This Element Doesn't Fit the Periodic Table
TLDRThis video explores the unique position of hydrogen in the periodic table, highlighting the debate among chemists about where it truly belongs. Hydrogen's properties resemble those of alkali metals, group 14 elements, and halogens, making it difficult to categorize. The video explains the significance of the periodic table as a predictive tool and how hydrogen's placement impacts our understanding of elemental behavior. It concludes by emphasizing hydrogen's uniqueness and the importance of recognizing its special properties in the study of chemistry.
Takeaways
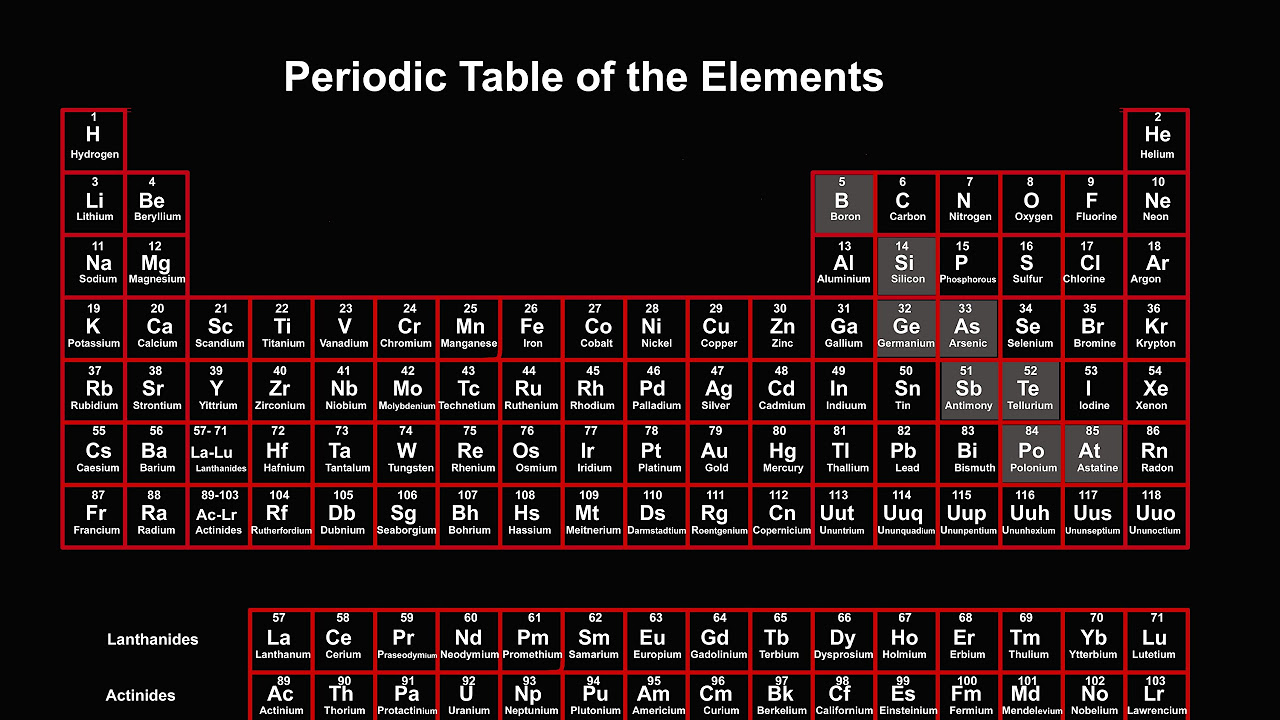
- 🧩 Hydrogen's Placement: Hydrogen is a unique element with no clear place in the periodic table, causing disagreement among chemists.
- 🔍 Periodic Table Evolution: The periodic table is a work in progress and not as fixed as it may seem in a classroom setting.
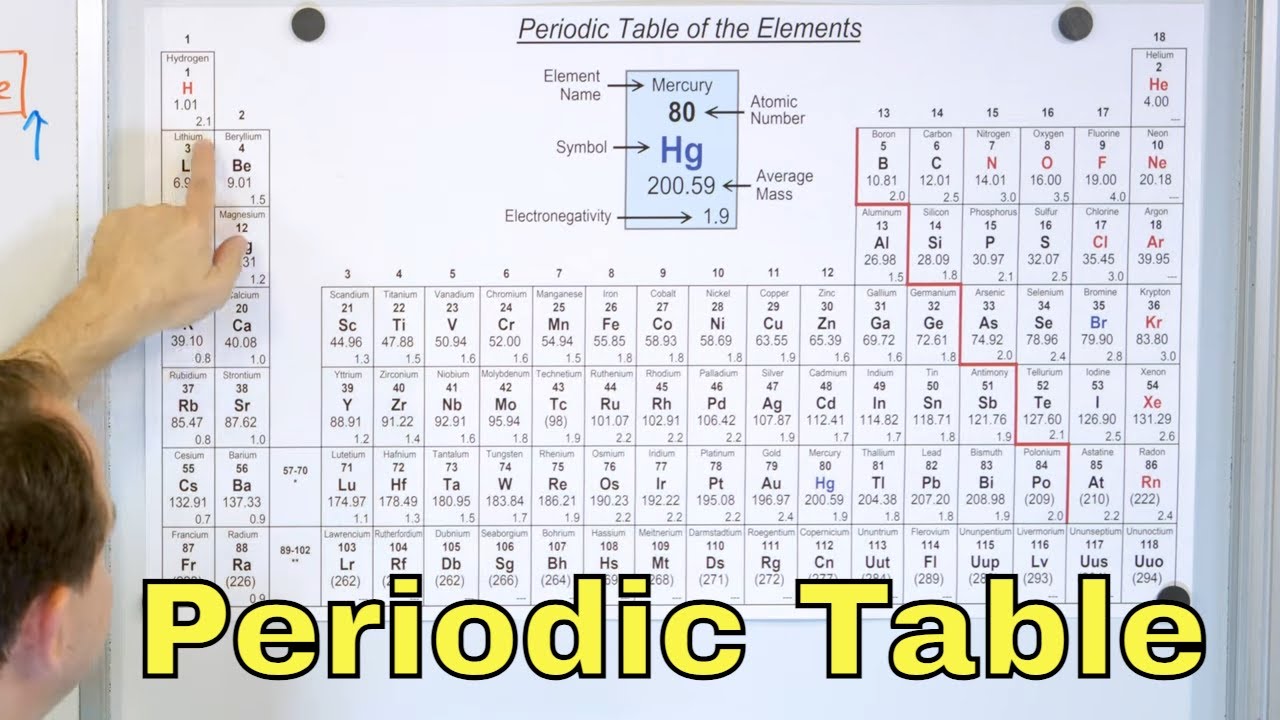
- 🔬 Atomic Structure: Elements are listed by atomic number, which correlates with their chemical properties due to electron configurations.
- 🔁 Quantum Mechanics: The specific patterns of electron filling are explained by quantum mechanics and the distribution of energy in subshells.
- 🔄 Periodic Properties: The repetition of electron configurations leads to the periodic properties that categorize elements into groups.
- 🌐 Group 1 Similarities: Hydrogen resembles alkali metals like lithium and sodium due to having a single outer electron that it tends to lose.
- 💨 Halogens Comparison: Hydrogen can also form ions similar to halogens by gaining an electron to become H-, similar to F- or Cl-.
- 🔗 Carbon Group Parallels: Hydrogen shares similarities with group 14 elements like carbon in electronegativity and types of bonds formed.
- 🚫 Unique Challenges: Hydrogen's unique properties make it difficult to categorize, challenging traditional groupings and predictions.
- 🔮 Predictive Tool: The periodic table serves as a predictive tool for understanding and forecasting chemical behaviors of elements.
- 🎓 Learning Curve: Studying chemistry involves recognizing hydrogen's uniqueness and the unpredictability of some of its properties.
Q & A
Why is there confusion about where to place hydrogen on the periodic table?
-Hydrogen's placement on the periodic table is confusing because it behaves similarly to elements in at least three different groups, and thus doesn't fit neatly into any single category.
What is the significance of the periodic table's arrangement in terms of chemical properties?
-The periodic table's arrangement is significant because elements are listed in order of ascending atomic number, which correlates with their chemical properties. This is due to the specific patterns in which electrons fill subshells around the atom.
What is the primary reason for the repeating properties among elements in the periodic table?
-The repeating properties among elements are due to the electron configurations around their atoms. When subshells fill up, the pattern repeats in new subshells, leading to similar chemical behaviors in elements with similar electron configurations.
Why does hydrogen's behavior resemble that of alkali metals like lithium and sodium?
-Hydrogen resembles alkali metals because it has one lone electron in a shell that can accommodate two electrons, similar to alkali metals which also have a single outer electron that they tend to lose to form a positively charged ion.
What are some differences between hydrogen and alkali metals like lithium and sodium?
-While hydrogen behaves similarly to alkali metals in some ways, it is not a metal and forms different compounds even when bonding with the same elements. For example, hydrogen chloride is a corrosive gas, whereas sodium chloride is a common salt used in food.
How does hydrogen's behavior compare to that of halogens like fluorine and chlorine?
-Hydrogen can form ions similar to halogens by gaining an electron to become a hydride ion (H-), similar to how halogens form negatively charged ions (e.g., F- and Cl-). They also share the property of existing as diatomic gases at room temperature.
Why might placing hydrogen above fluorine on the periodic table be problematic?
-Placing hydrogen above fluorine would be problematic because fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it is most likely to attract electrons from bonding partners. If hydrogen were placed above it, one might expect hydrogen to be even more electronegative, but in reality, hydrogen is more willing to share electrons.
What similarities exist between hydrogen and elements in group 14, such as carbon?
-Hydrogen and elements in group 14, like carbon, have similar electronegativities and tend to form similar types of bonds, including with each other. They can also participate in similar chemical reactions.
What are some alternative proposals for placing hydrogen on the periodic table?
-Some alternative proposals for placing hydrogen include positioning it with both the halogens and the alkali metals, linking it to them with a dotted line, or placing it somewhere in the middle of the table.
Why is it important for hydrogen to be placed correctly on the periodic table?
-Correct placement of hydrogen is important because the periodic table is a predictive tool. If an element is misplaced, it can lead to incorrect predictions about its behavior, affecting both educational understanding and scientific research.
Outlines
😅 The Dilemma of Hydrogen's Placement in the Periodic Table
This paragraph discusses the ongoing debate among chemists about where to place hydrogen in the periodic table. Despite being the simplest element, hydrogen doesn't neatly fit into any of the established groups due to its unique properties. It resembles alkali metals like lithium and sodium because it has one electron in its outer shell, similar to group 14 elements which have half-filled outer shells, and also the halogens because it can accept an electron to form a hydride ion. The paragraph explains that hydrogen's behavior is somewhat similar to alkali metals in that it tends to lose its outer electron, but it differs in that it is not a metal and forms different compounds. The periodic table's arrangement is crucial for predicting chemical behavior, and hydrogen's ambiguous placement complicates this predictive power.
🤔 The Unique Nature of Hydrogen and Its Implications for Chemistry
The second paragraph delves into the similarities and differences between hydrogen and other elements, particularly group 14 elements like carbon. It points out that while hydrogen and carbon share some chemical behaviors, such as forming similar bonds and participating in comparable reactions, there are significant differences. Carbon is known for forming four bonds at once, a characteristic not seen with hydrogen. The paragraph also touches on alternative proposals for hydrogen's placement in the periodic table, such as linking it to both halogens and alkali metals or placing it in the middle of the table. The importance of the periodic table as a predictive tool is emphasized, and the paragraph concludes by acknowledging hydrogen's unique properties and suggesting that it should embrace its special status rather than being embarrassed by it.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Hydrogen
💡Periodic Table
💡Alkali Metals
💡Electron Configuration
💡Quantum Mechanics
💡Subshells
💡Halogens
💡Electronegativity
💡Group 14 Elements
💡Chemical Reactions
💡Brilliant.org
Highlights
Hydrogen's placement in the periodic table is a subject of debate among chemists.
There are at least three credible positions for hydrogen in the periodic table.
The periodic table is a work in progress and not fixed or immutable.
Elements are listed by atomic number, which correlates with their chemical properties.
Electron configurations and subshells are key to understanding the periodic table's organization.
Hydrogen resembles alkali metals due to having a lone outer electron.
Hydrogen also shares similarities with group 14 elements and halogens.
Hydrogen's behavior is unique and doesn't strictly adhere to periodic rules.
Hydrogen can form ions similar to alkali metals, but it is not a metal itself.
Hydrogen forms different compounds compared to alkali metals, even when bonding with the same element.
Hydrogen can gain an electron to form a hydride ion, similar to halogens.
Hydrogen differs significantly from fluorine in electronegativity and bonding behavior.
Comparisons between hydrogen and carbon highlight similarities in electronegativity and bonding types.
The debate over hydrogen's placement affects the predictive power of the periodic table.
Hydrogen's unique properties make it difficult to categorize within traditional periodic table groups.
Brilliant.org offers a course on molecules in collaboration with MinuteEarth.
The Brilliant course aims to enhance understanding of molecular structures.
The partnership with MinuteEarth brings a unique interactive learning experience.
SciShow viewers are offered a 30-day free trial and discount on Brilliant's annual premium subscription.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: