AP Physics Workbook 8.C Internal Force
TLDRThis tutorial from the AP Physics Workbook covers Unit 8 on electrical charges and forces. It explains the internal forces acting on spheres A, B, and C, using Coulomb's Law to determine the magnitude and direction of these forces. The video illustrates how opposite charges attract and like charges repel, creating a balanced scenario where no net external force affects the system, resulting in equilibrium and zero acceleration.
Takeaways
- 📚 The tutorial covers Unit 8 on electrical charges and forces, focusing on internal forces within a system of spheres.
- 🔋 Sphere A experiences two forces: an attractive force from Sphere B (due to opposite charges) and a weaker force from Sphere C (due to greater distance).
- 📈 The strength of the electrical force is determined by Coulomb's Law, which states that force is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- 🎯 The direction and magnitude of the forces are illustrated in a free-body diagram, showing the forces acting on each sphere from the perspective of each other sphere.
- 🔄 Newton's Third Law is highlighted, explaining that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, which applies to the forces between the spheres.
- 🌐 The net electrical force on the system of three spheres is considered to be zero due to internal forces canceling each other out, assuming no external forces are acting on the system.
- 🧲 Sphere B is attracted to Sphere A and repelled by Sphere C, resulting in a balance of forces that can be visualized and calculated using the free-body diagram.
- 🏆 The tutorial emphasizes the importance of correctly labeling and drawing the relative lengths of the force vectors to accurately represent the interactions between charged spheres.
- 📊 A free-body diagram for the entire system of spheres is drawn, showing that all internal forces cancel out, resulting in no acceleration or movement of the system if released from rest.
- 🤔 The scenario demonstrates the concept of equilibrium, where an object will remain at rest if there is no net force acting upon it, as is the case with the system of spheres.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the tutorial?
-The main topic of the tutorial is 'Electrical Charges and Electrical Forces', which is part of a physics workbook covering Unit 8.
What is the fundamental law discussed in the script that governs the electrical force between two charges?
-The fundamental law discussed is Coulomb's Law, which states that the electrical force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
How does the distance between two charges affect the strength of the electrical force according to the script?
-According to the script, the smaller the distance between two charges, the greater the electrical force between them. This is reflected in Coulomb's Law, where the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r^2).
What are the two forces acting on sphere A in the scenario described in the script?
-The two forces acting on sphere A are the attractive force from sphere B (due to opposite charges) and a weaker force from sphere C (because C is farther away).
What is the net electrical force on the system of all three spheres according to the script?
-The net electrical force on the system of all three spheres is considered to be zero. This is because the internal forces between the spheres cancel each other out due to Newton's Third Law of Motion.
What would be the behavior of the system if released from rest, according to the script?
-If the system is released from rest, it will remain at equilibrium and not accelerate, as there is no net force acting on it. This is due to the fact that the electrical field of the system is zero and all forces are balanced.
How does the tutorial script use Newton's Third Law of Motion to explain the interaction between spheres A, B, and C?
-The tutorial script uses Newton's Third Law of Motion to explain that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This is seen in the forces between the spheres, where each sphere exerts a force on the others that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, leading to a net force of zero on the system.
What is the significance of the free body diagram in understanding the forces acting on each sphere?
-The free body diagram is significant as it visually represents all the forces acting on a particular object or system. In this case, it helps to illustrate the individual and combined effects of the electrical forces on spheres A, B, and C, and how they result in the system's equilibrium.
How does the script differentiate between the forces acting on sphere B from A and C?
-The script differentiates the forces acting on sphere B by discussing their magnitudes and directions. It mentions that the force from A (attraction) is stronger than the force from C (repulsion) due to the distance between B and C being greater than the distance between B and A.
What is the role of vector representation in the tutorial script when explaining the forces?
-Vector representation plays a crucial role in the tutorial script as it helps to visually depict the direction and magnitude of the forces. The script uses the length of the vectors to indicate the relative strengths of the forces and their directions to show which way the forces are acting.
How does the tutorial script relate the concepts of electrical charges, forces, and fields?
-The tutorial script relates these concepts by explaining how electrical charges give rise to electrical fields, which in turn exert forces on other charges. It shows how the interactions between charged spheres can be analyzed in terms of the forces in an electric field, and how these forces are governed by Coulomb's Law and Newton's Laws of Motion.
Outlines
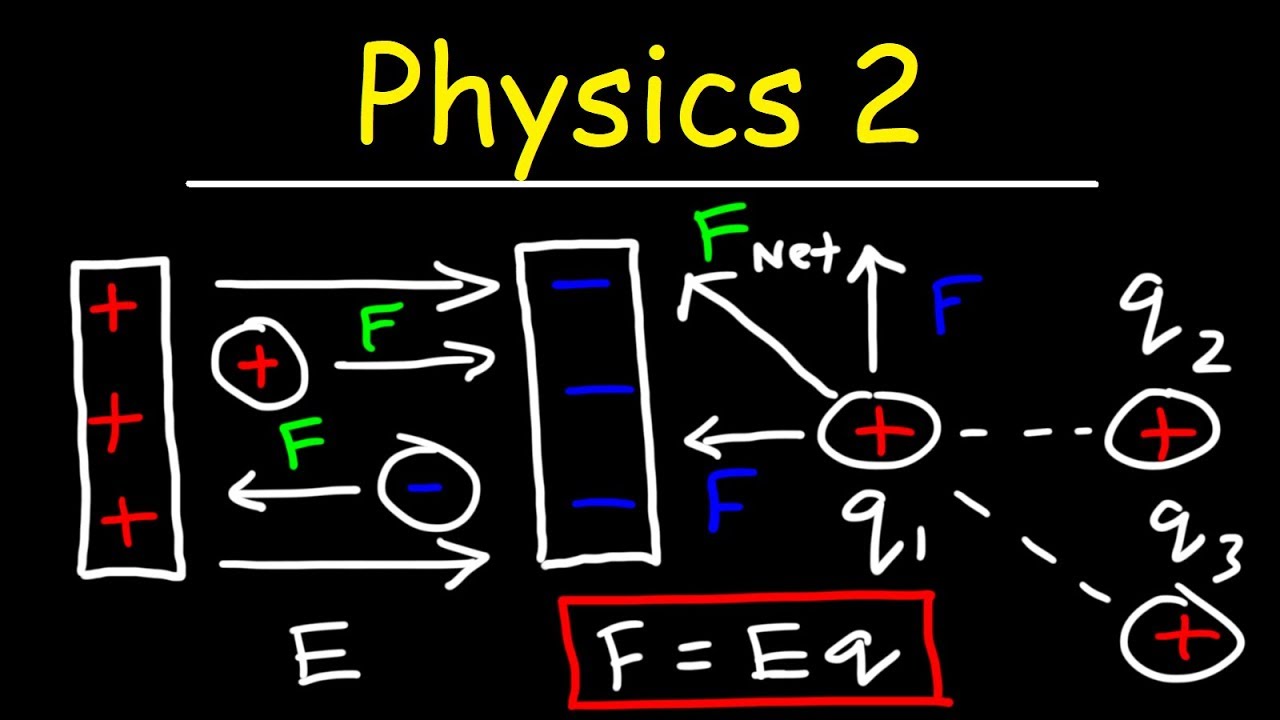
📘 Understanding Electric Charges and Forces
This paragraph introduces the topic of electrical charges and forces, focusing on the internal forces within a system of three spheres (a, b, and c). It explains the forces acting on sphere 'a' from 'b' and 'c', with 'b' exerting a stronger attractive force due to opposite charges and a closer distance, as described by Coulomb's law. The force from 'c' on 'a' is weaker due to a greater distance. The paragraph also discusses the forces acting on 'b', including the attraction from 'a' and the repulsion from 'c', and emphasizes the importance of considering the relative lengths of these forces in accordance with Coulomb's law. The summary highlights the concept of balance in forces and the role of distance in determining the magnitude of electrical forces.
📙 Analyzing the System's Free Body Diagram
This paragraph delves into the creation of a free body diagram for the system of three spheres, illustrating and labeling the electric field forces acting on each sphere. It explains how to represent the relative lengths of the force vectors, ensuring they match up in accordance with Newton's third law. The paragraph clarifies the forces acting on 'c', including the pull from 'a' and the repulsion from 'b', and uses color coding to distinguish between different forces. The main point is that the net electrical force on the system is considered zero due to the internal forces canceling each other out, leading to the conclusion that if the system is released from rest, it will remain at rest due to the absence of a net force and therefore no acceleration.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Electrical Charges
💡Electrical Forces
💡Coulomb's Law
💡Free Body Diagram
💡Newton's Third Law
💡Equilibrium
💡Vector
💡System
💡Acceleration
💡Electromagnetic Force
💡Inverse Square Law
Highlights
The tutorial is focused on Unit 8 of the AP Physics Workbook, which covers electrical charges and electrical forces.
The section specifically discusses the internal forces acting on a sphere (point A) from other charges (points B and C).
There are two forces acting on sphere A: an attractive force from B due to opposite charges, and a weaker force from C because of a greater distance.
Coulomb's Law is referenced to explain that the electrical force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between charges.
In part B, the analysis shifts to sphere B, which experiences an attractive force from A and a repulsive force from C.
The forces acting on B are of equal magnitude but opposite direction due to Newton's Third Law of Motion.
When considering the entire system of three spheres, the internal forces cancel each other out, resulting in a net electrical force of zero on the system.
The system of spheres is in equilibrium as there are no external electrical forces acting on it, leading to zero acceleration.
The tutorial provides a detailed explanation of how to draw a free-body diagram for the electric field forces acting on the spheres.
The concept of equilibrium is discussed in relation to the net force and acceleration of the system.
The tutorial emphasizes the importance of understanding the direction and magnitude of forces in analyzing physical systems.
The scenario presented in the tutorial is a practical application of fundamental physics principles related to electrostatics.
The tutorial methodically breaks down complex concepts, making it easier for learners to grasp the underlying physics.
The use of visual aids, such as free-body diagrams, is highlighted as an effective way to represent and analyze forces in physics problems.
The tutorial touches on the balance of attractive and repulsive forces and how they contribute to the overall behavior of a system.
The relationship between charge, distance, and force is explored through the example of the spheres, providing a clear understanding of electrostatic interactions.
The tutorial concludes with a comprehensive summary of the system's behavior under the influence of internal and external forces.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: