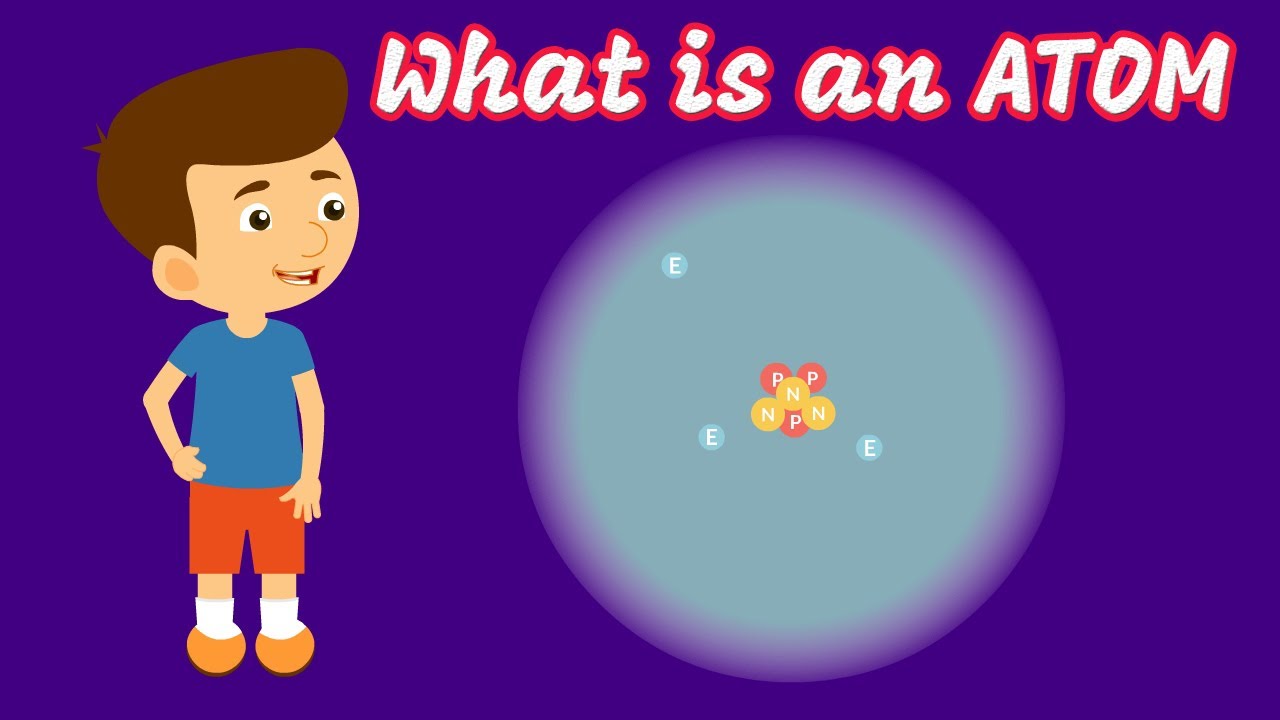
What's Inside an Atom? Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons!
TLDRAtoms, the building blocks of everything, are composed of protons, electrons, and neutrons. The number of protons defines an element's identity and is listed as the atomic number on the periodic table. Electrons, negatively charged, orbit protons due to the electric force, balancing their positive charge. Neutrons are essential as they counteract the protons' repulsion through the strong nuclear force, acting as a binding glue. Without neutrons, all matter would disintegrate into hydrogen.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Atoms are composed of protons, electrons, and neutrons.
- 🎯 The number of protons in an atom determines the element and its position on the periodic table.
- 🔢 There are 118 known elements, each with a unique number of protons.
- 🔴 Protons carry a positive electrical charge.
- 🔵 Electrons carry a negative electrical charge and orbit the nucleus at high speeds, forming an electron cloud.
- 🤲 The electric force is the attraction between opposite charges of protons and electrons.
- 💥 Neutrons help maintain the structure of the atom by counteracting the repulsion between protons through the strong nuclear force.
- 🧱 Without neutrons, the electric force would cause protons to repel each other, potentially resulting in a universe composed only of hydrogen.
- 🔬 The atomic number, visible on the periodic table, represents the number of protons in an atom.
- ⚖️ Electrons balance the number of protons in a stable atom, maintaining electrical neutrality.
Q & A
What are the three fundamental particles that make up an atom?
-The three fundamental particles that make up an atom are protons, electrons, and neutrons.
What determines the identity of an element?
-The identity of an element is determined by the number of protons in its atoms, which is also known as the atomic number.
How does the periodic table organize elements?
-The periodic table organizes elements according to their atomic number, which is the number of protons in their atoms.
What is the role of electrons in an atom?
-Electrons orbit the nucleus of an atom at high speeds, forming an electron cloud, and their negative charge is attracted to the positive charge of protons due to the electric force.
Why do atoms have the same number of electrons and protons?
-Atoms have the same number of electrons and protons because the electric force between them keeps them together, forming a stable atom.
What is the purpose of neutrons in an atom?
-Neutrons serve to counteract the electric force between protons, preventing them from being pushed apart due to the strong nuclear force that acts as a binding glue within the nucleus.
What would happen if an atom did not have neutrons?
-Without neutrons, the protons in an atom would be pushed apart by the electric force, and all matter would essentially revert to hydrogen, the simplest element.
What is the strong nuclear force and how does it relate to the structure of an atom?
-The strong nuclear force is a fundamental force that acts between neutrons and protons in an atom's nucleus, holding them together despite the repulsive electric force between protons.
How do the properties of elements like gold, carbon, and oxygen differ, and what causes these differences?
-The properties of elements like gold, carbon, and oxygen differ due to the number and arrangement of protons, electrons, and neutrons in their atoms, which determine their chemical and physical characteristics.
What is the atomic number of the first three elements in the periodic table?
-The atomic numbers of the first three elements in the periodic table are hydrogen with one proton, helium with two protons, and lithium with three protons.
What is the highest atomic number of an element currently known?
-The highest atomic number of an element currently known is oganesson, which has 118 protons.
Outlines
🌟 Understanding Atoms: Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons
This paragraph delves into the fundamental components of atoms, which are protons, electrons, and neutrons. It explains that atoms are the building blocks of everything and that there are 118 known types of atoms, each with unique properties. The paragraph highlights the role of protons in defining the element, as the number of protons determines the atomic number and thus the identity of the element. The importance of electrons is also discussed, as they orbit the nucleus at high speeds, creating an electron cloud and contributing to the chemical behavior of elements. The paragraph further explains the necessity of neutrons, which counteract the electric force that would otherwise cause protons to repel each other, and introduces the concept of the strong nuclear force that holds the nucleus together.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Atoms
💡Protons
💡Electrons
💡Neutrons
💡Electric Force
💡Strong Nuclear Force
💡Atomic Number
💡Periodic Table
💡Element
💡Chemical Bonds
Highlights
Atoms are composed of three fundamental particles: protons, electrons, and neutrons.
There are 118 known elements, each with unique properties determined by their atomic structure.
The number of protons in an atom defines the element and is referred to as its atomic number.
Hydrogen has one proton, helium has two, and lithium has three, illustrating the atomic number sequence.
Electrons orbit the nucleus at high speeds, forming an electron cloud around the atom.
The negative charge of electrons is attracted to the positive charge of protons due to electric force.
The stable elements have an equal number of protons and electrons, maintaining electrical neutrality.
Neutrons prevent protons from repelling each other due to their positive charges.
The strong nuclear force is a powerful interaction that keeps the nucleus together, acting like glue.
Without neutrons, all matter would revert to hydrogen due to the lack of strong nuclear force.
The properties of elements such as gold, carbon, and oxygen are determined by the number and arrangement of subatomic particles within their atoms.
The periodic table organizes elements by their atomic number, showcasing the incremental increase in protons.
The electron cloud's formation is a result of the interaction between the negatively charged electrons and positively charged protons.
The strong nuclear force is responsible for counteracting the electrostatic repulsion between protons.
The absence of neutrons would result in a lack of diversity in elements, as everything would simply be hydrogen.
The atomic number is a key identifier on the periodic table of elements, allowing for the classification and prediction of an element's properties.
The balance between electric force and strong nuclear force is crucial for the stability and variety of elements.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: