TEAS 7 Chemistry: Introduction to Atoms
TLDRThis educational video aims to simplify the basics of atoms and their structure, particularly for those preparing for the TEAS exam. It clarifies common misconceptions found in prep materials, introducing atoms as tiny particles constituting all matter and existing in various types known as elements. The script delves into the atom's subatomic particles—electrons, protons, and neutrons—detailing their charges and masses. It emphasizes the importance of valence electrons for chemical bonding and dismisses the complexity of electron orbitals, focusing instead on the traditional model of electron shells. The video concludes with practice questions to reinforce the concepts covered.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The video aims to explain the basics of atoms and their structure, particularly for those preparing for the TEAS exam.
- 🔬 Atoms are the tiny particles that make up all matter, and they can be arranged in groups called molecules or in neat grids.
- 📚 Different types of atoms are referred to as elements, and there are over a hundred different elements in nature.
- 🧬 If observed closely, atoms have a complex structure containing subatomic particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons.
- 🚀 Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge, with protons and neutrons residing in the nucleus.
- ⚖️ The mass of a proton or neutron is approximately 1 atomic mass unit (AMU), while electrons are so light they are considered to have zero AMU.
- 🌀 Electrons are constantly moving and are organized into energy levels or shells, with the outermost shell known as the valence shell.
- 🔗 Valence electrons are crucial for chemical bonding, which is the process of atoms attaching to each other.
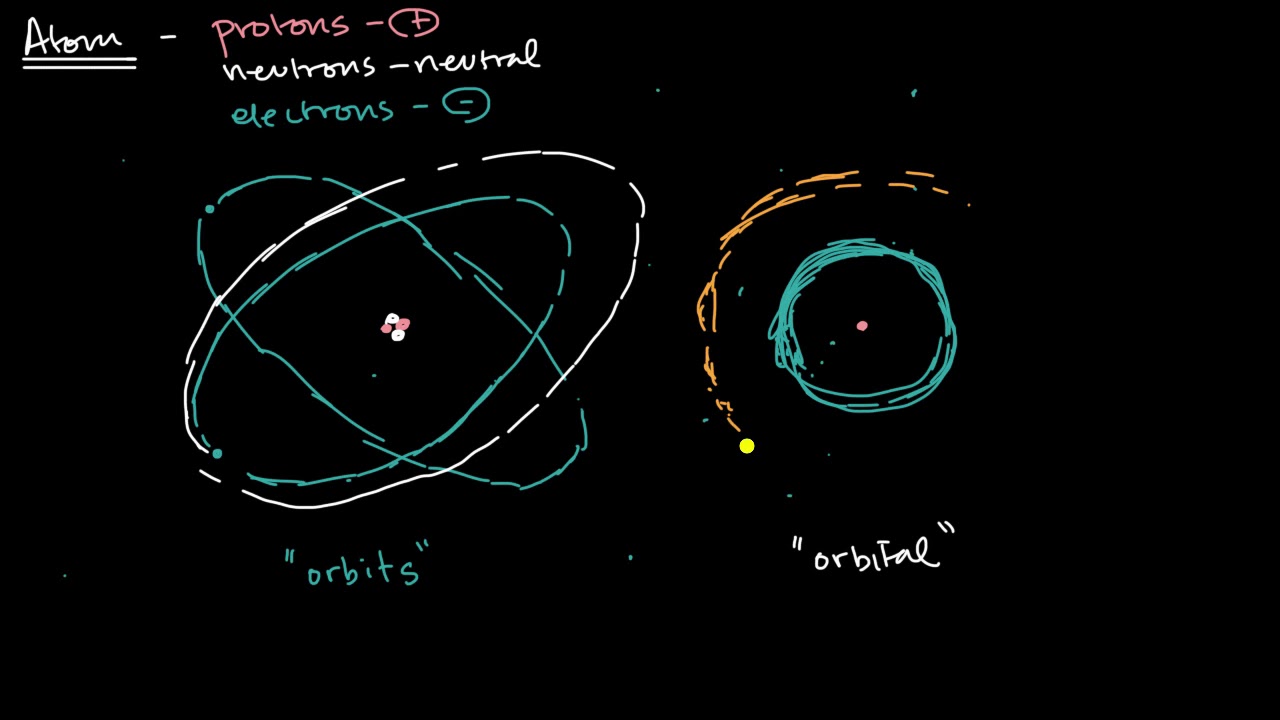
- 🤯 The script addresses the confusion caused by traditional explanations of electron behavior, suggesting they move in random patterns rather than fixed orbits.
- 🌀 Modern understanding of electron behavior involves the concept of orbitals and electron clouds, represented by letters like s, p, d, and f, but this complexity is not required for the TEAS exam.
- 📝 The video emphasizes the importance of memorizing the basic characteristics of subatomic particles for the TEAS exam.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The video focuses on explaining the basics of atoms and their structure, specifically targeting individuals preparing for the TEAS exam.
Why did the presenter create this video?
-The presenter created the video because they found many TEAS prep materials confusing and impossible to understand, and they wanted to teach the subject in a clear and understandable way.
What are atoms?
-Atoms are tiny particles that make up everything. If you could zoom in infinitely, you would see that all objects are made of these tiny particles.
What are the different types of atoms called?
-Different types of atoms are called elements. Examples given in the video are copper, hydrogen, oxygen, sodium, and chlorine.
What are subatomic particles?
-Subatomic particles are smaller than atoms and make up atoms. The three main types are electrons, protons, and neutrons.
What is the charge of a proton?
-A proton has a positive one electrical charge.
What is the charge of a neutron?
-A neutron is neutral, meaning it has a zero electrical charge.
What is the mass of a proton and a neutron in atomic mass units (AMU)?
-Both a proton and a neutron have a mass of 1 AMU.
What is the charge of an electron?
-An electron has a negative one electrical charge.
What is the mass of an electron in AMU?
-The mass of an electron is so small that it is essentially considered to be zero AMU.
Where are protons and neutrons located within an atom?
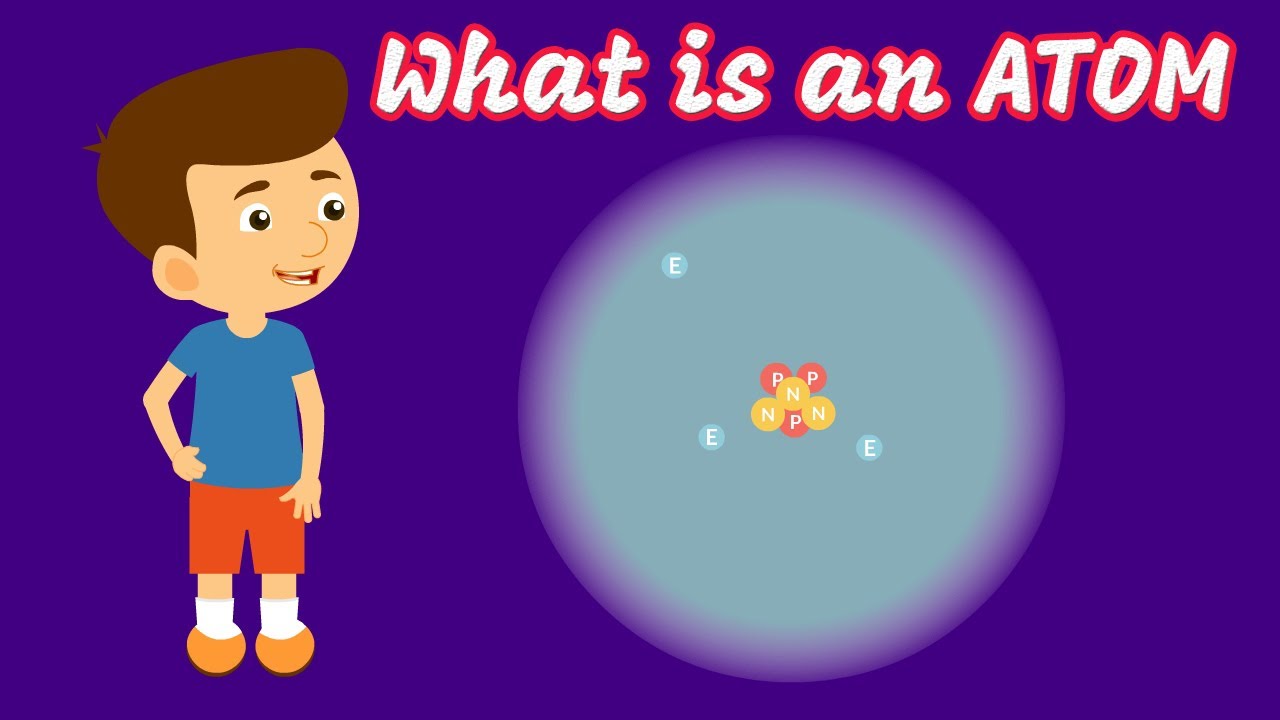
-Protons and neutrons are located in the center of the atom, in the nucleus.
What is the term for the outermost energy level of electrons in an atom?
-The outermost energy level is called the valence level or valence shell.
What are valence electrons?
-Valence electrons are the electrons in the valence level, which are crucial for chemical bonding.
Why might the traditional depiction of electrons as orbiting in circles be outdated?
-The traditional depiction is outdated because scientists now understand that electrons move randomly and exist in 3D shapes called orbitals, often referred to as electron clouds.
What is the significance of the valence electrons in chemical bonding?
-Valence electrons are significant in chemical bonding because they are the ones that interact with other atoms to form chemical bonds.
How many valence electrons does a carbon atom have?
-A carbon atom has four valence electrons.
What is the purpose of the practice questions in the video?
-The practice questions are designed to reinforce the understanding of the concepts taught in the video and to prepare viewers for the types of questions they might encounter on the TEAS exam.
Outlines
🔬 Introduction to Atoms and Structure
This paragraph introduces the topic of atoms and their structure, specifically tailored for individuals preparing for the TEAS exam. The speaker aims to clarify common confusions in chemistry materials and offers a short course with helpful resources. Atoms are described as the fundamental particles that constitute all matter, organized in molecules or in a grid pattern in solids. Different types of atoms, known as elements, are highlighted, with examples like copper, hydrogen, oxygen, sodium, and chlorine. The paragraph also delves into the subatomic structure of atoms, mentioning subatomic particles such as electrons, protons, and neutrons, which will be further explored in the video.
🌐 Subatomic Particles and Their Properties
The second paragraph focuses on the characteristics of subatomic particles within an atom. Protons and neutrons, which reside in the nucleus, are detailed with their respective electrical charges and masses. Protons carry a positive charge and a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (AMU), while neutrons are neutral and also have a mass of 1 AMU. Electrons, which are much lighter and can be considered to have negligible mass, are found orbiting the nucleus and carry a negative charge. The paragraph also includes a TEAS practice question to reinforce the understanding of subatomic particles and their properties.
🌀 Electron Organization and Valence Electrons
This section discusses the organization of electrons outside the nucleus, highlighting their constant motion and arrangement into energy levels or shells. The outermost energy level, known as the valence level, is emphasized as it contains valence electrons, which play a crucial role in chemical bonding. The paragraph addresses common confusions regarding electron depictions and clarifies that while modern scientific understanding suggests electrons move in 3D orbitals, the TEAS exam and this video will stick to the traditional model of circular energy levels for simplicity and relevance to the exam.
📚 Review and Practice Questions on Atomic Structure
The final paragraph provides a review of the key concepts covered in the lesson, including the definition of atoms, the structure of atoms with protons, neutrons, and electrons, and the significance of valence electrons. It also presents two practice TEAS questions to test the viewer's understanding. The first question involves identifying subatomic particles in a model of an oxygen atom, while the second asks for the number of valence electrons in a different atom diagram. The paragraph concludes by encouraging viewers to check the video description for a link to a full course and expresses the speaker's eagerness to assist in exam preparation.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Atom
💡Subatomic Particles
💡Electron
💡Proton
💡Neutron
💡Nucleus
💡Valence Electrons
💡Energy Levels
💡Atomic Mass Unit (AMU)
💡TEAS Exam
💡Chemical Bonding
Highlights
The video aims to clarify the basics of atoms and their structure for those preparing for the TEAS exam.
The presenter offers a short course and resources for a clearer understanding of atoms.
Atoms are the tiny particles that constitute all matter, sometimes arranged in molecules or neat grids.
Different types of atoms are categorized as elements, with over a hundred existing in nature.
Subatomic particles—electrons, protons, and neutrons—make up the structure of an atom.
Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom, with electrons orbiting outside.
Protons have a +1 charge and a mass of 1 AMU, while neutrons are neutral with the same mass.
Electrons have a -1 charge and are considered to have negligible mass.
Electrons are organized into energy levels or shells, with the outermost being the valence shell.
Valence electrons are crucial for chemical bonding between atoms.
Outdated models of electron depiction are simplified for TEAS exam purposes.
Modern understanding of electron behavior involves random movement in 3D orbitals.
The video reassures viewers that complex electron orbitals are not required for the TEAS exam.
A TEAS practice question is provided to test knowledge of subatomic particles.
The video concludes with a review of the lesson and two practice questions.
The presenter encourages viewers to check the description for a link to the full course.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

(a) Protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of their relative charges and masses

Atomic Structure full topic
Shells, subshells, and orbitals | Atomic structure and properties | AP Chemistry | Khan Academy
What is an Atom? - Structure of an Atom - Atom video for kids

Inside Atoms: The Proton Numbers

Valence Electrons and the Periodic Table
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: