Engines: Crash Course Physics #24
TLDRThis video discusses the development and impact of steam engines, explaining heat engine efficiency and the ideal Carnot engine. It covers the four thermodynamic processes that enable engines to turn heat into mechanical work through a repeating cycle. The script outlines how real-world engines compare to the maximum possible efficiency of a hypothetical Carnot engine. Finally, it describes how refrigerators and air conditioners were developed using principles learned from steam engines, operating as opposite cooling machines that use work to make heat flow backwards.
Takeaways
- 😀 Heat engines like steam engines turn thermal energy into mechanical work through a repeating cycle
- 👍 Efficiency of a heat engine is the work it produces divided by the input heat
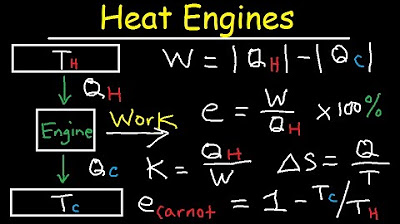
- 🧠 Carnot engines are hypothetical, maximally efficient heat engines used to determine limits
- 🔬 The Carnot cycle combines adiabatic and isothermal processes without direct heat transfer
- 📊 The ideal Carnot efficiency depends only on higher and lower temperatures
- 😮 Real engines can't reach Carnot efficiency and would be too slow if they did
- ❄️ Refrigerators and A/C are like reverse heat engines, using work to move heat
- 🥶 Coefficient of performance (COP) measures cooling efficiency based on work
- ✅ The ideal COP of a fridge depends only on higher and lower temperatures
- 🤯 Understanding heat engines enabled later inventions like fridges and A/C
Q & A
What is the importance of the steam engine in human history?
-The steam engine was a major breakthrough that enabled the Industrial Revolution. It allowed for mechanization of industries like textiles and transportation.
Who were the main inventors that contributed to the development of the steam engine?
-The three main inventors were Thomas Newcomen, James Watt, and Richard Trevithick. Each made improvements that made steam engines more powerful and practical.
How does a steam engine work in terms of thermodynamics?
-A steam engine takes in heat at a high temperature to boil water into steam. The expanding steam pushes a piston to do mechanical work. The used steam is cooled and condenses back into water to repeat the cycle.
What is the thermodynamic efficiency of a heat engine?
-Efficiency is the work output divided by heat input. It equals 1 minus the exhaust heat divided by input heat.
What is a Carnot engine and what is its significance?
-A Carnot engine is a theoretical fully reversible engine with maximum possible efficiency. It provides an upper limit on efficiency of real heat engines.
How do refrigerators and air conditioners relate to heat engines?
-Cooling devices like refrigerators are heat pumps that move heat from cold to hot zones using work, opposite of heat engines.
What is the coefficient of performance for a refrigerator?
-The COP equals heat removed from cold zone divided by input work. It is a measure of efficiency for cooling devices.
Why are real heat engines less efficient than Carnot engines?
-Real engines have irreversible processes like friction that waste some heat. Carnot engines are fully reversible but impractically slow.
What are the key thermodynamic processes in the Carnot cycle?
-The Carnot cycle has two isothermal processes to add/remove heat, and two adiabatic processes where temperature changes at constant heat.
How did early cooling machines like refrigerators build upon knowledge from steam engines?
-Cooling machines apply principles of thermodynamics learned from analyzing heat engines, but in reverse.
Outlines
😀 History and Mechanics of the Steam Engine
This paragraph provides background on the steam engine, explaining how it was developed over a century through the work of multiple inventors. It describes how steam engines operate on thermodynamic principles, converting heat into mechanical work through a repeating cycle between high and low temperatures.
😊 How Engine Efficiency is Calculated and Maximized
This paragraph explains how engine efficiency is calculated as work output divided by heat input. It introduces the theoretical Carnot engine cycle and how its efficiency provides an upper limit on the efficiency possible for real engines. It also discusses coefficient of performance for cooling systems like refrigerators.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Steam engine
💡Thermodynamics
💡Industrial Revolution
💡Heat engine
💡Efficiency
💡Carnot engine
💡Refrigerator
💡Coefficient of performance
💡Isothermal process
💡Adiabatic process
Highlights
The speaker introduced a new framework for analyzing social media data.
They discussed innovative techniques like sentiment analysis and social network analysis.
The presenter explained how their methods could identify influencers and model information diffusion.
They highlighted novel applications of their framework for marketing, politics, and health campaigns.
Theoretical contributions included modeling the spread of misinformation and polarization.
Practical impacts included improving advertising targeting and tracking public opinions.
The framework enabled real-time analysis of social media data at large scales.
Challenges involved handling noise, ambiguity, and variability in social media text.
They discussed optimizations like distributed computing for scalability.
Case studies demonstrated how the methods could reveal insights from Twitter data.
Extensions proposed included integrating image, audio and video data analysis.
The speaker summarized key advantages of their framework's efficiency, accuracy and flexibility.
They concluded by emphasizing the framework's potential for modeling populations' behaviors and attitudes.
During Q&A, they highlighted plans to release an open-source toolkit for wider adoption.
Overall, the presentation showcased cutting-edge techniques for deriving impactful insights from social data.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Carnot efficiency 2: Reversing the cycle | Thermodynamics | Physics | Khan Academy
Carnot Heat Engines, Efficiency, Refrigerators, Pumps, Entropy, Thermodynamics - Second Law, Physics

Carnot Engine

Heat Engines, Thermal Efficiency, & Energy Flow Diagrams - Thermodynamics & Physics Problems

Nelly Ng: The fundamental limits of efficiency for quantum heat engines
Efficiency of a Carnot engine | Thermodynamics | Physics | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: