Consumer and Producer Surplus (KristaKingMath)
TLDRThis educational video from integralcalc.com explains how to calculate consumer and producer surplus by first determining the market equilibrium quantity and price. The presenter guides viewers through solving a quadratic equation to find the equilibrium quantity (q=20), then uses it to find the equilibrium price (p=15). The script continues with calculating consumer surplus through integration of the demand function and subtracting the area under the equilibrium price, resulting in a consumer surplus of 80. Producer surplus is found by subtracting the integral of the supply function from the total revenue, yielding a producer surplus of 160. The video is a comprehensive guide to understanding these economic concepts.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is about finding consumer and producer surplus, starting with determining the equilibrium quantity and price.
- 🔍 To find the equilibrium, the demand and supply curves are set equal to each other, leading to a quadratic equation in terms of quantity (q).
- 🧩 The equation is simplified by moving all terms to one side and factoring, aiming to solve for the equilibrium quantity (q).
- 🔢 The quadratic equation is made easier by multiplying through by 100 to eliminate decimals, resulting in a new equation: 3q^2 + 40q - 2000 = 0.
- ❌ An initial solution of q = -100/3 is discarded as quantity cannot be negative, leaving q = 20 as the feasible equilibrium quantity.
- 💡 The equilibrium price is found by substituting the equilibrium quantity back into either the demand or supply equation, resulting in a price of 15.
- 🛒 Consumer surplus is calculated by integrating the demand function from 0 to the equilibrium quantity and subtracting the area equivalent to the equilibrium price times quantity.
- 📉 The consumer surplus calculation involves integrating the demand function and evaluating it from 0 to 20, resulting in a consumer surplus of 80.
- 📈 Producer surplus is determined by multiplying the equilibrium quantity by the equilibrium price and subtracting the integral of the supply function from 0 to 20.
- 📊 The integral of the supply function is evaluated over the same range, and when subtracted from the product of equilibrium price and quantity, it yields a producer surplus of 160.
- 👋 The video concludes with a summary of how to find equilibrium quantity and price, and then use these values to calculate consumer and producer surplus.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic discussed in the video is the concept of consumer and producer surplus, including how to calculate them given a demand and supply scenario.
Why is it necessary to find the equilibrium quantity and price before calculating consumer and producer surplus?
-It is necessary to find the equilibrium quantity and price first because they represent the market-clearing point where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied, which is the basis for calculating surpluses.
What is the demand curve equation given in the script?
-The demand curve equation given in the script is -0.4q + 23.
What is the supply curve equation mentioned in the script?
-The supply curve equation mentioned in the script is 0.03q^2 + 3.
How does the script suggest solving for the equilibrium quantity?
-The script suggests solving for the equilibrium quantity by setting the demand and supply curves equal to each other, moving all terms to one side to set the equation to zero, and then factoring.
What is the equilibrium quantity found in the script?
-The equilibrium quantity found in the script is 20 units.
How is the equilibrium price determined in the video?
-The equilibrium price is determined by plugging the equilibrium quantity back into either the demand or supply equation and solving for the price.
What is the equilibrium price found in the script?
-The equilibrium price found in the script is 15.
What formula is used to calculate consumer surplus in the video?
-The formula used to calculate consumer surplus in the video involves integrating the demand function from zero to the equilibrium quantity and then subtracting the product of the equilibrium quantity and price.
What is the consumer surplus calculated in the video?
-The consumer surplus calculated in the video is 80.
How is producer surplus calculated in the video?
-Producer surplus is calculated by multiplying the equilibrium quantity by the equilibrium price and then subtracting the integral of the supply curve from zero to the equilibrium quantity.
What is the producer surplus calculated in the video?
-The producer surplus calculated in the video is 160.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Consumer and Producer Surplus
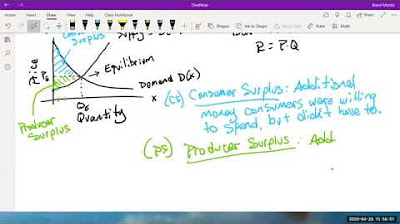
This paragraph introduces the topic of consumer and producer surplus, explaining the necessity to first determine the market equilibrium by setting the demand and supply curves equal to each other. The process involves solving for the equilibrium quantity (q) by rearranging the equations and factoring, which in this case yields an infeasible negative solution and a feasible solution of q = 20. The equilibrium price is then calculated by substituting q back into the demand equation, resulting in a price of $15. The paragraph sets the stage for further analysis of consumer and producer surplus using these equilibrium values.
💰 Calculating Consumer and Producer Surplus
The second paragraph delves into the actual calculation of consumer and producer surplus based on the previously determined equilibrium quantity and price. Consumer surplus is calculated by integrating the demand function from zero to the equilibrium quantity and then subtracting the area under the demand curve, which represents the consumer's willingness to pay. The integral calculation leads to a consumer surplus of $80. Producer surplus is found by multiplying the equilibrium quantity by the equilibrium price and subtracting the integral of the supply curve from zero to the equilibrium quantity. The calculation results in a producer surplus of $160. The paragraph concludes with a summary of how to find equilibrium quantity and price and subsequently calculate consumer and producer surplus, providing a clear guide for viewers.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Consumer Surplus
💡Producer Surplus
💡Equilibrium Quantity
💡Equilibrium Price
💡Demand Curve
💡Supply Curve
💡Integration
💡Factoring
💡Definite Integral
💡Exponent
💡Roots of an Equation
Highlights
Introduction to the topic of consumer and producer surplus.
The necessity of finding equilibrium quantity and price before calculating surplus.
Setting demand and supply curves equal to find equilibrium.
Equation setup for equilibrium quantity by equating demand and supply functions.
Method of solving for equilibrium quantity by rearranging and factoring the equation.
Multiplication by 100 to simplify the equation and eliminate decimals.
Factoring the quadratic equation to find possible values for q.
Determining the feasible solution for equilibrium quantity, q = 20, by rejecting negative values.
Calculating the equilibrium price by substituting the equilibrium quantity into the demand equation.
Result of equilibrium price calculation, P = 15.
Transition to calculating consumer surplus using the equilibrium values.
Integration method for calculating consumer surplus with the demand function.
Subtraction of equilibrium quantity times price from the integral result to find consumer surplus.
Final calculation of consumer surplus, resulting in a value of 80.
Introduction to calculating producer surplus using equilibrium price and quantity.
Integration of the supply function to find producer surplus.
Final calculation of producer surplus, resulting in a value of 160.
Summary of the process for finding equilibrium quantity, price, consumer surplus, and producer surplus.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Consumers' Surplus Producers' Surplus from given Demand and Supply functions

consumer surplus and producer surplus

Consumer Surplus (CS) and Producer Surplus (PS) Example

Business Calculus: Producer and Consumer Surplus

Consumers' Surplus , Producers' Surplus & Total Surplus from demand & supply Functions #PS
Math 11 - Section 5.1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: