Introduction to Steam Tables
TLDRThis screencast explores the use of steam tables, which detail properties of water in liquid and vapor states, including specific volume, enthalpy, internal energy, and entropy. The video demonstrates how to calculate the density of water at its critical point (373.95°C) and determine the quality of water at 100°C using given enthalpy values. It explains the concept of quality as the fraction of water in vapor phase and uses steam tables to find the enthalpy of liquid and vapor at saturation conditions, concluding that the water is 83% vapor and 17% liquid at this temperature.
Takeaways
- 💧 The script discusses the use of steam tables for understanding properties of water in different states.
- 🔍 The critical point of water is identified where liquid and vapor volumes are equal, occurring at 373.95°C.
- 📏 The critical volume of water is provided as 0.003106 m³/kg, which is used to calculate density.
- 📉 The density of water at the critical point is calculated as the reciprocal of its volume, resulting in approximately 323 kg/m³.
- 🌡 The script explains how to calculate the quality of water at a given temperature, using 100°C as an example.
- 🔥 The concept of 'quality' is defined as the fraction of water that is in the vapor phase at saturation conditions.
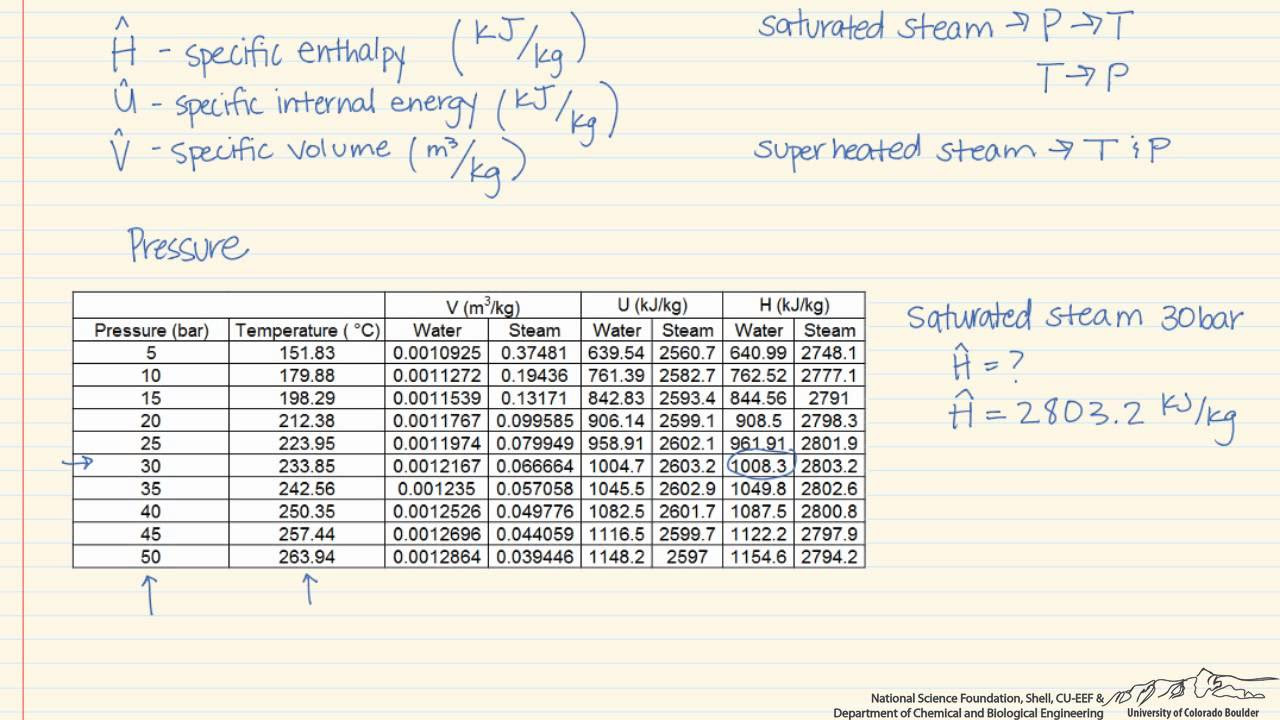
- 📚 Reference is made to a thermodynamics textbook by Elliott and Lira for specific enthalpy values from steam tables.
- ♨️ At 100°C, the enthalpy of water is given as 2300 kJ/kg, which is used to determine the quality of the water.
- 🔄 The quality calculation involves the enthalpy of both the liquid and vapor phases at saturation conditions.
- 📈 The script concludes that at 100°C with an enthalpy of 2300 kJ/kg, the water is 83% vapor and 17% liquid.
- 📝 The importance of using accurate and significant figures in scientific calculations is highlighted throughout the script.
Q & A
What are steam tables used for?
-Steam tables are used to provide compilations of properties for water, such as specific volume, specific enthalpy, internal energy, entropy, saturation pressures, and saturation temperatures, for both liquid and vapor phases.
What is the critical point of water?
-The critical point of water is the temperature and pressure at which the liquid and vapor phases have the same volume, which is at 373.95 degrees Celsius.
What is the density of water at its critical point?
-The density of water at its critical point is calculated as the reciprocal of its specific volume, which is 1 / 0.003106 m^3/kg, resulting in approximately 322.5 kg/m^3 when rounded to three significant figures.
What does the term 'quality' refer to in the context of thermodynamics?
-In thermodynamics, 'quality' refers to the fraction of the total mass that is in the vapor phase in a mixture of liquid and vapor at saturation conditions.
What is the given enthalpy value for water at 100 degrees Celsius in the script?
-The given enthalpy value for water at 100 degrees Celsius is 2300 kJ/kg.
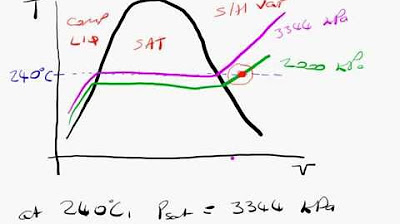
What are saturation conditions in the context of steam tables?
-Saturation conditions refer to the state where the liquid and vapor phases are in equilibrium at a given temperature and pressure, with the vapor phase being in contact with the liquid phase.
How is the quality of water calculated at a given temperature and enthalpy?
-The quality of water is calculated using the known enthalpies of the liquid and vapor phases at saturation conditions and the enthalpy of the mixture. It involves solving for the fraction of the vapor phase using the formula that relates the mixture's enthalpy to the enthalpies of the liquid and vapor phases.
What is the significance of the enthalpy of liquid and vapor at saturation conditions?
-The enthalpy values for liquid and vapor at saturation conditions are crucial for determining the quality of the mixture, as they represent the energy content of each phase and are used to calculate the overall energy state of the mixture.
What is the calculated quality of water at 100 degrees Celsius with an enthalpy of 2300 kJ/kg?
-The calculated quality of water at 100 degrees Celsius with an enthalpy of 2300 kJ/kg is approximately 83% vapor, indicating that 83% of the water is in the vapor phase and 17% is in the liquid phase.
Where can one find the enthalpy values for liquid and vapor at saturation conditions?
-The enthalpy values for liquid and vapor at saturation conditions can be found in steam tables, which are typically included in thermodynamics textbooks or engineering reference materials.
What textbook is mentioned in the script for reference to steam tables?
-The script mentions a thermodynamics textbook by Elliott and Lira as a reference for steam tables.
Outlines
🔍 Understanding Steam Tables and Water's Critical Point
This paragraph introduces the concept of steam tables, which are essential tools in thermodynamics for determining properties of water in both liquid and vapor phases. The focus is on the critical point of water, where the densities of liquid and vapor are equal, occurring at 373.95 degrees Celsius. The critical volume is provided, and the density is calculated as its reciprocal, resulting in a value with three significant figures.
🌡 Calculating the Quality of Water at 100 Degrees Celsius
The second paragraph delves into the calculation of water's quality at 100 degrees Celsius, given its enthalpy as 2300 kJ/kg. Quality refers to the fraction of water in the vapor phase. Using steam tables from a thermodynamics textbook by Elliott and Lira, the enthalpy values for liquid and vapor at saturation conditions are identified. The paragraph explains the formula for calculating the quality of the water, which involves the enthalpy of both the liquid and vapor phases. The calculation reveals that at this temperature, the water is 83% vapor and 17% liquid.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Steam Tables
💡Critical Point
💡Density
💡Quality of Water
💡Enthalpy
💡Saturation Conditions
💡Vapor Phase
💡Liquid Phase
💡Fraction
💡Thermodynamics Textbook
💡Significant Figures
Highlights
Introduction to steam tables as compilations of properties for water in liquid and vapor phases.
Explanation of specific volume, specific enthalpy, internal energy, and entropy listed in steam tables.
Mention of saturation pressures and temperatures included in steam tables.
Task to determine the density of water at its critical point.
Identification of the critical point as where liquid and vapor volumes are equal.
Statement of the critical point occurring at 373.95 degrees Celsius.
Calculation of density at the critical point using the formula 1 over volume.
Presentation of the density value with three significant figures.
Calculation of the quality of water at 100 degrees Celsius given an enthalpy of 2300 kJ/kg.
Definition of quality as the fraction of water in the vapor phase.
Use of saturation conditions to determine enthalpy values from steam tables.
Reference to a thermodynamics textbook by Elliott and Lira for enthalpy values.
Explanation of how to calculate the quality using the enthalpy of liquid and vapor phases.
Determination that the fraction of vapor phase is 83% at 100 degrees Celsius.
Calculation of the remaining 17% as the liquid phase fraction.
Emphasis on solving for quality with attention to significant figures.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: