what is a pKa value
TLDRThe video script delves into the concept of pKa values in acid-base reactions, explaining their significance in determining the strength of an acid. It outlines the reversible process where an acid donates a proton to a base, forming a conjugate base and acid. The equilibrium constant, Ka, is introduced, which is refined to account for the constant concentration of water in dilute acid solutions. The pKa value, defined as the negative base-10 logarithm of Ka, offers a convenient measure to compare the strength of acids. Strong acids have a large Ka and thus a negative pKa, while weak acids have a small Ka, resulting in a positive pKa. This insight allows for the quick assessment of an acid's dissociation potential in water.
Takeaways
- 📚 Acid-base reactions are reversible processes where an acid donates a proton to a base, forming a conjugate acid and a conjugate base.
- 🔄 The equilibrium constant (K) describes the ratio of concentrations of products to reactants in an acid-base reaction.
- 💧 The concentration of water (H2O) is typically constant in dilute acid reactions, allowing for simplification of the equilibrium expression.
- 🎯 The Ka constant is derived by multiplying the equilibrium constant (K) by the constant concentration of water, providing a new way to express the reaction.
- 📉 pKa is the negative base-10 logarithm of the Ka value, which is a convenient measure for the strength of an acid.
- 🔢 Lower pKa values (< 0) indicate strong acids that dissociate significantly in water, yielding high concentrations of H3O+.
- 🔝 Higher pKa values (> 0) represent weak acids that have a lower tendency to dissociate, resulting in lower concentrations of H3O+.
- 📊 Comparing pKa values allows for quick determination of an acid's strength relative to others.
- 🌟 The pKa scale is a valuable tool in chemistry for understanding and predicting the behavior of acids in reactions with water.
- 🔍 By examining pKa values, one can assess how readily an acid will dissociate and the resulting concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+).
- 📚 Understanding the concept of pKa is fundamental for studying acid-base chemistry and predicting the outcomes of such reactions.
Q & A
What is the basic process of an acid-base reaction?
-In an acid-base reaction, an acid loses a proton (H+) to a base, resulting in the formation of a conjugate base and a conjugate acid. This is a reversible process, meaning the reaction can proceed in both the forward and reverse directions.
How is the equilibrium constant (K) expressed in the context of an acid-base reaction?
-The equilibrium constant (K) for an acid-base reaction is expressed as the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the starting materials. This gives us a value that describes the relative concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium.
Why is the concentration of water considered constant in acid-base reactions involving dilute acids?
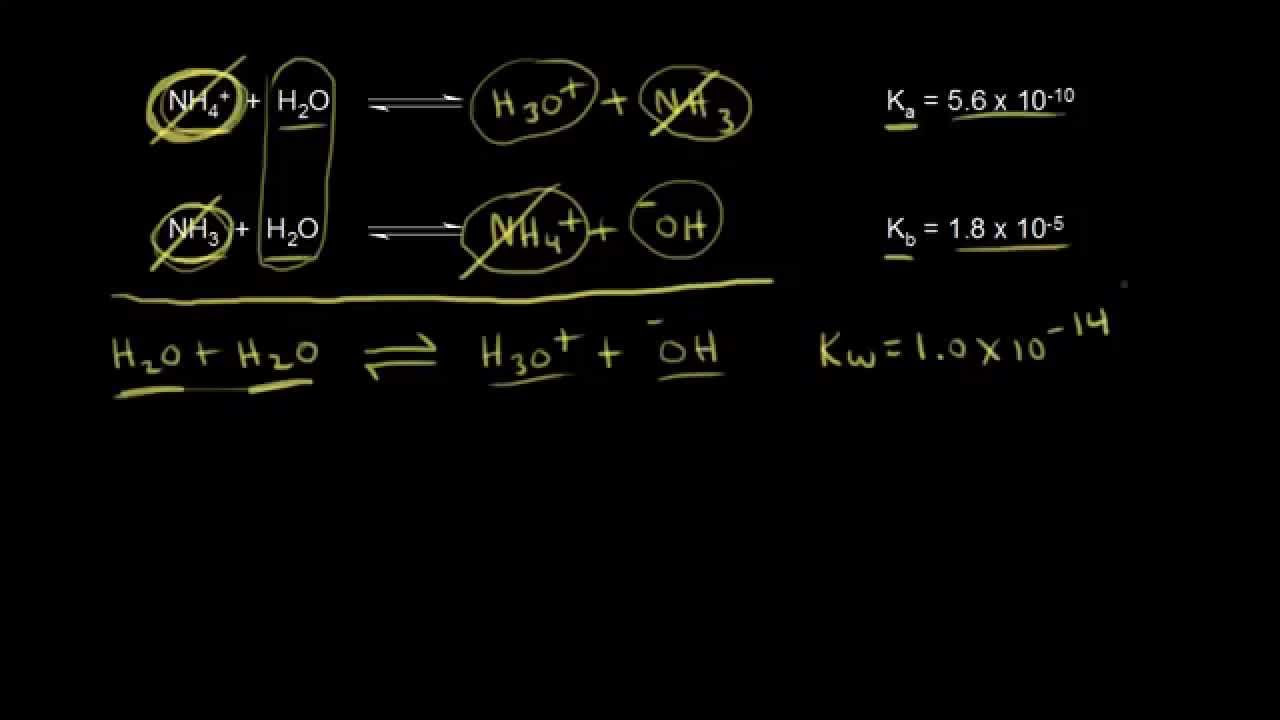
-The concentration of water is typically constant in such reactions because it is present in high amounts (approximately 55 moles per liter in pure water), and its concentration does not significantly change under the conditions of the reaction. This allows us to simplify the equilibrium expression by including water's concentration on the same side as the equilibrium constant.
What is the Ka expression derived from?
-The Ka expression is derived from the equilibrium constant (K) by multiplying both sides of the expression by the concentration of water, since water's concentration is roughly constant. This new expression, which includes the constant concentration of water, is the Ka expression for the acid-base reaction.
How is the pKa value defined?
-The pKa value is defined as the negative base-10 logarithm of the Ka value. This transformation allows for a more intuitive understanding of the strength of an acid, with lower pKa values indicating stronger acids and higher pKa values indicating weaker acids.
What does a low pKa value indicate about an acid?
-A low pKa value (less than 0) indicates that the acid is a strong acid, meaning it has a high tendency to donate protons and dissociate in water, resulting in high concentrations of the conjugate base (H3O+).
What does a high pKa value signify for an acid?
-A high pKa value (greater than 0) signifies that the acid is a weak acid. It means the equilibrium favors the reactants (the acid) rather than the products, indicating that the acid does not dissociate completely and only forms small concentrations of the conjugate base (H3O+) in solution.
How can we use pKa values to compare the strength of different acids?
-By comparing pKa values, we can quickly determine the relative strength of different acids. A lower pKa value corresponds to a stronger acid, which will dissociate more completely in solution, while a higher pKa value corresponds to a weaker acid with less dissociation.
What is the practical significance of pKa values in chemistry and everyday life?
-pKa values are significant in chemistry as they provide a measure of the strength of acids, which is crucial for understanding chemical reactions involving acids. In everyday life, the acidity or alkalinity of soil and water, which can be related to pKa values, is important for agriculture and the health of ecosystems. Additionally, the pH of various products, from food to cleaning agents, is related to acid-base chemistry and can affect their functionality and safety.
How do the concepts of reversible reactions and equilibrium relate to acid-base chemistry?
-In acid-base chemistry, the concept of reversible reactions is essential because it acknowledges that both the forward reaction (acid donating a proton) and the reverse reaction (conjugate base accepting a proton) can occur. The concept of equilibrium indicates that these reactions reach a balance where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, which is a fundamental principle in understanding the behavior of acids and bases in solution.
What is the relationship between the equilibrium constant (K) and the equilibrium constant for water (Kw) in acid-base reactions?
-In acid-base reactions, the equilibrium constant (K) is related to the equilibrium constant for water (Kw) through the autoionization of water. The autoionization constant for water (Kw) is a separate equilibrium expression that describes the self-ionization of water into H+ and OH− ions. While the Ka expression simplifies the equilibrium expression by considering the concentration of water as constant, it is still implicitly related to the overall acid-base equilibrium, which includes the autoionization of water.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Acid-Base Reactions and pKa
This paragraph introduces the concept of pKa values in the context of acid-base reactions. It explains that these reactions are reversible processes where an acid donates a proton to a base, forming a conjugate base and a conjugate acid. The equilibrium constant (K) is used to describe this reaction, with its value depending on the concentrations of the reactants and products. The paragraph further clarifies that the concentration of water (H2O) is constant in such reactions, allowing for a simplified expression of the equilibrium constant, which is then related to the Ka value. The pKa value, defined as the negative base-10 logarithm of Ka, is highlighted as a useful tool for comparing the strength of acids, with strong acids having a pKa less than 0 and weak acids having a pKa greater than 0. This information is crucial for understanding how acids behave in solution and their dissociation tendencies.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡acid-base reaction
💡reversible process
💡equilibrium constant (K)
💡conjugate acid
💡conjugate base
💡pKa value
💡H2O concentration
💡logarithm
💡strong acid
💡weak acid
💡dissociation
Highlights
The concept of pKa values is introduced as a measure of acid strength.
Acid-base reactions are described as reversible processes.
The equilibrium constant K is defined in terms of the concentrations of reactants and products.
The presence of water in acid-base reactions is accounted for by its constant concentration.
The Ka expression is derived from the equilibrium constant K by including water's concentration.
The pKa value is defined as the negative base-10 logarithm of Ka.
pKa values provide a quick method to compare the strength of different acids.
Strong acids have large Ka values and consequently have negative pKa values.
Weak acids have small Ka values leading to pKa values greater than 0.
The equilibrium for weak acids favors the reactants, resulting in small Ka values.
pKa values can be used to determine if an acid strongly or weakly dissociates in water.
The concentration of water is approximately 55 moles per liter under standard conditions.
Multiplying both sides of the equilibrium equation by the concentration of water yields the Ka expression.
The pKa scale allows for immediate comparison of acid strengths through their pKa values.
A strong acid will have a high concentration of H3O+ when mixed with water.
A weak acid will produce a low concentration of H3O+ upon dissociation.
The pKa value is a practical tool for assessing the strength of an acid in an acid-base reaction.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: