5 Concepts in Statistics You Should Know | Data Science Interview
TLDRIn this informative video, Dan, the founder of Datant.com, introduces five essential statistics concepts for data science interviews: central tendency, dispersion, correlation, normal distribution, and hypothesis testing. He explains each concept with examples and emphasizes their importance for entry-level data scientists or those looking to refresh their statistical knowledge. Dan also recommends Datant.com for interview preparation resources and hints at upcoming videos covering additional statistical topics.
Takeaways
- 📚 Dan, the founder of datant.com, introduces five essential statistics concepts for data science interviews: central tendency, dispersion, correlation, normal distribution, and hypothesis testing.
- 🔢 Central tendency is described by mean, median, and mode, with mean being the sum of values divided by the count, median as the middle value in an ordered set, and mode as the most frequent number.
- 📈 The mean is sensitive to outliers, while the median is robust against them but only uses one value, and the mode is useful for categorical data but also only considers one value.
- 📊 Dispersion is the spread of data in a distribution, measured by variance (the average of the squared differences from the mean) and standard deviation (the square root of variance).
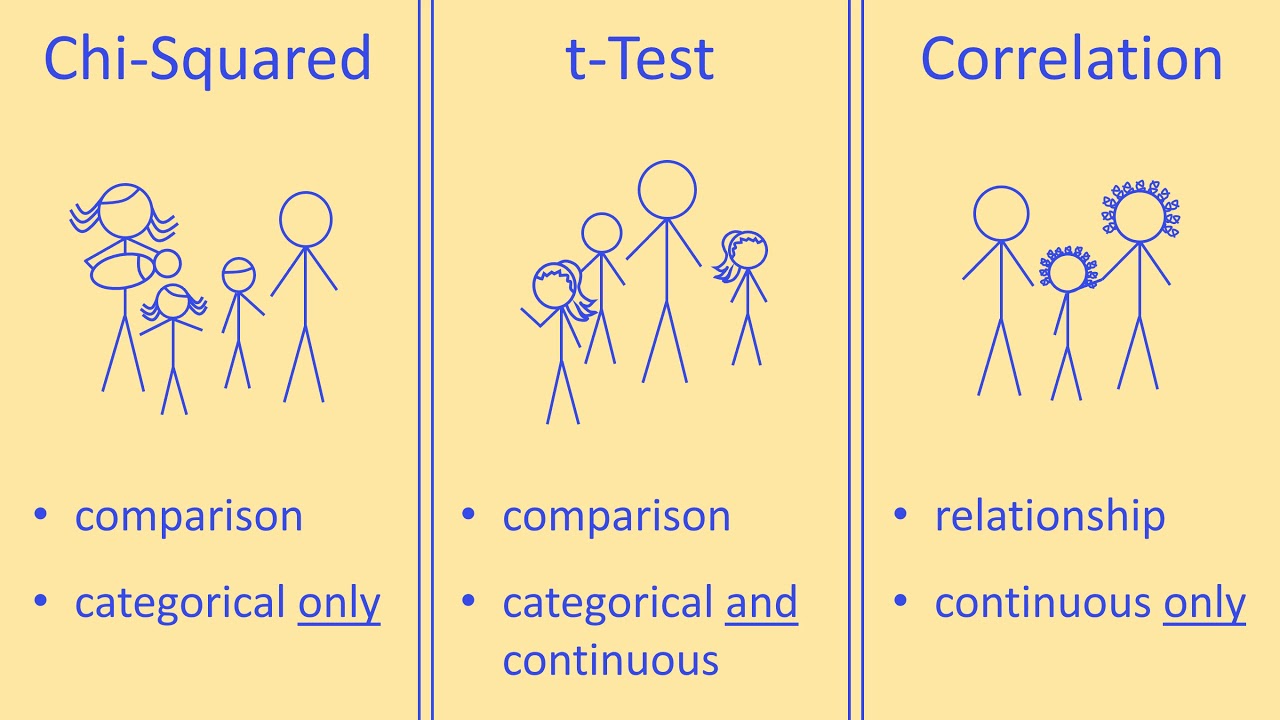
- 🤝 Correlation measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables, with Pearson correlation being a common method that scales the covariance between -1 and 1.
- 📉 The presence of outliers can affect correlation values, and techniques like the interquartile range (IQR) or robust scaling can help correct for this.
- 📚 The normal distribution is symmetrical and characterized by the 66-95-99.7 rule, which describes the percentage of data within one, two, or three standard deviations from the mean.
- 🌐 The central limit theorem states that the distribution of sample means will approximate a normal distribution as the sample size increases, regardless of the original distribution.
- ⚖️ Hypothesis testing is a statistical method to test assumptions about a population parameter, involving setting up hypotheses, calculating a p-value, and making a decision based on the significance level.
- 📉 In hypothesis testing, a p-value less than the significance level (commonly set at 0.05) indicates statistical significance to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative.
- 🔮 Additional statistical concepts for data science interviews include distributions, Bayes theorem, ANOVA, sampling, non-parametric tests, permutation tests, confidence and credible intervals, regression modeling, non-normal distributions, and maximum likelihood.
Q & A
What are the five key statistics concepts covered in the video for data science interviews?
-The five key statistics concepts covered in the video are central tendency, dispersion, correlation, normal distribution, and hypothesis testing.
What does central tendency describe in a data distribution?
-Central tendency describes where most of the data lies in the distribution, and it can be measured using mean, median, and mode.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using the mean as a measure of central tendency?
-The advantage of using the mean is that it utilizes all of the values, providing a comprehensive measure of central tendency. However, it is sensitive to outliers or extreme values, which can skew the result.
How is the median different from the mean, and when might you choose to use it?
-The median is the middle value in an ordered set and is robust against outliers. You might choose to use the median when the data set contains outliers or is skewed, as it uses only one value and is less affected by extreme data points.
What is the mode, and when is it particularly useful?
-The mode is the most frequent number in a data set. It is particularly useful when describing categorical variables or when you want to know the most common value in a distribution.
Can you provide an example of how to describe the distribution of daily search queries per user using central tendency measures?
-The distribution of daily search queries per user can be described as normal with a mean, median, and mode all centered around a particular value, for example, 8.
What is dispersion, and how is it measured?
-Dispersion describes the spread of data in a distribution. It can be measured using variance, which is the average of the squared differences from the mean, and standard deviation, which is the square root of variance.
What is the correlation, and how is it calculated?
-Correlation describes the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables. It is calculated using the Pearson correlation formula, which involves summing the product of the differences from the means of the two variables, divided by the product of their standard deviations.
What does the normal distribution represent, and what is the significance of the 66-95-99.7 rule?
-The normal distribution represents a symmetrical distribution of data around the center, with the extremes tapered off. The 66-95-99.7 rule signifies that approximately 66% of the data falls within one standard deviation, 95% within two standard deviations, and 99.7% within three standard deviations of the mean.
What is the Central Limit Theorem, and why is it important in statistics?
-The Central Limit Theorem states that the distribution of sample means approximates a normal distribution as the sample size gets larger, regardless of the population distribution. It is important because it allows for the application of normal distribution properties to sample data, which is crucial for hypothesis testing and confidence intervals.
Can you explain the concept of hypothesis testing and its steps?
-Hypothesis testing is a statistical method to test an assumption about a population parameter. The steps include stating the null hypothesis (H0) and alternative hypothesis (H1), taking a sample, calculating the test statistic and p-value, and making a decision based on the p-value and significance level (alpha). If the p-value is less than alpha, the null hypothesis is rejected.
What is a p-value, and how does it relate to the significance level in hypothesis testing?
-A p-value is the probability of observing a sample value or more extreme given that the null hypothesis is true. It is compared to the significance level (alpha) to make a decision in hypothesis testing. If the p-value is less than alpha, the null hypothesis is rejected, indicating statistical significance.
What additional statistical concepts should one review in preparation for data science interviews, according to the video?
-Additional statistical concepts to review include distributions, Bayes theorem, ANOVA, sampling, non-parametric tests, permutation tests, confidence and credible intervals, regression modeling, non-normal distribution, and maximum likelihood.
Outlines
📊 Essential Statistics Concepts for Data Science Interviews
Dan, the founder of datant.com and a data scientist, introduces five key statistics concepts crucial for data science interviews: central tendency, dispersion, correlation, normal distribution, and hypothesis testing. He suggests that these topics are vital for entry-level data scientists or those looking to refresh their statistical foundations. Dan also recommends visiting datainq.com for interview preparation resources and coaching services tailored for data scientists. The video then delves into explaining central tendency with examples of mean, median, and mode, discussing their applications and limitations, especially in the presence of outliers.
📈 Understanding Dispersion and Correlation in Data
The script moves on to explain the concept of dispersion, focusing on variance and standard deviation as measures that quantify the spread of data in a distribution. Variance is calculated as the average of the squared differences from the mean, while standard deviation is the square root of variance, making it more interpretable. The explanation includes the importance of memorizing the variance formula for interviews. The paragraph also covers correlation, describing it as a measure of the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. Pearson correlation is introduced with a formula, and examples of different correlation strengths are provided, along with how to interpret them visually and address outliers in correlation analysis.
📚 In-Depth Look at Normal Distribution and Central Limit Theorem
The video script discusses the normal distribution, highlighting its symmetrical shape and the importance of the 66-95-99.7 rule, which describes the proportion of data within one, two, or three standard deviations from the mean. The central limit theorem is introduced, stating that the distribution of sample means will approximate a normal distribution as the sample size increases, regardless of the original population distribution. This concept is crucial for understanding confidence intervals and solving related interview problems.
🤔 Hypothesis Testing in Data Science: A Step-by-Step Guide
Hypothesis testing is the final concept covered in the script, presented as an essential tool for data scientists to evaluate claims about population parameters. The process involves setting up null and alternative hypotheses, calculating the test statistic (z-statistic in this case), determining the p-value, and making a decision based on the significance level (alpha). An example problem is given where a product manager's claim about average monthly spending on Amazon is tested using a sample mean of users. The steps to calculate the z-statistic and p-value are outlined, emphasizing the decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on the p-value compared to alpha.
🔍 Additional Statistical Concepts for Comprehensive Interview Preparation
In the concluding paragraph, Dan acknowledges that the five concepts covered do not encompass all the statistical knowledge required for data science interviews. He lists additional topics such as distributions, Bayes theorem, ANOVA, sampling, non-parametric tests, permutation tests, confidence and credible intervals, regression modeling, non-normal distributions, and maximum likelihood that should be reviewed. He also mentions upcoming videos and a statistics course to cover these concepts in more detail, encouraging viewers to stay tuned for further educational content.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Central Tendency
💡Dispersion
💡Correlation
💡Normal Distribution
💡Hypothesis Testing
💡Mean
💡Median
💡Mode
💡Variance
💡Standard Deviation
💡Significance Level (Alpha)
Highlights
Dan, the founder of datant.com, covers five essential statistics concepts for data science interviews.
Central tendency is crucial for describing the shape of a distribution using mean, median, and mode.
Mean calculates the average, median the middle value, and mode the most frequent number in a dataset.
Pros and cons of mean, median, and mode are discussed for different data scenarios.
Example problems illustrate how to describe distributions of daily search queries and Facebook usage minutes.
Dispersion is detailed through variance and standard deviation to explain data spread.
Variance formula is essential for calculating the spread from scratch in interviews.
Correlation measures the strength of linearity between two variables using Pearson correlation.
Correlation values are interpreted with guidance on their ranges for strong, no, or weak association.
Outliers' impact on correlation is discussed with solutions like IQR method and robust scaling.
Normal distribution is characterized by its symmetrical shape and the 66-95-99.7 rule.
Central Limit Theorem states that sample means form a normal distribution as sample size increases.
Hypothesis testing is introduced as a method to test assumptions about population parameters.
The four steps of hypothesis testing are outlined: hypothesis, sample data, statistical tests, and decision.
P-value calculation using z-statistics and standard normal distribution table is explained.
Significance level (alpha) determines the threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis.
A business case example demonstrates hypothesis testing with a claim about average spending on Amazon.
Additional statistical concepts for data science interviews are suggested for further review.
An upcoming statistics course is teased for comprehensive coverage of these concepts.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

A/B Testing in Data Science Interviews by a Google Data Scientist | DataInterview

Descriptive Statistics: FULL Tutorial - Mean, Median, Mode, Variance & SD (With Examples)

Probability Distributions Made Easy: Top 3 to Know for Data Science Interviews

Tutorial 1- What Is Statistics And What Are Its Types In Hindi?
Choosing a Statistical Test for Your IB Biology IA
Ace Statistics Interviews: A Data-driven Approach For Data Scientists
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: