Weak Interaction: The Four Fundamental Forces of Physics #2
TLDRThe video script delves into the weak force, one of the four fundamental forces of physics, which operates at extremely short distances. It is crucial for processes like the sun's energy production, the existence of certain elements, and carbon-14 dating. The weak force can change a particle's identity by altering quark 'flavors', with up and down quarks being the most common. Protons and neutrons are composed of these quarks, and the weak force can transform a neutron into a proton, as demonstrated through the decay of a carbon-14 atom into nitrogen-14. This force is conveyed through W and Z bosons and is integral to our understanding of particle physics.
Takeaways
- 🌌 The weak force is one of the four fundamental forces of physics and acts over very short distances.
- ☀️ Without the weak force, the sun would not emit light and elements like radium or plutonium would not exist.
- 🔬 The weak force is essential for processes like carbon-14 dating, which relies on particle decay.
- 🧬 The weak force can change the identity of particles, such as turning a proton into a neutron, by altering quark 'flavor'.
- 🤹♂️ Quarks come in six 'flavors': up, down, strange, charm, top, and bottom, with up and down quarks being the most common.
- 🔄 The weak force, like the strong force, acts on quarks, but it changes their flavor rather than their color.
- 🌀 Neutrons are composed of one up quark and two down quarks, while protons consist of two up quarks and one down quark.
- 🤝 The weak force can also interact with leptons, including electrons and neutrinos, in addition to quarks.
- 🚀 The weak force operates through the exchange of force carriers, specifically the W and Z bosons.
- 🌀 A neutrino passing by can cause a neutron to decay into a proton via the emission of a positively-charged W boson.
- 📅 Carbon-14 dating is made possible by the weak force, which allows carbon-14 atoms to decay into nitrogen-14 atoms.
Q & A
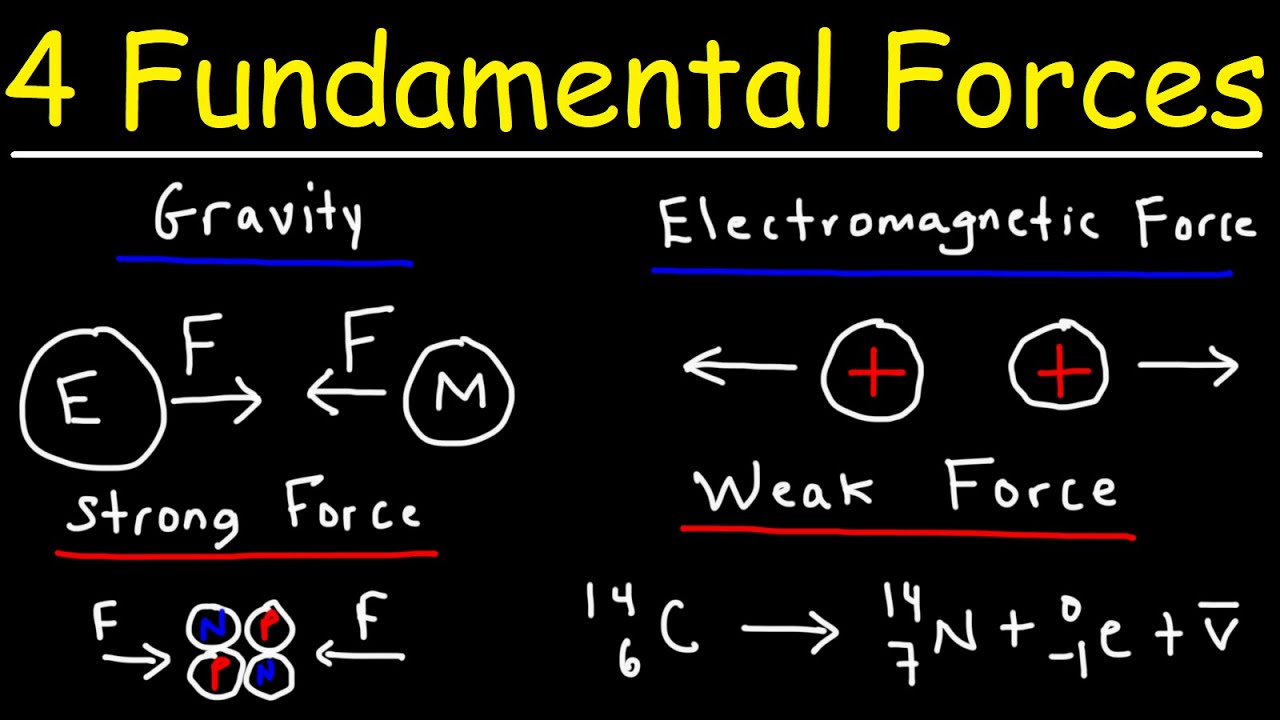
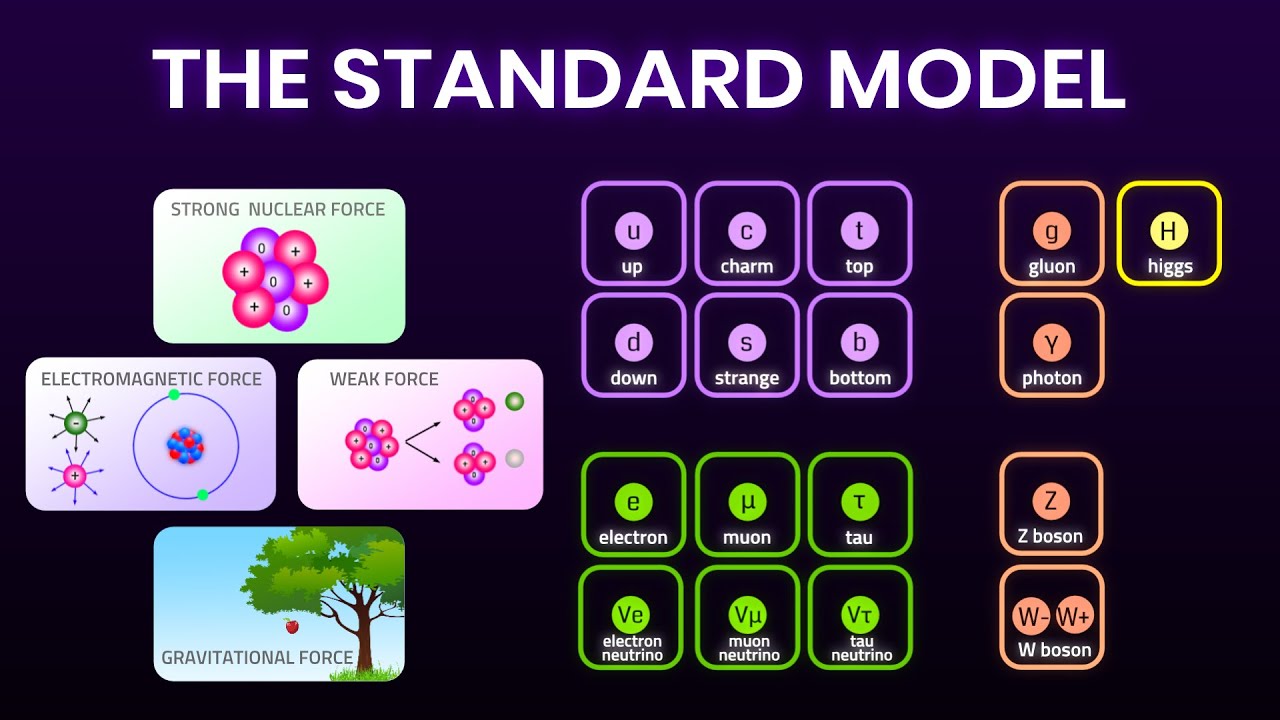
What are the four fundamental forces of physics?
-The four fundamental forces of physics are the gravitational force, electromagnetic force, strong nuclear force, and weak nuclear force.
Why is the weak force considered 'weak'?
-The weak force is considered 'weak' because it has a very short range of influence, operating only within about 0.1% of the diameter of a proton.
What are the roles of the weak force in the universe?
-The weak force is responsible for processes such as beta decay in atomic nuclei, which is essential for the sun to shine and for the creation of elements like radium and plutonium. It also enables carbon-14 dating.
How does the weak force interact with quarks?
-The weak force interacts with quarks by changing their 'flavor' rather than their color. It can transform one type of quark into another, which can change the identity of a particle, such as turning a neutron into a proton.
What are the six flavors of quarks?
-The six flavors of quarks are up, down, strange, charm, top, and bottom.
What is the composition of a neutron in terms of quarks?
-A neutron is composed of one up quark and two down quarks.
What is the composition of a proton in terms of quarks?
-A proton is composed of two up quarks and one down quark.
What are the force carriers of the weak force?
-The weak force has two force carriers: the W bosons, which can be positively or negatively charged, and the Z bosons, which have no charge.
How does the weak force facilitate the change of a neutron into a proton?
-The weak force can cause a down quark within a neutron to change into an up quark through the exchange of a positively-charged W boson, thus converting the neutron into a proton.
Can you explain the process of carbon-14 dating in relation to the weak force?
-Carbon-14 dating relies on the weak force to facilitate the decay of carbon-14 atoms into nitrogen-14 atoms. This decay process changes the composition of the nucleus, allowing scientists to measure the amount of remaining carbon-14 to determine the age of an object.
What happens when a neutrino is involved in a weak interaction?
-When a neutrino is involved in a weak interaction, it can emit a positively-charged W boson, which changes a down quark into an up quark, and the neutrino itself becomes an electron after losing the positive charge.
Outlines
🌌 The Weak Nuclear Force: Universe's Particle Transformer
This paragraph delves into the weak nuclear force, one of the four fundamental forces of physics, which operates at an incredibly small scale. The weak force is crucial for processes like the sun's nuclear fusion, the existence of certain radioactive elements, and carbon-14 dating. It enables quarks, the building blocks of protons and neutrons, to change their 'flavor,' effectively transforming one type of particle into another. The weak force can also interact with leptons, including electrons and neutrinos. The force is mediated by force carriers, specifically the W and Z bosons, which facilitate the change in particle identity. An example of this is the transformation of a neutron into a proton through the interaction with a neutrino, involving the exchange of a positively-charged W boson. This process is key to carbon-14 dating, illustrating the weak force's significant role in particle decay and the evolution of elements.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Fundamental Forces
💡Weak Force
💡Quarks
💡Flavor Change
💡Neutron
💡Proton
💡Leptons
💡Force Carriers
💡W Bosons
💡Z Bosons
💡Carbon-14 Dating
Highlights
The weak force acts over very short distances and is crucial for processes like the sun's energy production and carbon-14 dating.
Without the weak force, elements like radium and plutonium would not exist.
Quarks, a fundamental component of protons and neutrons, can change their 'flavor' due to the weak force.
There are six types of quarks: up, down, strange, charm, top, and bottom, with up and down quarks being the most common.
Protons consist of two up quarks and one down quark, while neutrons are made of one up quark and two down quarks.
The weak force can transform a proton into a neutron by changing the flavor of a quark within it.
Leptons, including electrons and neutrinos, also interact with the weak force.
The weak force involves the exchange of force carriers, specifically W and Z bosons.
W bosons can be positively or negatively charged, while Z bosons are neutral.
A neutrino passing by can cause a neutron to decay into a proton through weak interaction.
The weak force operates within an extremely short range, approximately 0.1% of a proton's diameter.
A positively-charged W boson can change a down quark into an up quark, altering the identity of a particle.
The change in quark composition can transform one element into another, such as carbon-14 into nitrogen-14.
Carbon-14 dating relies on the weak force-induced decay of carbon-14 atoms into nitrogen-14 atoms.
The weak force is essential for understanding fundamental particle interactions and the composition of elements.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: