Globalization I - The Upside: Crash Course World History #41
TLDRThis Crash Course World History video examines globalization and international trade. It traces the journey of a t-shirt, analyzing how technological innovations, government policies, and multinational corporations have enabled faster, cheaper worldwide shipping. This has connected humanity while also dislocating domestic industries. Cultural blending coexists with Westernization of global culture. The unprecedented scale of recent population growth and lifespan increases signify humanity's ambition and invincibility, but also great danger. As living standards rise unevenly, we must remember what's gained and lost in modernization.
Takeaways
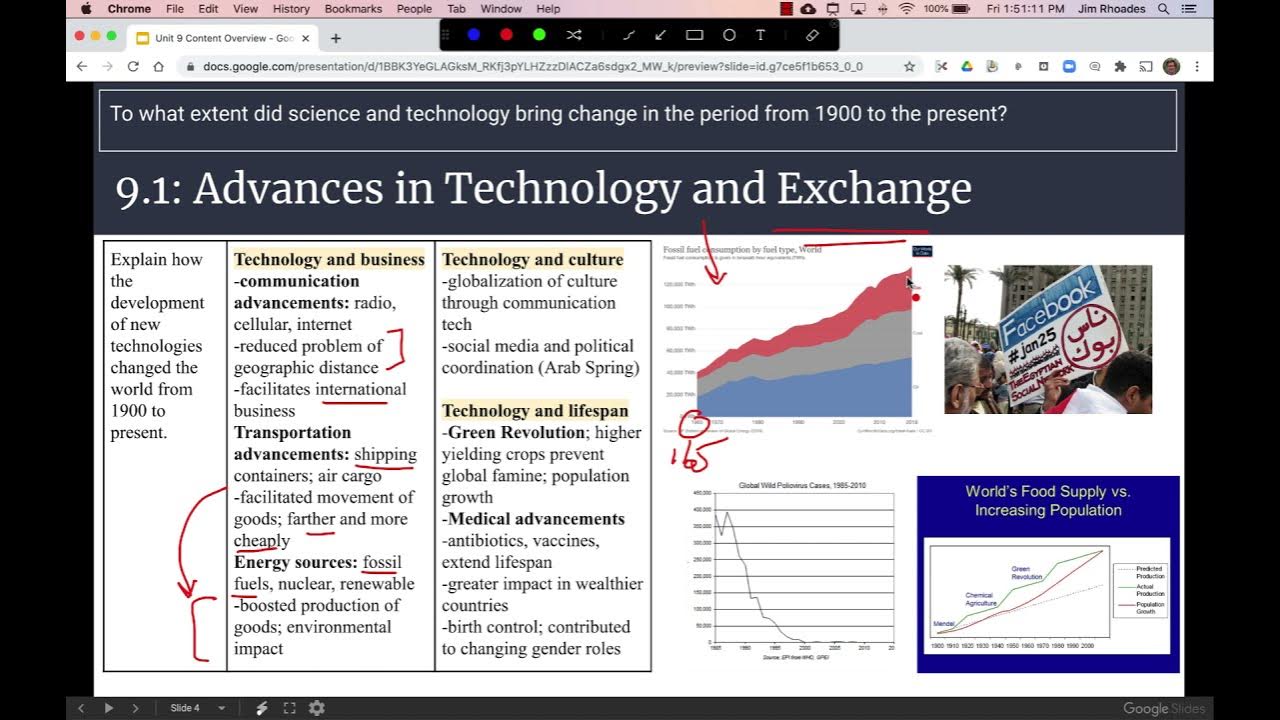
- 😊 Globalization has dramatically increased the scale and interconnectedness of international trade
- 📈 Governments have reduced regulations and tariffs, leading to more 'free trade'
- 🚢 Cheap, fast transportation and communication enables global supply chains
- 👕 The life story of a simple t-shirt shows how globalized trade works
- 💰 Subsidies and wage differences drive where cotton is grown and shirts sewn
- ✈️ More migration than ever before with complex cultural blending
- 🍽 Access to diverse cultural experiences has increased greatly
- 🌎 The world population and lifespan have increased dramatically
- 🤔 These gains also come with challenges we must thoughtfully address
- 📚 Understanding history helps us contextualize the scale of change
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic is globalization - its history, economic and cultural impacts, pros and cons, and how it has transformed the modern world.
How has air travel contributed to globalization?
-Cheap and accessible air travel has made it easier for people to migrate and move between countries, promoting the blending of cultures.
What are some positive impacts of globalization?
-Positive impacts include: increased worldwide economic output, improved standards of living and poverty reduction for many people, greater access to information and culture from around the world.
What are some negative impacts or concerns about globalization?
-Concerns include: harm to families and the environment, loss of languages and cultural diversity, and increased economic inequality between countries.
How have governments influenced global trade?
-Governments have reduced tariffs and regulations, under pressure from international institutions and economists, which has opened up markets but reduced protections.
Why does the video trace the life story of a t-shirt?
-The t-shirt illustrates how globalized and complex even simple modern production chains are today, with ingredients and production spanning multiple countries.
How has life expectancy changed over time?
-Average global life expectancy has more than doubled in the past two centuries, largely due to improved maternal and infant healthcare.
What is the purpose of studying history?
-To understand massive changes like globalization, to appreciate what humanity has gained and lost in the process, and avoid dangers of feeling overly powerful.
What is remittance and how does it relate to globalization?
-Remittances are money sent home by migrant workers abroad, now a huge source of income for developing countries, facilitated by global money transfer services.
What does the spread of football indicate about cultural globalization?
-The growth of football (soccer) fandom and leagues around the world shows cultural blending and the emergence of new global passions alongside Western media exports.
Outlines
📽️ Introducing the Global Economy and Trade
John Green introduces himself and Crash Course World History. He states that this episode will focus on globalization and international trade. He gives an overview of reasons why scale of trade has increased dramatically, including rise of multinational corporations, cheaper transportation, and reduced trade barriers. He traces the journey of a t-shirt to illustrate the global economy and explain the role of government subsidies and regulations.
📝 An Open Letter about Consumption
John Green reads an open letter directed at Cookie Monster about consumption and not having a stomach. He draws an analogy between Cookie Monster's relentless cookie eating despite having no stomach and contemporary consumer patterns of endless consumption.
🌐 Evaluating the Effects of Contemporary Global Capitalism
John Green evaluates effects of contemporary global capitalism. He acknowledges it has increased economic output and allowed more people to live better globally by moving manufacturing jobs to lower wage countries. However, he notes there are concerning side effects like environmental damage and species endangerment that will be explored further.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡globalization
💡trade
💡subsidize
💡tariff
💡migration
💡culture
💡developing countries
💡technology
💡environment
💡inequality
Highlights
Globalization is a cultural phenomenon reflected in contemporary art, population migration, and linguistic changes.
Economic interdependence and cultural borrowing are not new, but the scale has dramatically increased due to multinational corporations, cheaper travel, and reduced trade barriers.
Most t-shirts contain cotton from the U.S. because it's subsidized, making it cheaper than similar cotton from other countries.
T-shirt production spans the globe, with cotton from various countries, spinning and weaving in lower wage countries, and screen printing in the U.S. or Europe.
Wholesale t-shirt blanks cost as little as $3; most expense is in printing, retail, and design.
Trade today is unregulated by institutions or governments due to economists arguing successfully that regulations limit prosperity.
Emerging markets lower tariffs and regulations often to appease the IMF in order to get low interest loans.
While most early manufactured goods were produced and consumed domestically, since the 1960s consumer goods are often manufactured in developing countries for foreign markets.
While globalization may have negatively impacted families and the environment, economic output has increased and 600 million people have risen from extreme poverty.
Migration has increased due to cheaper travel and communication tools to stay in touch with distant families.
Globalization brings blended culture - some see increasing Americanization, while individual access to diverse cultural experiences has never been greater.
A comfortable shirt hundreds of years ago would have cost 10 times as much work as a t-shirt purchased online today that has traveled further than Magellan.
The world's population and life expectancy have more than doubled in the past two centuries.
These changes are so radical we struggle to contextualize them - all knowledge in Alexandria library could fit on one phone today.
It's easy to feel big, powerful and even invincible in today's world - and dangerous to feel that way.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
APWH Modern Unit 9 Overview

AP World History (WHAP) Unit 9 Part 3: International Cooperation

World War II Part 2 - The Homefront: Crash Course US History #36

Free Trade vs. Protectionism

AP World History (WHAP) Unit 9 Part 2: Economic Transformation (20th c.)

Drought and Famine: Crash Course World History #208
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: