Periodic Table of Elements Song
TLDRThis script is an educational journey through the periodic table, highlighting the properties and uses of various elements. It introduces viewers to the atomic structure, including the nucleus with protons and neutrons, and the significance of atomic number. The script explores different groups of elements, such as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, and metalloids, along with their applications. It also covers non-metals, halogens, and noble gases, providing a comprehensive overview of the periodic table's layout and the unique characteristics of each element family.
Takeaways
- 🌌 The script is a musical journey through the periodic table, highlighting the fascination with chemistry and the building blocks of the universe - atoms.
- 🔬 Atoms are composed of a nucleus containing neutrons and protons, with electrons orbiting the nucleus, and the number of protons determines an element's identity.
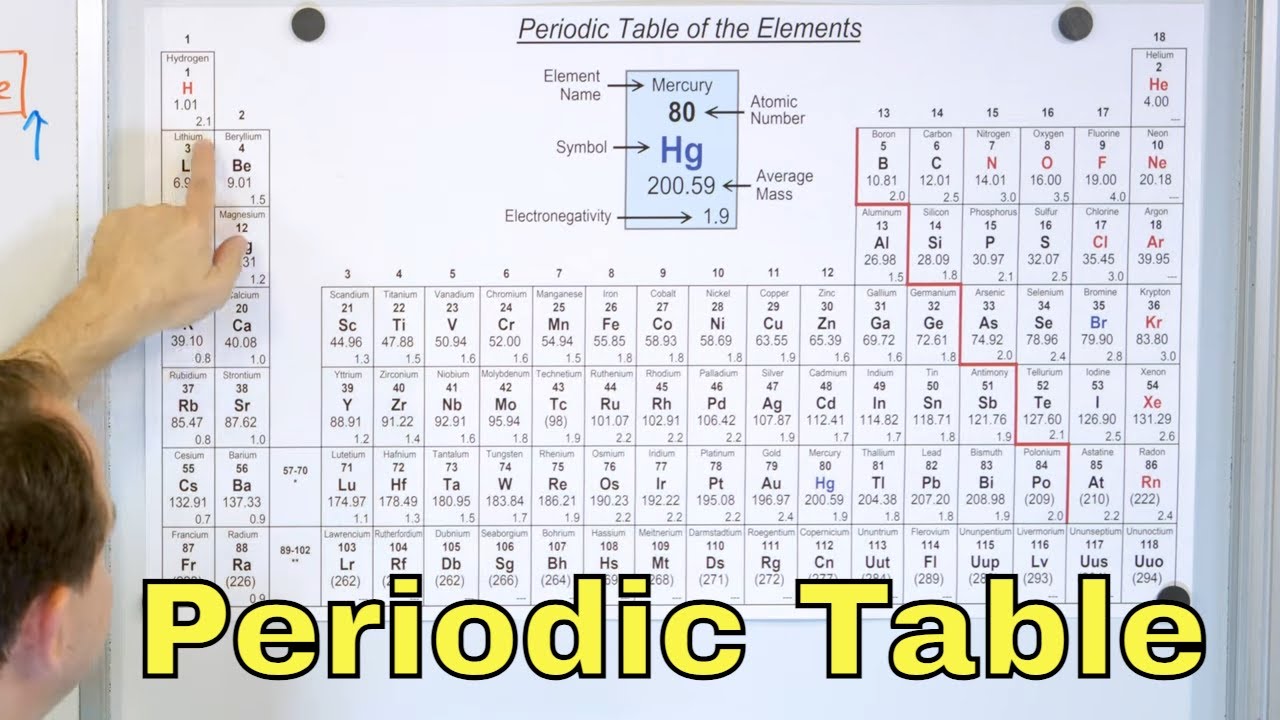
- 📊 The periodic table is organized into periods (horizontal rows) and groups (vertical columns), with elements in the same group sharing similar properties.
- 🏷️ Each element on the periodic table has a unique symbol, atomic number (number of protons), and atomic mass (protons plus neutrons).
- 📚 The script introduces different groups of elements, such as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, metalloids, and non-metals, each with distinct characteristics.
- 🛠️ Specific elements and their uses are mentioned, such as lithium in batteries, sodium in table salt, and helium for balloons and scientific equipment.
- ⚠️ Some elements are highlighted for their reactivity or radioactivity, emphasizing safety and practical applications.
- 🌐 The script touches on the importance of elements in various technologies, including electronics, energy production, and lighting.
- 🔬 The periodic table is presented as a tool for learning about the properties, uses, and history of elements, with a promise to explore each element in more detail in future content.
- 🎶 The educational content is delivered through a catchy musical format, making the information memorable and engaging for the audience.
- 🔍 The script provides a comprehensive overview of the periodic table, encouraging curiosity and further exploration of chemistry and the elements.
Q & A
What is the smallest particle of an element that retains all of its properties?
-The smallest particle of an element that retains all of its properties is an atom.
What are the two main components of an atom's nucleus?
-The two main components of an atom's nucleus are neutrons and protons.
What determines an element's physical properties?
-An element's physical properties are determined by the number of protons in its nucleus.
What is the term for the negatively charged particles that revolve around the nucleus of an atom?
-The negatively charged particles that revolve around the nucleus of an atom are called electrons.
How many horizontal rows are there in the periodic table, and what are they called?
-There are seven horizontal rows in the periodic table, and they are called periods.
What are the vertical columns on the periodic table called, and how many are there?
-The vertical columns on the periodic table are called groups, and there are 18 of them.
What does the atomic number represent on the periodic table?
-The atomic number represents the amount of protons in an atom's nucleus.
What is the significance of an element's atomic mass?
-The atomic mass of an element is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons within its nucleus.
What are the alkali metals, and how are they represented on the periodic table?
-Alkali metals are a group of elements in the first column of the periodic table, known for their reactivity and tendency to form +1 ions. They include lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium.
What are the alkaline earth metals, and where can they be found on the periodic table?
-Alkaline earth metals are a group of elements in the second column of the periodic table, known for their relatively low density and reactivity. They include beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, and radium.
What is the significance of the transition metals on the periodic table?
-Transition metals are found in groups 3 through 12 of the periodic table. They are known for their ability to form various oxidation states and are often used in alloys, catalysts, and for their magnetic properties.
What are the lanthanoids or rare earth metals, and where can they be found on the periodic table?
-The lanthanoids or rare earth metals are a group of elements with atomic numbers 57 to 71. They are located at the bottom of the periodic table and are characterized by their similar chemical properties and uses in various technologies.
What are the actinide metals, and how are they different from other metals on the periodic table?
-Actinide metals are a series of 15 radioactive elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103. They are found in group 3 and period 7 of the periodic table and are known for their use in nuclear reactors and as sources of nuclear energy.
What is the role of metalloids in the periodic table, and where can they be located?
-Metalloids are elements that have properties intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals. They can be found in groups 13 through 16 and periods 2 through 6 of the periodic table and include elements like boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, antimony, tellurium, and polonium.
What are the non-metals, and how do they differ from metals on the periodic table?
-Non-metals are elements that mostly lack metallic attributes and are found on the right side of the periodic table. They include hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, and others, known for their diverse chemical properties and applications.
What are the halogens, and what is the significance of their name?
-The halogens are a group 17 elements in the periodic table, including fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, tennessine, and others. The name 'halogen' means 'salt former' and refers to their tendency to readily form salts.
What are the noble gases, and what makes them unique among the elements?
-The noble gases are a group of chemically inert elements in group 18 of the periodic table, including helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, and oganesson. They are unique for their lack of reactivity and are used in various applications such as lighting and medical treatments.
Outlines
🌌 Journey Through the Periodic Table
This paragraph introduces a musical exploration of the periodic table, emphasizing the fascination with chemistry. It explains the fundamental concept of atoms as the smallest particles of elements with distinct properties. The nucleus, composed of neutrons and protons, is highlighted as the dense center of an atom, with protons determining an element's identity. The periodic table is described as a chart organizing elements into periods and groups, each with unique characteristics. The video promises to delve into each element's specifics in future episodes, aiming to educate viewers on the composition of all things in the universe, including themselves.
🔍 Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals
This section focuses on two groups of metals found in the periodic table: the alkali metals and the alkaline earth metals. Alkali metals, including lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium, are characterized by their atomic structure, with an emphasis on their atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons, and their atomic mass, the sum of protons and neutrons. Their electron configuration is also mentioned, illustrating how electrons orbit the nucleus. Alkaline earth metals, found in column two, are introduced with berylliuim, magnesium, calcium, and others, each with its atomic number and mass provided. The paragraph highlights the uses of these metals, such as sodium in table salt and magnesium in chlorophyll, emphasizing their importance in everyday life and nature.
🛠 Transition Metals and Their Applications
The paragraph delves into the properties and uses of transition metals, which are located in groups 3 through 12 of the periodic table. It describes metals such as scandium, titanium, vanadium, and others, detailing their atomic numbers, atomic masses, and symbols. Each metal's unique characteristics and applications are highlighted, such as scandium in aerospace alloys, titanium for its strength and temperature resistance, and chromium in stainless steel. The paragraph also touches on the importance of these metals in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics, showcasing their versatility and significance in modern technology and manufacturing.
🌟 The Role of Post-Transition and Metalloid Elements
This section introduces post-transition metals and metalloids, emphasizing their distinct roles in the periodic table and their applications. Post-transition metals like aluminum, gallium, indium, and thallium are described, with their atomic numbers and masses provided. Their uses in everyday items, electronics, and even solar panels are highlighted. Metalloids such as boron, silicon, germanium, arsenic, and antimony are also discussed, noting their positions in the periodic table and their significance in various industries, including electronics and manufacturing. The paragraph underscores the importance of these elements in the development of technology and their diverse applications.
🌿 Non-Metal Elements and Their Diverse Uses
The paragraph discusses the non-metal elements found in the periodic table, including hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur, and selenium. Each element's atomic number, atomic mass, and symbol are provided, along with a description of their properties and uses. Hydrogen, the lightest element, is highlighted for its abundance in the universe, while carbon is noted as a key component in fuels like coal and oil. Nitrogen's importance in the chemical industry for fertilizers and explosives is mentioned, as well as oxygen's role as the third most abundant element in the universe. Phosphorus, sulfur, and selenium are also discussed, emphasizing their agricultural, industrial, and nutritional roles.
💧 Halogens: The Salt-Forming Elements
This section focuses on the halogens, non-metallic elements in group 17 of the periodic table, known for their ability to form salts. The paragraph introduces fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, tennessine, and the predicted element 117, detailing their atomic numbers, atomic masses, and symbols. The halogens' reactivity and common states at room temperature are highlighted, with specific applications such as chlorine in water treatment and bromine in pool sanitation. The paragraph also mentions the rarity of astatine and the recent discovery of tennessine, providing a comprehensive overview of this group's characteristics and significance.
🌀 Noble Gases: Inert and Versatile Elements
The noble gases, found in group 18 of the periodic table, are the subject of this paragraph. The elements helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, radon, and the predicted element oganesson are introduced, with their atomic numbers, atomic masses, and symbols provided. The paragraph highlights the inert nature of these gases, making them chemically stable and less reactive. Applications such as helium in balloons, neon in advertising signs, and argon in providing inert atmospheres are discussed. The paragraph also touches on the recent synthesis of oganesson and its status as the element with the highest atomic number and mass, showcasing the ongoing exploration and discovery in the field of chemistry.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Periodic Table
💡Atoms
💡Nucleus
💡Electrons
💡Protons
💡Neutrons
💡Atomic Number
💡Valence Electrons
💡Alkali Metals
💡Alkaline Earth Metals
💡Transition Metals
Highlights
Atoms are the building blocks of all things in the universe, including humans.
An atom's nucleus, composed of neutrons and protons, determines an element's identity and properties.
The atomic number, which is the count of protons, differentiates one element from another.
Electrons, negatively charged particles, orbit the nucleus and are crucial for chemical bonding.
The periodic table is organized into periods and groups, reflecting elements' properties and electron configurations.
Groups on the periodic table represent families of elements with the same number of valence electrons.
Each element on the periodic table has a unique symbol and atomic number.
Alkali metals, including lithium, sodium, and potassium, are in the first group and have one electron in their outermost shell.
Alkaline earth metals, such as beryllium, magnesium, and calcium, are in column two and are known for their metallic properties.
Transition metals, found in groups 3 through 12, are known for their ability to conduct electricity and heat.
Metalloids, like silicon and germanium, have properties between metals and non-metals and are used in electronics.
Non-metals, including hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen, lack metallic attributes and have various applications in the chemical industry.
Halogens, such as fluorine, chlorine, and bromine, are non-metallic elements in group 17 known for forming salts.
Noble gases, including helium and neon, are in group 18 and are used in lighting and advertising due to their inert properties.
Actinide metals, such as uranium and plutonium, are radioactive and have applications in nuclear energy and research.
Post-transition metals, like aluminum and lead, are to the right of the transition metals and have diverse uses in various industries.
The periodic table also includes synthetic elements, such as moscovium and tennessine, which are created in laboratories.
Oganesson, a synthetic noble gas, has the highest atomic number and mass and is radioactive.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Periodic Table of Elements - Element Classes
The Periodic Table of the Elements in Chemistry - [1-2-12]

3.2 Introduction to the Periodic Table | High School Chemistry

Modern Periodic Table

Periodic Table Explained: Name Origin

Periodic Table of Elements Explained - Metals, Nonmetals, Valence Electrons, Charges
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: