What is Energy, Force, Motion & Waves in Physics?
TLDRThis introductory physics lesson aims to excite learners about the subject by covering fundamental concepts at a high level. Starting from the basics of motion and the application of mathematics in physics, it progresses through topics like forces, energy, collisions, gravity, orbits, gases, fluids, and waves. The lesson emphasizes the importance of calculus in understanding change and predicts future states of objects. It highlights the profound nature of physical laws, such as the conservation of energy and momentum, and their impact on our understanding of the universe.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Physics is the application of mathematics to the real world, allowing us to predict and calculate future events based on current understanding.
- 📚 The study of physics begins with understanding motion, which can be predicted using equations that take into account initial velocity, acceleration, and time.
- 🔢 Calculus, specifically derivatives, plays a crucial role in physics as it helps describe how things change over time, such as the velocity and acceleration of an object.
- 📐 Vector quantities like velocity and acceleration have both magnitude and direction, and can be broken down into components along different axes for easier analysis.
- 🔄 The law of conservation of energy states that energy can change forms but the total amount remains constant, as seen in the transformation between potential and kinetic energy.
- 💥 Forces in physics, such as gravitational and electric forces, can be described and calculated using Newton's laws of motion, with F = ma being a fundamental equation.
- 🌐 Gravity is an attractive force between masses that decreases with the square of the distance between them, influencing orbits and the motion of celestial bodies.
- 🚀 Orbits are the result of a balance between an object's velocity and the gravitational pull of a larger body, like a planet, keeping the object in a continuous path around it.
- 🌬️ Waves, including sound and electromagnetic waves, can exhibit constructive and destructive interference, which is crucial for understanding various phenomena in modern physics.
- 🔄 The concept of momentum is introduced in collisions, where the total momentum of a system is conserved, allowing for predictions of collision outcomes.
- 🌡️ Heat is understood as the motion of atoms within an object, rather than a separate substance, and is central to the study of thermodynamics.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of the lesson on physics introduced in the script?
-The primary goal is to make the student excited about learning physics.
How does the lesson plan to cover the breadth of physics topics?
-The lesson plans to start from basic concepts and progress through most topics covered in a typical calculus-based physics course for engineering or science, culminating in advanced material like Maxwell's equations and electromagnetic waves.
What is physics described as in the script?
-Physics is described as applied mathematics applied to the real world.
Why is calculus important in the study of physics according to the script?
-Calculus allows for the solving of more complex problems in physics by dealing with how things change and how to sum up infinite numbers of forces or elements, which is indispensable for understanding change and accumulation in the physical world.
What are the two main topics within calculus that are emphasized as important for physics?
-The two main topics are the derivative, which calculates how things change, and the integral, which is a way to sum up a bunch of different things or forces.
How is the basic equation of motion introduced in the script?
-The basic equation of motion introduced is delta x = v0t + 1/2 at^2, which calculates the change in position based on initial velocity, acceleration, and time.
What is the significance of vectors and scalars in the physics lesson described?
-Vectors and scalars are fundamental for understanding physics because vectors have both magnitude and direction (e.g., velocity, acceleration) and are crucial for analyzing forces, while scalars have only magnitude (e.g., temperature, pressure).
What example is used to explain the concept of gravitational force and its equation?
-The gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon is used as an example, with the equation F = G(m1m2)/r^2, highlighting how the force of gravity depends on the masses involved and the distance between them.
How does the script illustrate the conversion between kinetic and potential energy?
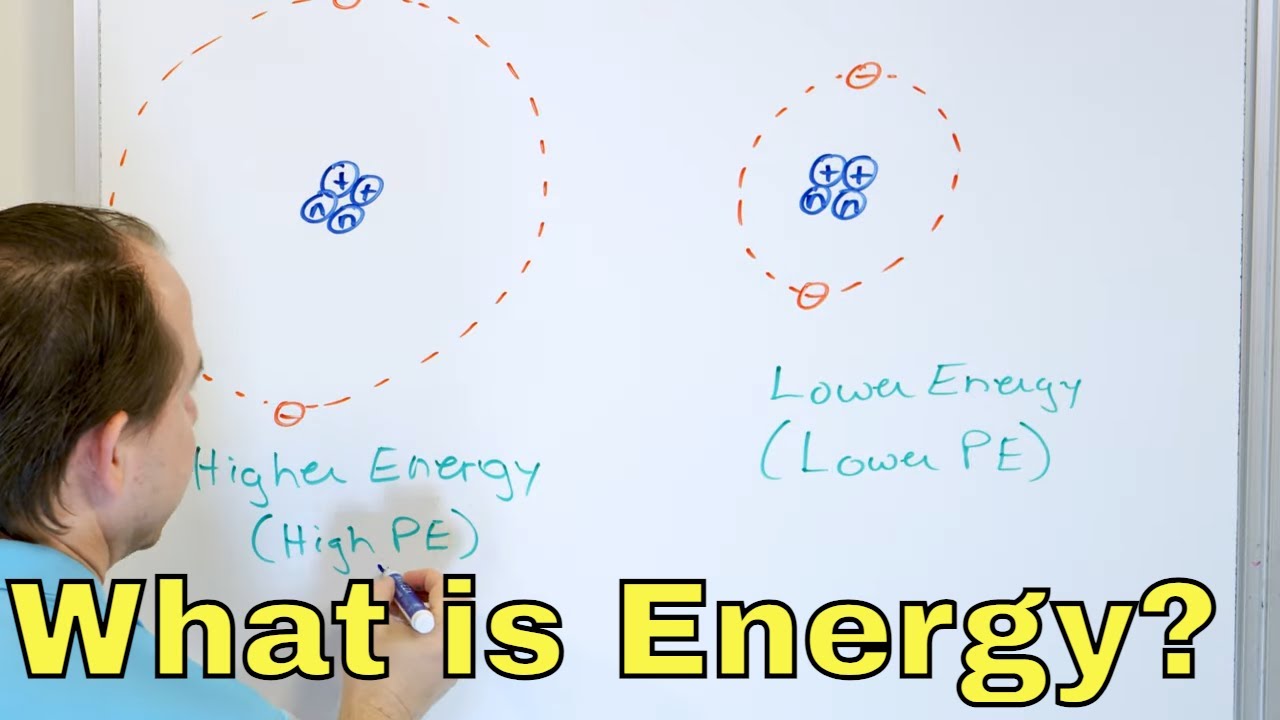
-The script uses a roller coaster example, illustrating how at the top of a ride there's maximum potential energy and minimal kinetic energy, and as the ride descends, potential energy converts into kinetic energy, highlighting the conservation of energy principle.
What is the importance of the law of conservation of energy as described?
-The law of conservation of energy, stating that the total energy in a system remains constant and only changes form (e.g., from potential to kinetic energy), is fundamental in physics for understanding how energy is conserved and transformed in various processes.
Outlines
🚀 Introduction to Physics and Learning Goals
The video begins with an introduction to physics, emphasizing the goal of exciting learners about the subject. Physics is described as the application of mathematics to the real world, with a focus on understanding and predicting phenomena through quantitative analysis. The lesson aims to provide an overview of topics covered in a typical physics course, from basic concepts to advanced material like Maxwell's equations and electromagnetic waves. The importance of calculus in solving complex physics problems is highlighted, and the video promises to guide learners through both the physics and calculus necessary to understand these concepts.
📚 The Role of Calculus in Physics
This paragraph delves into the necessity of calculus in the study of physics. It explains that calculus is essential for describing change over time or space, such as the motion of objects or the behavior of forces. The two main topics of calculus, derivatives and integrals, are introduced. Derivatives are used to calculate how things change over time, while integrals are used to sum up quantities, such as forces acting on an object. The video script emphasizes that while simplifications can be made without calculus, a deeper understanding of physics requires it, especially when dealing with complex problems.
🌌 Understanding Motion and Equations
The script discusses the fundamental concept of motion in physics, starting with the ancient Greeks' understanding and progressing to the development of equations that predict motion. It introduces a simple equation of motion, explaining the significance of each term and how they relate to changes in position, velocity, and acceleration. The importance of units in physics is highlighted, showing how they help in making sense of equations and calculations. The paragraph emphasizes the need to approach physics with an open mind and patience, as understanding complex concepts takes time and practice.
🔄 The Relationship Between Position, Velocity, and Acceleration
This section of the script explores the interrelationship between position, velocity, and acceleration. It explains how velocity is the rate of change of position with respect to time, and acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time. The script uses the concept of calculus, specifically derivatives, to describe these relationships mathematically. It also draws parallels between the equations of motion and those learned in algebra, emphasizing that understanding these connections is crucial for applying mathematical concepts to physical situations.
📈 Projectile Motion and Vector Quantities
The script moves on to discuss projectile motion, using the example of a ball being kicked at an angle. It explains how the motion can be broken down into horizontal and vertical components, each of which can be analyzed separately. The concept of vector quantities is introduced, emphasizing that vectors have both magnitude and direction. The script also touches on the idea of splitting vector quantities into their x and y components to simplify the analysis of complex motions, such as the curved path of a projectile.
🔧 Forces, Scalars, and the Electric Field
This paragraph introduces the concept of forces in physics, differentiating between vector quantities (like forces, velocities, and accelerations) and scalars (like temperature and pressure). It explains that forces can be represented by vectors, which include both magnitude and direction. The script also discusses the electric field as an example of a vector field, which, along with magnetic fields, plays a crucial role in understanding electromagnetic phenomena. The lesson highlights the incredible strength of electric and magnetic forces compared to gravity, using the example of a magnet lifting a pin against the force of Earth's gravity.
📐 Newton's Laws of Motion and Energy
The script introduces Newton's laws of motion, particularly the concept that forces cause acceleration and that an object at rest or in motion will remain so unless acted upon by an external force. It explains the equation F=ma (force equals mass times acceleration) and its implications, including the idea that forces are vectors with both magnitude and direction. The concept of energy is introduced, with a focus on kinetic energy (energy of motion) and potential energy (energy of position or condition). The script discusses the conservation of energy, using the example of a roller coaster to illustrate how potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and vice versa.
🌍 Gravity and Orbital Motion
The script discusses the force of gravity, describing it as an attractive force between objects with mass. It introduces the formula for gravitational force, which depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them. The concept of orbits is explained, using the example of a spacecraft moving around the Earth. The script clarifies that gravity is always present in orbit, causing a centripetal acceleration that changes the direction of the spacecraft's velocity. The importance of understanding gravity and motion for studying physics is emphasized.
🌬️ Waves, Interference, and Quantum Mechanics
The final paragraph of the script introduces the topic of waves, focusing on wave properties such as speed, frequency, and wavelength. It explains how waves can interfere with each other, either constructively (adding together) or destructively (subtracting from each other). The script suggests that the principles of wave interference are crucial for understanding many aspects of modern physics, including quantum mechanics, which is described as a wave theory of matter. The lesson sets the stage for further exploration of waves and their applications in physics.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Physics
💡Calculus
💡Equation of Motion
💡Force
💡Energy
💡Gravity
💡Waves
💡Electromagnetic Waves
💡Momentum
💡Thermodynamics
Highlights
The goal of the lesson is to make students excited about learning physics.
Physics is applied mathematics to the real world, showing why math is important.
The course covers a range of topics from basic motion to advanced material like Maxwell's equations and electromagnetic waves.
The importance of calculus in physics is emphasized, especially in understanding change and solving complex problems.
The basic equation of motion is introduced, showing how to predict the future position of an object based on its initial conditions.
The concept of vectors is explained, highlighting their significance in physics, especially in the context of motion and forces.
The difference between scalars and vectors is discussed, with examples like temperature and velocity.
The strength of electric and magnetic forces is compared to gravity, showing that they are much stronger.
Newton's second law of motion is introduced, explaining the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration.
The concept of action and reaction forces is discussed, using the example of pushing on a wall.
Energy is defined and its importance in physics is highlighted, with a focus on kinetic and potential energy.
The law of conservation of energy is explained, showing how energy changes forms but the total amount remains constant.
Gravity is introduced as a fundamental force, with its equation and how it affects planetary motion.
Orbits are explained as a result of the balance between an object's velocity and the gravitational pull of a planet.
The concept of waves, including wave speed, frequency, and wavelength, is introduced.
Constructive and destructive interference of waves is explained, with implications for modern physics theories.
Thermodynamics is briefly introduced as the study of heat and motion of atoms within objects.
The importance of understanding waves for future studies in quantum mechanics is hinted at.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Introduction to Motion in Physics

Elastic and Inelastic Collisions - Physics 101 / AP Physics 1 Review with Dianna Cowern

Symmetries & Conservation Laws: A (Physics) Love Story
What is Energy & Work in Chemistry & Physics? - [1-1-6]

Discovering the Laws of Physics | Wondrium Perspectives

Intro to Chemistry & What is Chemistry? - [1-1-1]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: