Step by Step Gas Stoichiometry - Final Exam Review
TLDRIn this educational video, Selena Sanchez collaborates with a student to tackle gas law problems, focusing on the ideal gas law PV=nRT. The transcript outlines a step-by-step approach to solving for moles and mass of gases, emphasizing the importance of unit conversion and stoichiometry. It highlights the methodical process of identifying given variables, selecting the appropriate formula, and solving for the unknown, making complex gas law calculations more accessible. For further practice and detailed notes, viewers are directed to Melissa Mirabelle's website.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is a tutorial focusing on gas laws, specifically preparing for a final exam series part 4.
- 🔍 Selena Sanchez and the instructor are working together to review gas laws, emphasizing the importance of understanding the ideal gas law (PV=nRT) for solving problems.
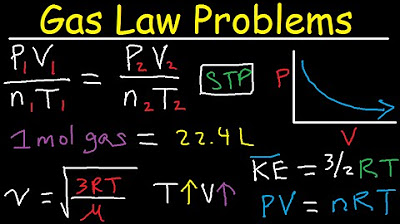
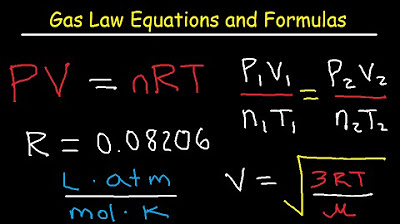
- 🔑 The ideal gas law is identified as the primary formula to use for questions involving pressure, volume, and temperature of gases.
- 📐 The importance of using correct units for calculations is stressed, specifically atmospheres for pressure, liters for volume, and Kelvin for temperature.
- 📈 The process involves converting given values into the appropriate units before applying the ideal gas law formula.
- 🔬 The tutorial demonstrates how to calculate the moles of a gas (O2 in this case) using the ideal gas law.
- 🔄 The concept of stoichiometry is introduced to relate the moles of one substance to another (from moles of O2 to moles of silver oxide).
- 📘 Molar mass is used to convert moles of a substance to grams, which is necessary for solving the problem presented.
- 📝 The script includes a step-by-step approach to solving gas law problems, starting with identifying what is given and what needs to be found.
- 🔍 The tutorial highlights the need to pay attention to which substance the given values correspond to, as it affects the formula and calculations.
- 🎯 The video script is part of a series of educational content aimed at helping students master gas laws and prepare for exams.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is understanding and applying gas laws, specifically the ideal gas law, to solve chemistry problems related to gases.
Why is the ideal gas law the primary formula discussed in the script?
-The ideal gas law is the primary formula discussed because it includes variables for pressure, volume, and temperature, which are the given values in the problems presented in the script.
What is the significance of the units used in the ideal gas law?
-The units are significant because they must be consistent with the standard units used in the ideal gas law formula, which are atmospheres for pressure, liters for volume, and Kelvin for temperature.
What is the role of stoichiometry in the script's chemistry problems?
-Stoichiometry is used to relate the moles of one substance to another in a chemical reaction, allowing the conversion from moles of one gas to moles of another or to grams of a compound.
Why is it important to identify the given values in a gas law problem?
-Identifying the given values is important because it helps determine which gas law formula to use and guides the process of solving for the unknown quantity.
What is the relationship between moles and grams in the context of the script?
-The relationship between moles and grams is established through the molar mass of a substance. The number of moles is used to calculate the mass of a substance in grams.
How does the script differentiate between diatomic molecules like O2 and N2?
-The script indicates that diatomic molecules like O2 and N2 exist in pairs, meaning that when they are part of a chemical formula or reaction, they are represented with a subscript of 2.
What is the purpose of the detailed notes provided by Melissa Mirabelle?
-The purpose of the detailed notes is to offer a comprehensive guide on gas laws, including step-by-step solutions to problems, to help students better understand and practice the concepts discussed in the script.
How does the script handle the conversion of units for pressure?
-The script converts pressure from millimeters of mercury to atmospheres by using the conversion factor that one atmosphere is equal to 760 millimeters of mercury.
What is the final step in solving the gas law problems presented in the script?
-The final step in solving the gas law problems is to use the calculated moles of a substance and its molar mass to find the mass in grams, which is the quantity typically being sought in the problems.
Outlines
🎓 Preparing for Final Exam Series: Gas Laws and Stoichiometry
In this section, the focus is on the collaboration between YouTuber Selena Sanchez and the presenter in preparing for a final exam series. It covers a detailed explanation of gas laws and stoichiometry, including the importance of understanding molar mass and mole ratios. The Ideal Gas Law (PV = nRT) is introduced as a crucial formula for solving problems related to pressure, volume, and temperature. The method of identifying given values and selecting the appropriate formula based on these values is emphasized.
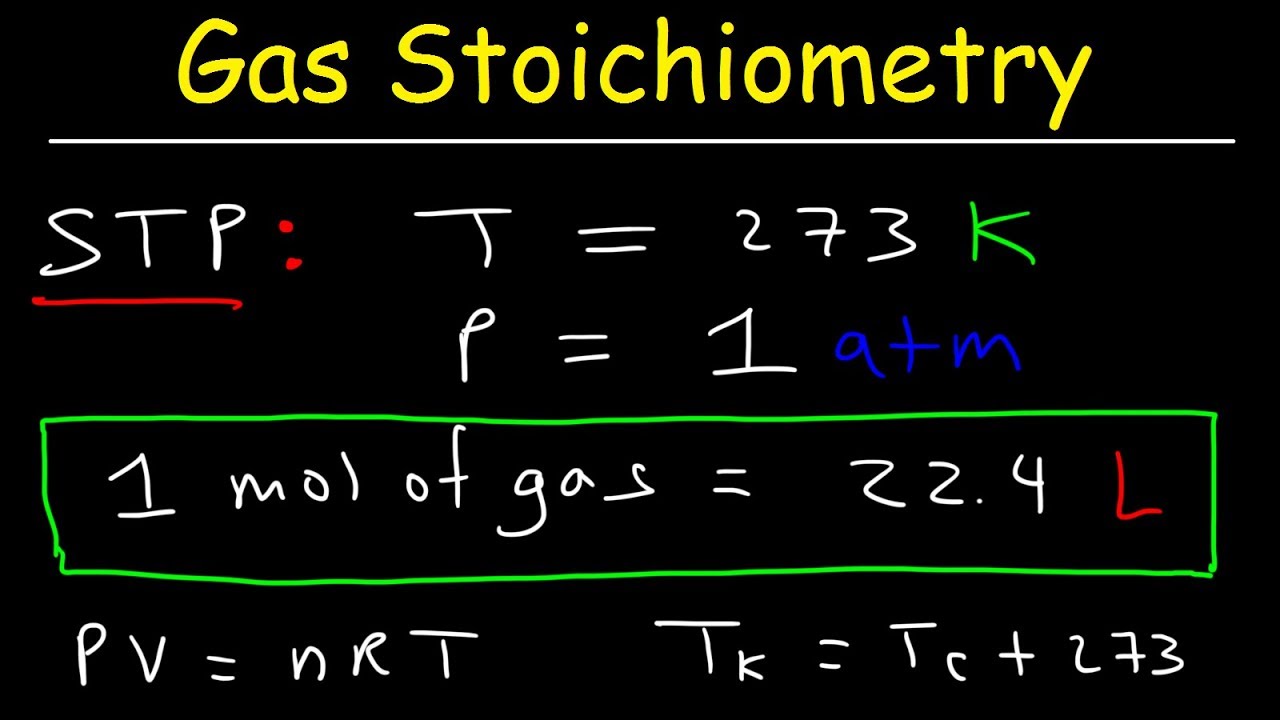
🔍 Converting Units for the Ideal Gas Law
This paragraph explains the necessary conversions for applying the Ideal Gas Law correctly. It details how to convert pressure to atmospheres and volume to liters, ensuring that all units align with the requirements of the Ideal Gas Law. The process of solving for moles of oxygen (O2) and subsequently using stoichiometry to find the mass of silver oxide (Ag2O) is described. The importance of using the correct molar masses and the steps involved in these conversions are highlighted.
🧪 Applying the Ideal Gas Law to Practice Problems
Here, the application of the Ideal Gas Law to solve practice problems is demonstrated. The paragraph walks through a sample problem involving nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitrogen (N2), illustrating how to convert grams to moles and solve for volume using the Ideal Gas Law. The importance of recognizing diatomic molecules and correctly associating given values with the respective compounds is stressed. The method of manipulating formulas to find the desired values is reiterated, providing a practical example for learners to follow.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Gas Laws
💡Ideal Gas Law
💡Molar Mass
💡Stoichiometry
💡Moles
💡Milliliters (mL)
💡Pressure
💡Temperature
💡Volume
💡Conversion Factors
💡Gas Constant (R)
Highlights
Introduction to preparing for a final exam series with a focus on gas laws and stoichiometry.
Availability of detailed notes on Melissa Mirabelle's website for a refresher on gas laws.
The importance of understanding conversion factors and molar mass in stoichiometry.
Explanation of the typical use of molar mass and multiple ratios in gas law problems.
A step-by-step approach to solving a problem involving the mass of silver oxide required to form oxygen gas.
The significance of recognizing the given variables in a problem to determine the appropriate gas law formula.
The identification of the ideal gas law (PV=nRT) as the primary formula for solving gas law problems.
Clarification on why other gas laws like Boyle's or Charles' Law are not applicable in certain scenarios.
The necessity of converting units to the proper format required by the ideal gas law.
A demonstration of converting millimeters mercury to atmospheres for pressure.
The process of converting volume from milliliters to liters for use in the ideal gas law.
The calculation of moles of oxygen gas using the ideal gas law with the given conditions.
The use of stoichiometry to relate moles of oxygen to moles of silver oxide.
The application of molar mass to convert moles of silver oxide to grams.
A reminder to pay attention to which molecule or compound the given units correspond to in a problem.
The distinction between the ideal gas law and the combined gas law in different problem contexts.
A practical example of converting grams of nitrogen gas to moles of nitrogen dioxide for a different problem.
The final step of using the ideal gas law to find the volume of a gas given its mass, pressure, and temperature.
Encouragement to practice gas law problems and access to more examples in detailed notes.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: