How WORLD WAR II Was Fought [AP World History Review—Unit 7 Topic 7]
TLDRThe video script discusses World War II, highlighting its nature as a total war with widespread devastation and civilian involvement. It emphasizes the immediate cause as Hitler's invasion of Poland and outlines the formation of Axis and Allied powers. The script delves into the strategies and ideologies of fascism, communism, and democracy in mobilizing for war, and the repression of basic freedoms across different nations. It also introduces new strategies like Blitzkrieg and firebombing, and the groundbreaking technology of the atomic bomb, which significantly influenced the war's outcome and led to the surrender of Japan.
Takeaways
- 🌍 World War II was a total war, involving the mobilization of entire populations and considering civilians as legitimate targets.
- 🥂 The immediate cause of World War II was Hitler's invasion of Poland, which led to Britain and France declaring war on Germany.
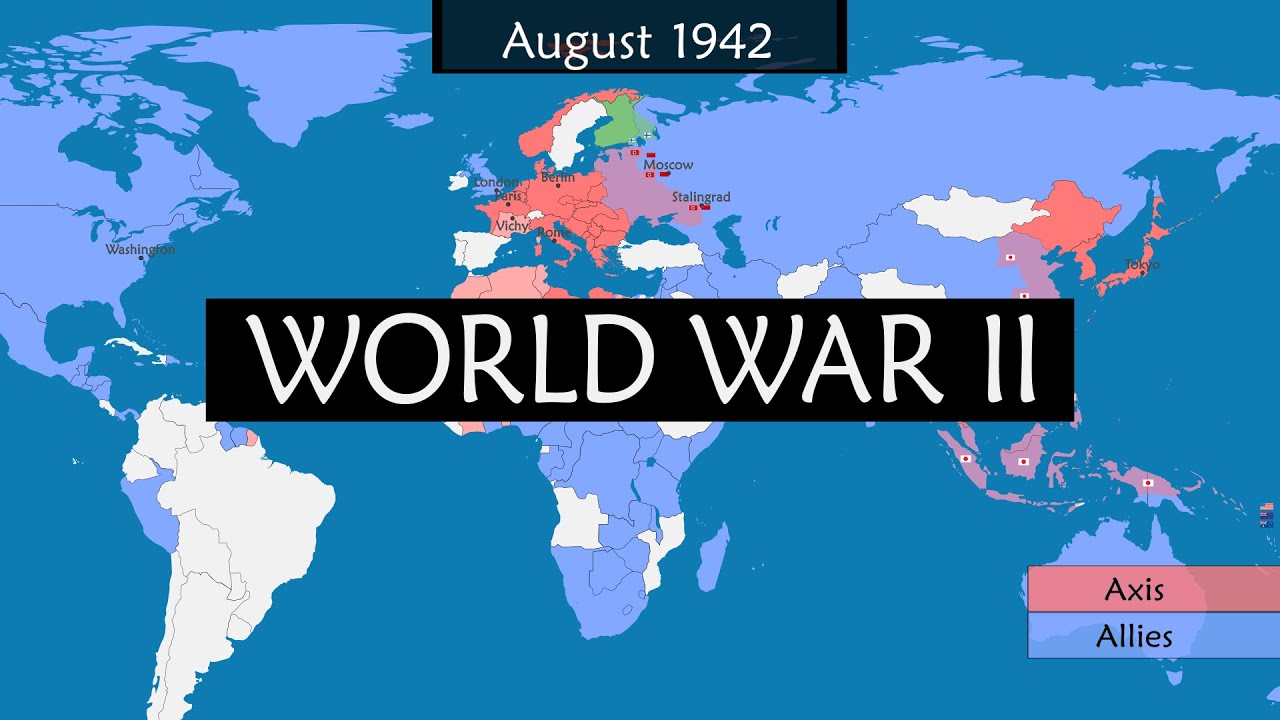
- 🔄 The war saw the formation of two rival alliances: the Axis powers (Germany, Italy, Japan) and the Allied Powers (Britain, France, Soviet Union, United States).
- 📜 The Soviet Union initially had a non-aggression pact with Germany but later joined the Allies after being invaded by Hitler.
- 💡 Propaganda played a crucial role in mobilizing populations and promoting nationalism during the war.
- 🤝 Governments relied on different ideologies to wage war: fascism in Axis powers, communism in the Soviet Union, and democracy in countries like Great Britain.
- 🚨 The war led to the repression of basic freedoms, with internment camps for Japanese Americans in the US and ghettos and concentration camps in Nazi Germany.
- 💥 New strategies like Blitzkrieg and firebombing, as well as the development of the atomic bomb, made World War II the deadliest conflict in history.
- 🌆 Firebombing campaigns, particularly in Dresden and Tokyo, resulted in the massive loss of civilian life and the creation of weather-altering fires.
- 💣 The atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki led to Japan's surrender and the end of the war in the Pacific.
- 🏆 The Allied Powers emerged victorious in both Europe and the Pacific, but the war's devastation would have lasting impacts on the world.
Q & A
What is the definition of a total war?
-A total war is a conflict that necessitates the mobilization of an entire country's population, both military and civilian, to participate in the war effort. In a total war, civilians are considered as legitimate targets as military ones.
What was the immediate cause of World War II?
-The immediate cause of World War II was Hitler's invasion of Poland on September 1st, 1939, which prompted Britain and France to declare war on Germany.
Which countries formed the Axis powers during World War II?
-The Axis powers during World War II included Germany, Italy, and Japan, all of which were led by fascist regimes.
How did the Soviet Union initially relate to Nazi Germany before becoming part of the Allies?
-Initially, the Soviet Union signed a non-aggression pact with Nazi Germany. However, after Hitler invaded the Soviet Union, the Soviets joined the Allies, which included Britain, France, and later the United States.
What role did the United States play in World War II before the attack on Pearl Harbor?
-Before the attack on Pearl Harbor, the United States followed a policy of isolationism but still provided financial and material support to Britain.
How did governments mobilize their populations for World War II?
-Governments used various tactics such as propaganda to evoke nationalism and demonize enemies, leaned on different ideologies like fascism, communism, and democracy to wage war, and made promises to expand the welfare state in exchange for wartime sacrifices.
What were the three ideologies compared in the script for how they influenced the war?
-The three ideologies compared were fascism, which glorified the state and used militaristic means; communism, which emphasized rapid industrialization and collectivization; and democracy, which relied on persuasion and cooperation of the people.
What was the Blitzkrieg strategy?
-The Blitzkrieg strategy, pioneered by Germany, was a rapid, coordinated attack using air and ground forces, including tanks and other armored vehicles, aimed at quickly overwhelming and defeating the enemy, effectively making trench warfare obsolete.
What is firebombing and how was it used during World War II?
-Firebombing involved the use of small clusters of explosive devices designed to start fires in urban areas, causing massive destruction and civilian casualties. It was used by the Allied Forces, notably in Dresden, Germany, and Tokyo, Japan.
What was the significance of the atomic bomb during World War II?
-The atomic bomb, developed by the United States, was a revolutionary technology that could destroy entire cities with a single blast. Its use on Hiroshima and Nagasaki led to Japan's surrender and the end of the war in the Pacific.
How did World War II impact the basic freedoms of people in various nations?
-The repression of basic freedoms occurred in varying degrees across fascist, communist, and democratic nations. For instance, in the United States, Japanese Americans were interned, and in Germany, Jews and other undesirables were forced into ghettos and concentration camps.
Outlines
🌍 World War II: Total War and Alliances
This paragraph discusses World War II as a total war, requiring the mobilization of entire populations and considering civilians as legitimate targets. It highlights the immediate cause of the war as Hitler's invasion of Poland and the formation of two rival alliances: the Axis powers (Germany, Italy, Japan) and the Allied Powers (Britain, France, Soviet Union, United States). The paragraph also touches on the roles of ideologies (fascism, communism, and democracy) in mobilizing for war and the shift from appeasement to active resistance against aggression.
💥 New Strategies and Technologies in World War II
This paragraph focuses on the innovative strategies and technologies that made World War II the deadliest conflict in history. It describes the Blitzkrieg tactic developed by Germany, which combined air assaults and rapid infantry movement, rendering trench warfare obsolete. The paragraph also discusses the firebombing strategy used by the Allied Forces, particularly the devastating bombings of Dresden and Tokyo. Lastly, it details the invention of the atomic bomb by the United States, which led to the bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, resulting in Japan's surrender and the end of the war in the Pacific.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Total War
💡Hitler's Invasion of Poland
💡Axis Powers
💡Allied Powers
💡Propaganda
💡Fascism
💡Communism
💡Democracy
💡Repression of Basic Freedoms
💡Blitzkrieg
💡Firebombing
💡Atomic Bomb
Highlights
World War II was a total war, requiring the mobilization of a country's entire population, both military and civilian.
Civilians were considered legitimate targets in World War II, just like military targets.
The immediate cause of World War II was Hitler's invasion of Poland.
Hitler aimed to acquire Lebensraum, or living space, for Germany by conquering and annexing European territories.
The alliance system in World War II formed into two rival sides: the Axis powers (Germany, Italy, Japan) and the Allied Powers (Britain, France, Soviet Union, United States).
The Soviet Union initially signed a non-aggression pact with Germany but later joined the Allies after Hitler invaded the Soviet Union.
The United States entered the war after Japan bombed the US Naval Base at Pearl Harbor.
Governments used propaganda to mobilize populations and provoke nationalism during World War II.
Fascism, communism, and democracy were the three ideologies that governments leaned on to wage World War II.
Fascist states were organized to serve the interests of the state, not the people, and glorified military conflict.
Stalin's Soviet Union industrialized rapidly, with collectivization and demands for increased output to support the war effort.
Winston Churchill, as the British Prime Minister, rallied the British people through persuasion and propaganda campaigns, unlike totalitarian leaders.
The British government promised to expand the welfare state in exchange for wartime sacrifices.
The repression of basic freedoms occurred in varying degrees across fascist, communist, and democratic nations during the war.
The United States interned over 100,000 Japanese Americans after the bombing of Pearl Harbor.
Germany implemented the Nuremberg Laws, leading to the forced ghettoization and later systematic extermination of Jews and other undesirables.
Blitzkrieg, a new strategy pioneered by Germany, aimed to eliminate the enemy with incredible speed using air and ground forces.
Firebombing was a strategy that involved dropping small clusters of explosive devices to start fires and cause massive destruction.
The atomic bomb, developed by the United States, was a revolutionary technology that could destroy an entire city with a single blast.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: