Wave Superposition
TLDRIn this AP Physics essentials video 113, Mr. Andersen explains the concept of wave superposition, where waves can either constructively or destructively interfere with each other. He demonstrates through experiments how waves add their amplitudes when they meet, creating either a larger wave or canceling each other out. The video also introduces the idea of standing waves, showing how waves can move in opposite directions and interfere constructively or destructively, forming nodes and antinodes.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Wave Superposition refers to the interaction of waves where they can either constructively build up or destructively cancel each other out.
- 📈 In the video, two transverse waves are shown interacting, with one possibility being the creation of a larger wave upon meeting.
- 🔄 When waves meet, they do not bounce off each other but instead pass through one another, interfering with each other's amplitude.
- 🤔 The concept is demonstrated using slinkies to visually show the addition of wave values when waves meet at a point.
- 📊 Constructive interference results in a larger amplitude when two waves are in phase and their amplitudes add together.
- 🚫 Destructive interference leads to a reduction or cancellation of amplitude, resulting in no movement at points where the waves cancel each other.
- 📹 The video uses a combination of visual demonstrations and algebraic explanations to describe wave superposition.
- 🌐 When waves continue after interacting, they maintain their individual characteristics and move in their original directions.
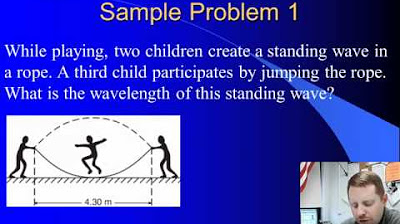
- 🔄 The concept of standing waves is introduced, which are waves that appear to be stationary due to the superposition of two waves moving in opposite directions.
- 📍 Nodes are points of total destructive interference in a standing wave, where there is no movement, while antinodes are points of constructive interference with the maximum amplitude.
- 🧪 The video suggests an experiment involving launching waves at each other and measuring the displacement before and during the interaction to understand wave superposition better.
Q & A
What is wave superposition?
-Wave superposition is a phenomenon where two or more waves interact with each other and their amplitudes combine to form a new wave pattern. This can result in either constructive interference, where the waves build up to form a larger wave, or destructive interference, where the waves cancel each other out.
What types of waves are being discussed in the video?
-The video discusses transverse waves, which are waves where the displacement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of the wave's energy transfer.
What happens when two waves meet at the point where the slinkies are connected?
-When two waves meet at the point where the slinkies are connected, they undergo superposition, resulting in the sum of their amplitudes to form one giant wave.
How can we visually determine if waves are undergoing constructive or destructive interference?
-Constructive interference can be visually identified when the waves build up to form a larger wave, while destructive interference is observed when the waves cancel each other out, resulting in no significant movement or amplitude at the point of interaction.
What is the difference between the waves' behavior in the video when they are in phase and when they are out of phase?
-When the waves are in phase, they have the same frequency and their peaks and troughs align, leading to constructive interference. When they are out of phase, their peaks align with the troughs of the other wave, leading to destructive interference.
How does the video demonstrate the concept of a standing wave?
-The video demonstrates a standing wave by showing a black wave that appears not to be moving, just oscillating up and down. This is created by the superposition of two waves moving in opposite directions, resulting in a wave pattern that seems stationary.
What are nodes and antinodes in the context of standing waves?
-Nodes are points in a standing wave where there is total destructive interference, resulting in no movement or displacement. Antinodes are points of maximum constructive interference, where the amplitude of the standing wave is the greatest.
How can one experimentally verify the principles of wave superposition?
-One can experimentally verify wave superposition by launching waves at each other, recording the interaction on video, and then measuring the displacement of the waves before and during the interaction to observe changes due to constructive and destructive interference.
What is the practical significance of understanding wave superposition?
-Understanding wave superposition is crucial in various fields such as physics, engineering, and acoustics, where the behavior of waves can impact the design of structures, the transmission of signals, and the analysis of wave phenomena.
How does the concept of wave superposition relate to other areas of physics?
-Wave superposition is a fundamental concept that is applicable in many areas of physics, including optics, quantum mechanics, and electromagnetism, where the principles of wave interference are essential for understanding the behavior of light, particles, and electromagnetic fields.
What are some real-world applications of the principles of constructive and destructive interference?
-Real-world applications include noise-canceling headphones that use destructive interference to reduce unwanted sound, medical imaging technologies like ultrasound that rely on constructive interference to create clear images, and the design of musical instruments where the control of interference patterns is crucial for sound quality.
Outlines
🌊 Wave Superposition in AP Physics Essentials
This paragraph introduces the concept of wave superposition, explaining how waves can either constructively build upon or destructively cancel each other when they interact. The explanation is illustrated with an example of two transverse waves meeting, resulting in either the creation of a larger wave or a point of no displacement, depending on their phase relationship. The concept is further clarified through the analogy of algebraic addition of wave values, emphasizing the principles of constructive and destructive interference.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Wave Superposition
💡Transverse Waves
💡Constructive Interference
💡Destructive Interference
💡Amplitude
💡Equilibrium
💡Standing Wave
💡Nodes
💡Antinodes
💡Experimentation
💡Displacement
Highlights
Wave superposition is the interaction where waves can either build each other up or tear each other down.
In the demonstration, two transverse waves are sent towards each other, resulting in superposition.
When waves meet, they add their values together, creating a giant wave through constructive interference.
Waves do not bounce off each other; instead, they move right through each other, interfering with one another.
Constructive interference leads to a larger wave, while destructive interference can result in complete cancellation.
The concept of superposition is fundamental in understanding wave behavior when they interact.
Experimentation is suggested as a way to observe and measure the effects of constructive and destructive interference.
Waves can be in phase or out of phase, leading to different interference patterns.
When two in-phase waves interact, their displacements add up, resulting in a larger displacement.
Destructive interference occurs when two waves have opposite displacements, resulting in a net displacement of zero.
Standing waves are created when waves reflect back and forth, creating a seemingly non-moving pattern.
The summation of two waves moving in opposite directions results in a standing wave.
Nodes are points of total destructive interference where there is no movement.
Antinodes are points of total constructive interference where the displacement is at its maximum.
The video aims to educate on the principles of wave superposition through visual demonstrations and practical applications.
The presenter encourages viewers to conduct their own experiments to better understand wave interference.
The video serves as an educational resource for understanding the complex behavior of waves in AP Physics essentials.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: