Periodic Table Explained: Introduction
TLDRThe video script offers an insightful journey into the world of elements, explaining the fundamental concept of an element as a substance composed of a single type of atom. It introduces the periodic table as a systematic arrangement of these elements, highlighting its structure with 118 elements, seven horizontal rows, and eighteen vertical groups. The script emphasizes the unique atomic number and symbol for each element, and how these characteristics help identify their position within the table. It also delves into the properties of elements, distinguishing between metals, which are typically to the left of the table and exhibit conductivity and malleability, and nonmetals, found on the right, which are often brittle and poor conductors. The video further explores the concept of semiconductors, elements that possess properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals, and the special case of hydrogen, which stands alone without a group. The periodic table is portrayed as an essential tool for understanding the universe's composition, likened to an alphabet that forms the basis of all substances.
Takeaways
- 🌌 **Everything is made of atoms**: All things in the world are composed of incredibly tiny particles known as atoms.
- 🏵️ **Different kinds of atoms**: There are 92 naturally occurring kinds of atoms, each kind representing a different element.
- 📚 **Elements are pure substances**: An element is a substance that consists of only one kind of atom, such as a nugget of pure gold.
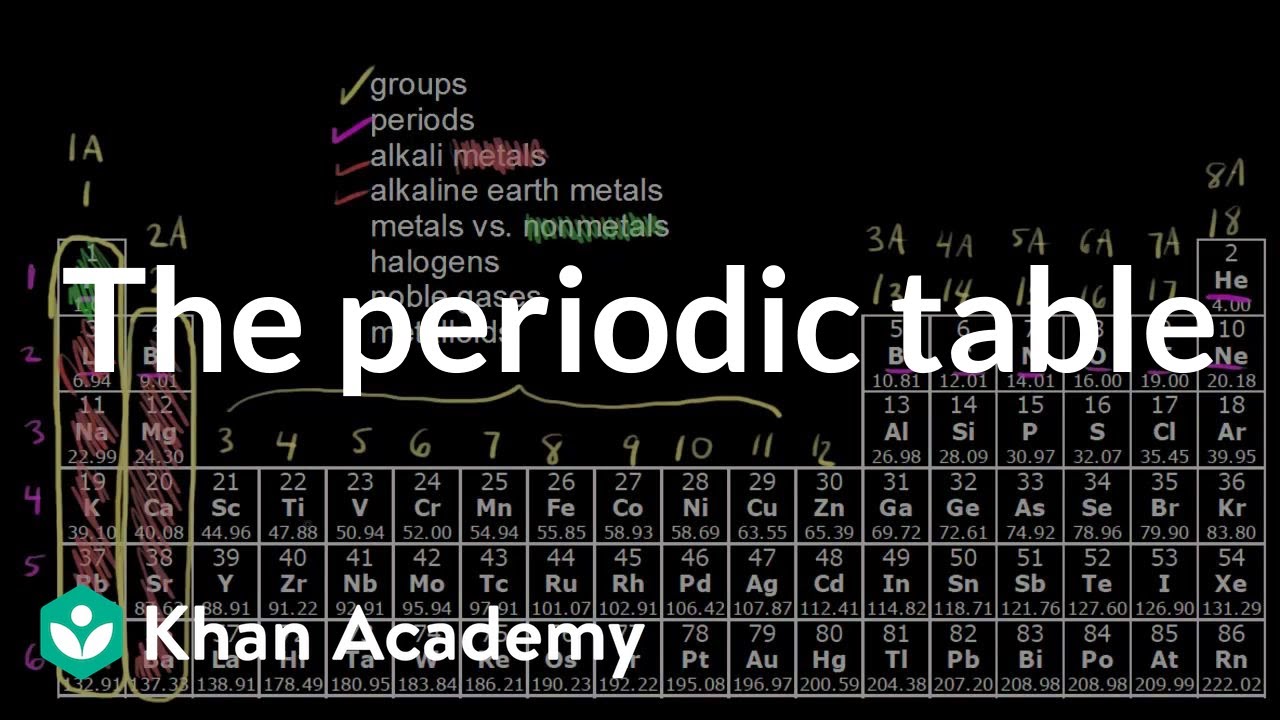
- 🔍 **The Periodic Table**: The periodic table is a list that organizes all known elements by increasing atomic number, starting with hydrogen and ending with uranium.
- 📏 **Atomic Number**: Each element has a unique atomic number that corresponds to its position in the periodic table.
- 🔠 **Element Symbols**: Elements are represented by one or two-letter symbols, like 'H' for hydrogen.
- 📏 **Rows and Columns**: The periodic table has seven horizontal rows (periods) and eighteen vertical columns (groups), with lanthanides and actinides extending the 6th and 7th rows.
- 👨👩👧👦 **Families of Elements**: Elements in the same group share similar properties, like the alkali metals or the halogens.
- 🔑 **Unique Positioning**: Each element has a unique combination of row and group on the periodic table, which helps identify its properties.
- 🛡️ **Metals and Nonmetals**: Elements are divided into metals (left side) and nonmetals (right side) by a diagonal line on the periodic table.
- 🌟 **Metallic Properties**: Metals are typically shiny, solid, good conductors of electricity and heat, and malleable.
- ⚡ **Nonmetallic Properties**: Nonmetals are often liquids or gases, poor conductors of electricity, and can be brittle.
- 💡 **Semiconductors**: Elements like silicon, which are in the diagonal band, have properties between metals and nonmetals, making them semiconductors.
- 🌟 **Hydrogen's Unique Place**: Hydrogen is a special case; it's placed above the metallic/nonmetal dividing line but is a gas and not a metal, often considered its own group.
- 🌍 **Abundance vs. Variety**: Although metals make up nearly three-quarters of the periodic table, elements like oxygen and silicon are more abundant in the Earth's crust, and hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe.
Q & A
What are the incredibly tiny particles that everything in the world is made of?
-Everything in the world is made of incredibly tiny particles called atoms.
How many different kinds of atoms are there?
-There are 92 different kinds of atoms.
What is an element?
-An element is a substance made of only one kind of atom.
What is the list that shows all the elements arranged by atomic number called?
-The list that shows all the elements arranged by atomic number is called the periodic table.
What is the atomic number of hydrogen?
-The atomic number of hydrogen, which is the lightest element, is 1.
How many horizontal rows does the periodic table have?
-The periodic table has seven horizontal rows.
What are the elements in the rows below the main body of the periodic table called?
-The elements in the rows below the main body of the periodic table are called the lanthanides and actinides.
How many elements are there in total on the periodic table?
-Including the artificial elements, there are 118 elements on the periodic table.
What are the vertical columns on the periodic table called?
-The vertical columns on the periodic table are called groups.
What is the name of the element with atomic number 30?
-The name of the element with atomic number 30 is Zinc (Zn).
Which group on the periodic table are the halogens?
-The halogens are in group 17 on the periodic table.
What property do metals have that nonmetals lack?
-Metals have the property of being malleable and good conductors of electricity and heat, which nonmetals generally lack.
What is a semiconductor?
-A semiconductor is an element that has properties between those of metals and nonmetals, capable of conducting electricity more than a nonmetal but less than a metal.
Why is hydrogen considered to be a group all by itself on the periodic table?
-Hydrogen is considered to be a group all by itself because it doesn't fit neatly into any of the existing groups; it has unique properties that don't align with the other alkali metals or any other group.
What is the significance of the periodic table in understanding the universe?
-The periodic table is significant as it organizes the elements in a pattern that reflects their properties and relationships, making it an 'alphabet of the universe' from which all substances can be composed.
Outlines
🌟 Understanding Elements and the Periodic Table
This paragraph introduces the concept of atoms as the building blocks of all matter and explains that there are 92 naturally occurring types, known as elements. An element is a substance composed of a single type of atom, like a nugget of pure gold. The periodic table is presented as a tool to organize and list all these elements, starting with the lightest, hydrogen, and ending with the heaviest, uranium. Each element has a unique symbol and atomic number. The paragraph also discusses the existence of additional, artificially created elements, expanding the total count beyond 92, and the structure of the periodic table, including its rows and groups.
🔬 Groups and Properties of Elements on the Periodic Table
This segment delves into the organization of the periodic table by groups, which are vertical columns containing elements with similar properties. It explains that elements in group 1, except for hydrogen, are alkali metals known for being soft and reactive, especially with water. The paragraph explores how the periodic table can be used to identify elements based on their atomic numbers and positions, and how it can predict an element's category as a metal or nonmetal based on its location relative to the diagonal dividing band on the table. Metals are typically to the left of this band, while nonmetals are on the right.
⚙️ Metals, Nonmetals, and Semiconductors in the Periodic Table
The final paragraph discusses the properties that distinguish metals from nonmetals. Metals, found on the left side of the periodic table's diagonal band, are often shiny, solid (except for mercury), and good conductors of electricity and heat. Nonmetals, on the right side, are usually liquids or gases, with some solids that are brittle and poor conductors. The paragraph also touches on elements within the diagonal band, which possess properties of both metals and nonmetals, making them semiconductors. Hydrogen is highlighted as a unique element that doesn't fit neatly into any group, being a nonmetal and a gas despite its position in group 1. The periodic table is lauded for its ability to organize the complex facts about elements into a coherent pattern, like an alphabet for the universe.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Atom
💡Element
💡Periodic Table
💡Atomic Number
💡Symbol
💡Groups
💡Metals and Nonmetals
💡Semiconductor
💡Alkali Metals
💡Hydrogen
💡Artificial Elements
Highlights
All things in the world are made of incredibly tiny particles called atoms.
There are 92 different kinds of atoms, each kind making up an element.
An element is a substance made of only one kind of atom, like a nugget of pure gold.
The periodic table is a list showing all the elements, ordered by atomic number.
Hydrogen, the lightest element, is at the top left of the periodic table with atomic number 1.
Elements in the periodic table have symbols represented by one or two letters.
The periodic table has seven horizontal rows and eighteen vertical groups.
Lanthanides and actinides are rows that extend the periodic table to include more elements.
There are 118 elements in total when including the artificial elements created in labs.
Elements in groups have similar properties, like family members.
Group 1 elements, except hydrogen, are soft, malleable metals that react explosively with water.
Metals are typically found on the left side of the periodic table and have metallic properties.
Nonmetals are on the right side of the table and are often liquids or gases with non-metallic properties.
Elements within the diagonal band of the table are semiconductors, having properties between metals and nonmetals.
Nearly three-quarters of the elements on the periodic table are metals, though not more abundant in the Earth's crust.
Hydrogen is unique and does not belong to any group; it's considered a group by itself.
The periodic table organizes the elements into a pattern, making it the alphabet of the universe.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
The periodic table | Atoms, elements, and the periodic table | High school chemistry | Khan Academy

Periodic Table Explained: Name Origin

Element, Compound and Mixture | Chemsitry

Periodic Table of Elements Song

Periodic Table of Elements Explained - Metals, Nonmetals, Valence Electrons, Charges

Lesson 11 - Overview Of The Periodic Table of Elements
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: