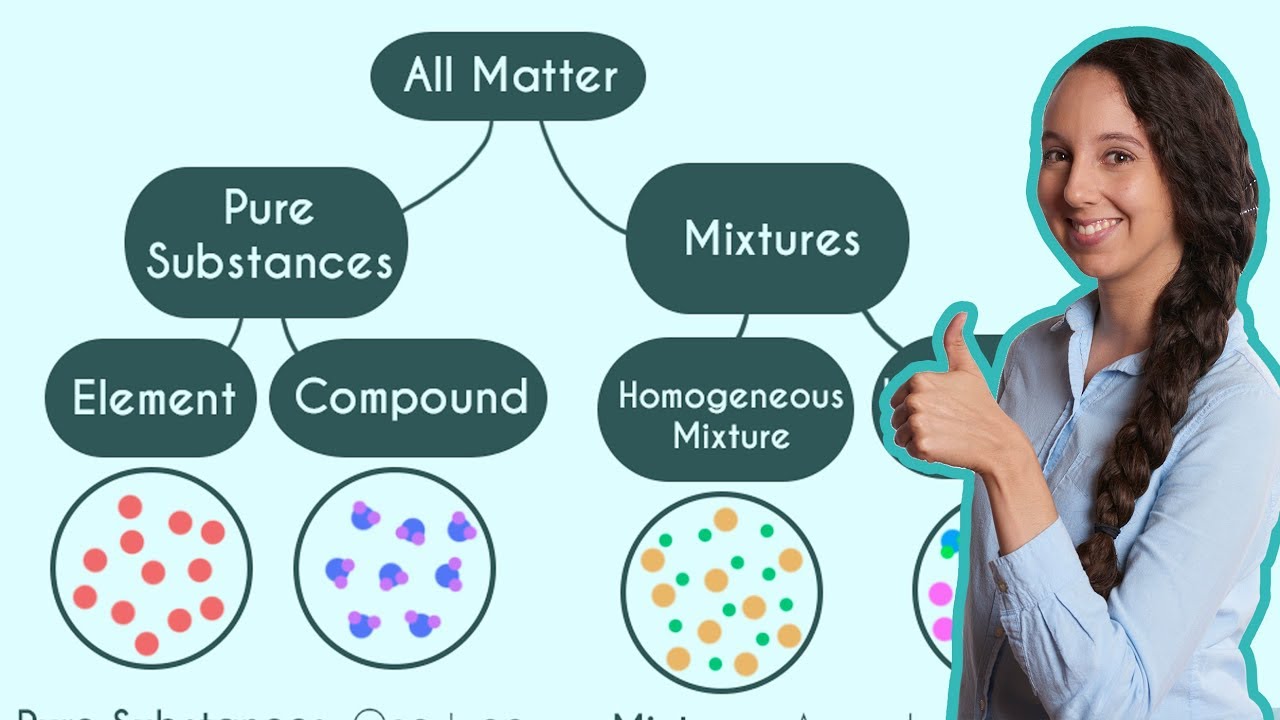
- 🔍 **Pure Elements and Compounds**: A pure element consists of only one type of atom, whereas a compound is made of two or more different types of atoms.
- ⚛️ **Ions**: Atoms become ions when they have unequal numbers of protons and electrons, resulting in a net charge.
- 🔋 **Aluminum Example**: Aluminum atoms and ions both have 13 protons, but the ion has a +3 charge due to having 10 electrons.
- 🔁 **Cations and Anions**: Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions.
- 🧲 **Ionic vs. Covalent Compounds**: Ionic compounds are typically formed between metals and nonmetals, while covalent compounds are formed between nonmetals.
- 🧬 **Electron Sharing**: In covalent compounds, electrons are shared between atoms, whereas in ionic compounds, electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
- ⚠️ **Exceptions to Rules**: Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is an ionic compound despite being composed of nonmetals because it contains ions.
- 📚 **General Rules**: As a general rule, compounds composed of a metal and a nonmetal are ionic, while those composed of two nonmetals are covalent, but exceptions exist.
Q & A
What is the fundamental difference between an atom and a molecule?
-An atom is the smallest unit of an element that retains the properties of that element, consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons. A molecule, on the other hand, is a group of two or more atoms bonded together, which can be of the same or different types of atoms.
How can you determine if a substance is a pure element or a compound?
-A substance is a pure element if it is composed of only one type of atom. If the substance consists of different types of atoms, it is a compound.
What are the characteristics of an ionic compound?
-Ionic compounds are typically formed between metals and nonmetals. They involve the transfer of electrons from the metal to the nonmetal, resulting in positively charged cations and negatively charged anions that are attracted to each other.
How do covalent or molecular compounds differ from ionic compounds in terms of bonding?
-Covalent or molecular compounds are formed when atoms share electrons, usually between nonmetals. Unlike ionic compounds, there is no transfer of electrons, and the compound is held together by shared electron pairs.
What is the difference between an atom and an ion?
-An atom is electrically neutral with an equal number of protons and electrons. An ion, however, has an unequal number of protons and electrons, resulting in a net charge. Cations are positively charged due to excess protons, while anions are negatively charged due to excess electrons.
Why is helium considered a pure element, and how is it different from hydrogen gas and water in terms of composition?
-Helium is considered a pure element because it consists of only helium atoms. It differs from hydrogen gas and water because hydrogen gas is a diatomic molecule (H2), and water (H2O) is a compound consisting of hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
How can you identify if a compound is ionic or covalent based on the elements involved?
-A compound is likely ionic if it involves a metal and a nonmetal. It is likely covalent if it involves only nonmetals. However, exceptions exist, such as ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), which is ionic despite involving nonmetals.
What is the role of neutrons in an atom, and how do they relate to the mass number of an element?
-Neutrons are subatomic particles in the nucleus of an atom that contribute to its mass but do not carry an electric charge. The mass number of an element is the sum of protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus.
null
-null
How does the charge of an ion affect the number of electrons it has compared to protons?
-In a positively charged ion (cation), there are more protons than electrons due to the loss of electrons. Conversely, in a negatively charged ion (anion), there are more electrons than protons because the atom has gained extra electrons.
What is the atomic number, and how is it used to calculate the number of electrons in a neutral atom or ion?
-The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and is equal to the number of electrons in a neutral atom. To calculate the number of electrons in an ion, subtract the charge of the ion from the atomic number.
Why is water (H2O) considered a compound and not a pure element?
-Water is considered a compound because it is composed of more than one type of atom, specifically hydrogen and oxygen atoms, which are chemically bonded together.
How can you distinguish between different types of compounds, such as ionic and covalent, without knowing the specific elements involved?
-Ionic compounds are typically composed of positive and negative ions due to the transfer of electrons. Covalent compounds, on the other hand, involve sharing of electrons between atoms. Ionic compounds often form crystalline structures and tend to be hard and brittle, while covalent compounds can be gases, liquids, or soft solids.
Outlines
🌟 Understanding Atoms and Molecules
This paragraph explains the fundamental differences between atoms and molecules. It uses helium, hydrogen gas, and water (H2O) as examples to illustrate the concepts. Helium is a pure element made up of individual helium atoms, while hydrogen gas and water are both composed of molecules. A molecule is a particle consisting of multiple atoms, which can be the same or different types. Water, for instance, is made up of one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms, making it a compound rather than a pure element. The paragraph also introduces the concept of pure elements and compounds, explaining that pure elements consist of only one type of atom, while compounds consist of different types of atoms.
🔬 Atoms, Ions, and Their Charges
The second paragraph delves into the distinction between atoms and ions, focusing on their electrical properties. Atoms are electrically neutral, having an equal number of protons and electrons. Ions, however, have an unequal number, resulting in a net charge. Using aluminum as an example, the paragraph explains how the atomic number corresponds to the number of protons, and the mass number includes both protons and neutrons. The difference between an atom and its ion lies in the number of electrons: atoms are neutral, while ions carry a charge due to the loss or gain of electrons. Cations are positively charged ions, and anions are negatively charged. The paragraph also touches on the classification of compounds into ionic and covalent, with sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O) serving as examples. Sodium chloride is an ionic compound because it's composed of a metal (sodium) and a nonmetal (chlorine), whereas water is a covalent compound as it's made up of nonmetals.
🔍 Covalent vs. Ionic Compounds
The third paragraph further explores the nature of covalent and ionic compounds. Covalent compounds, also known as molecular compounds, involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, as seen in water where hydrogen and oxygen share electrons. In contrast, ionic compounds involve a transfer of electrons, leading to the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, as in sodium chloride (NaCl). The paragraph provides a rule of thumb for identifying ionic compounds, which are typically formed between metals and nonmetals, and covalent compounds, which are usually composed of nonmetals. It also cautions about exceptions to this rule, such as ammonium chloride, which despite being composed of nonmetals, is considered an ionic compound due to the presence of ions. The paragraph concludes with additional examples of both types of compounds, reinforcing the concepts introduced.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Atom
💡Molecule
💡Pure Element
💡Compound
💡Ion
💡Cation
💡Anion
💡Ionic Compound
💡Covalent Compound
💡Neon
💡Ammonium Chloride
Highlights
An atom is the smallest unit of an element, consisting of a nucleus with protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons.
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms bonded together, which can be of the same or different elements.
Helium is a pure element made up of individual helium atoms, not molecules.
Hydrogen gas consists of molecules, each containing two hydrogen atoms (H2).
Water (H2O) is a molecule composed of one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms.
A pure element is made up of only one type of atom, while a compound contains different types of atoms.
Helium and hydrogen gas are pure elements, whereas water is a compound.
O2 (oxygen molecule) is a pure element consisting of two oxygen atoms bonded together.
CO2 (carbon dioxide) is a compound made of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms.
Neon is a pure element, with each particle being a single neon atom.
Atoms are electrically neutral with equal numbers of protons and electrons.
Ions have a different number of protons and electrons, leading to a net charge.
Aluminum atom and aluminum ion differ in their electron count due to charge.
Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged.
Ionic compounds are formed from the transfer of electrons between a metal and a nonmetal, resulting in charged ions.
Covalent or molecular compounds involve sharing of electrons between nonmetals.
Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound, while water (H2O) is a covalent compound.
Ammonium chloride is an exception to the rule, being composed of ions despite having no metal atoms.
General rule: compounds of a metal and a nonmetal are typically ionic, while two nonmetals usually form covalent compounds.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

What Distinguishes Compounds from Molecules?

BTEC Applied Science: Unit 1 Chemistry Elements

Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances

Element, Compound and Mixture | Chemsitry
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)
Intro to Elements, Compounds, & the Periodic Table - [1-1-3]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: