Distance Speed Time Word Problem Time to Overtake
TLDRThe script presents a problem-solving approach to a distance, speed, and time scenario involving two characters, Luci and Dave. Luci departs from Nagre at a speed of 80 km/h, while Dave starts an hour later at 100 km/h. The challenge is to determine how far from Nagre Dave overtakes Luci. The solution involves understanding the relationship between distance, speed, and time, which is illustrated through a triangle representing the formula D = S * T (where D is distance, S is speed, and T is time). The problem is then translated into a table format to organize the variables and units. By setting up an equation based on the equal distances covered by both at the point of overtaking, the script guides through solving for the time it takes for Dave to catch up to Luci. The final answer is obtained by multiplying the time by the speed, revealing that Dave overtakes Luci after 400 kilometers from Nagre. The summary emphasizes the importance of understanding the basic relationship between the three quantities and the step-by-step method to translate the problem into a solvable equation.
Takeaways
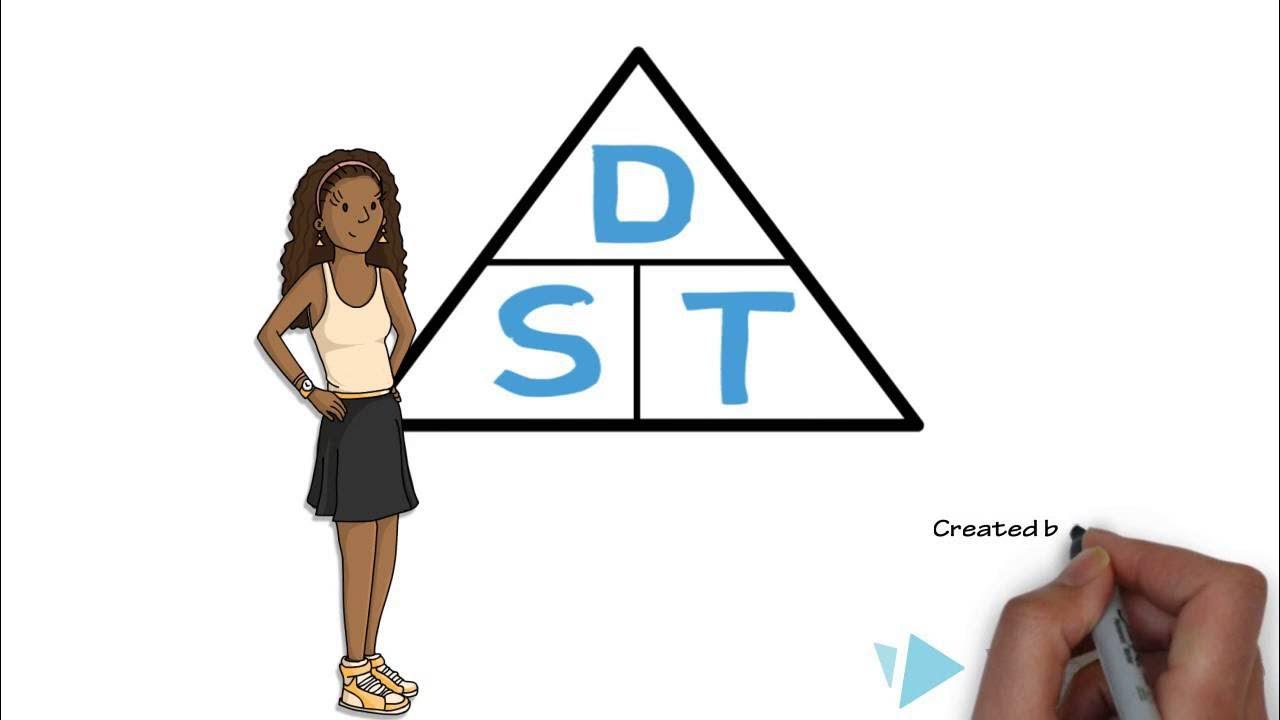
- 📐 **Relation Triangle**: The relationship between distance (D), speed (S), and time (T) is fundamental and can be represented as D = S * T, S = D / T, and T = D / S.
- 🚗 **Initial Conditions**: Lucy starts driving from Nagre at 80 km/h, while Dave starts one hour later from the same point at 100 km/h.
- ⏱️ **Time Consideration**: Dave's driving time is T - 1 hours, given he starts one hour after Lucy, where T is Lucy's driving time.
- 🔍 **Equal Distance for Overtaking**: When Dave overtakes Lucy, they have both covered the same distance from Nagre.
- 💡 **Setting Up the Equation**: The equation based on the distance covered by both Lucy and Dave at the time of overtaking is 100 * (T - 1) = 80 * T.
- 🧮 **Solving the Equation**: By solving the equation, we find that Dave overtakes Lucy after 5 hours of driving.
- 📏 **Calculating Distance Overtaken**: The distance from Nagre where Dave overtakes Lucy is found by multiplying Lucy's speed (80 km/h) by the time (5 hours), which equals 400 kilometers.
- 🔢 **Using Variables**: It's suggested to use a single variable (T) for both Lucy and Dave's driving times for simplicity, with Dave's time expressed as T - 1.
- 📈 **Tabular Representation**: Information is more digestible when presented in a table format, listing D, S, and T with their respective units.
- 📝 **Translating Word Problems**: Translate the given word problem into mathematical expressions and variables to set up the equation.
- 🔑 **Key Steps**: The steps to solve such problems include understanding the relation between D, S, and T, translating the problem into a table or equation, solving the equation, and interpreting the answer in the context of the problem.
- 📚 **Following the Process**: Following the outlined steps ensures a clear and structured approach to solving distance, speed, and time problems.
Q & A
What is the fundamental relationship between distance, speed, and time?
-The fundamental relationship between distance, speed, and time is represented by the formula: distance (D) equals speed (S) multiplied by time (T), speed equals distance divided by time, and time equals distance divided by speed.
How does the table format help in solving distance, speed, and time problems?
-The table format helps by organizing the given information into a structured layout, making it easier to visualize the relationship between the variables and to translate the problem into mathematical equations.
What is the speed at which Lucy drove from Nagre?
-Lucy drove from Nagre at a speed of 80 kilometers per hour (km/h).
How much later did Dave start driving from Nagre compared to Lucy?
-Dave started driving from Nagre one hour later than Lucy.
At what speed did Dave drive along the same road after starting one hour later?
-Dave drove along the same road at a speed of 100 kilometers per hour (km/h) after starting one hour later.
How can you represent the time Lucy and Dave spent driving in terms of a variable?
-Lucy's driving time can be represented as T hours, and Dave's driving time, since he started one hour later, can be represented as T - 1 hours.
What is the condition that must be met for Dave to overtake Lucy?
-The condition that must be met for Dave to overtake Lucy is that both must have covered the same distance from Nagre at the time of overtaking.
What is the equation that represents the distance covered by Lucy and Dave at the time of overtaking?
-The equation representing the distance covered by both Lucy and Dave at the time of overtaking is 100 * (T - 1) = 80 * T.
How many hours did it take for Dave to overtake Lucy?
-It took Dave 5 hours to overtake Lucy.
How far from Nagre did Dave overtake Lucy?
-Dave overtook Lucy 400 kilometers from Nagre.
What is the general approach to solving problems involving distance, speed, and time?
-The general approach involves understanding the relationship between distance, speed, and time, translating the problem into a table or equation form, forming an equation based on the given conditions, and solving the equation to find the answer.
What is the key to solving the problem presented in the script?
-The key to solving the problem is setting up the correct equation based on the distances covered by Lucy and Dave at the time of overtaking and solving for the unknown variable, which in this case is the time (T).
Outlines
🚗 Understanding Distance-Speed-Time Relationship
This paragraph introduces the fundamental concepts of distance, speed, and time in relation to solving problems involving motion. The presenter uses a triangle to illustrate the relationship between these three quantities, emphasizing that distance (D) is equal to speed (S) times time (T), speed is distance divided by time, and time is distance divided by speed. A table is proposed to organize the information clearly, with columns for distance, speed, and time. The problem presented involves Lucy driving from Nagre at 80 km/h and Dave starting one hour later at 100 km/h. The goal is to determine how far from Nagre Dave overtakes Lucy. The paragraph concludes by setting up the equation for the distances covered by both individuals at the point of overtaking.
🔍 Solving the Overtaking Problem
Building on the previous paragraph, this section focuses on solving the problem of Dave overtaking Lucy. The presenter translates the word problem into an equation, setting up the scenario where the distances covered by both Lucy and Dave are equal at the point of overtaking. The equation formed is 100(t - 1) = 80t, representing the respective speeds and times for each individual. By solving this equation, the presenter finds that Dave will overtake Lucy after 5 hours of travel. To find the distance from Nagre where the overtaking occurs, the presenter uses the speed and time for Lucy (80 km/h for 5 hours), resulting in a distance of 400 kilometers. The paragraph concludes with a summary of the steps to follow when solving distance-speed-time problems and a reminder to use the relationship between distance, speed, and time effectively.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Distance
💡Speed
💡Time
💡Relation
💡Table
💡Variable
💡Equation
💡Overtake
💡Units
💡Constants
💡Solve
Highlights
The problem involves solving a bullet problem with distance, speed, and time.
Lucy and Dave start from the same point, Nagre, at different times and speeds.
Lucy drives at 80 km/h, and Dave starts one hour later at 100 km/h.
The relation between distance, speed, and time is represented by a triangle for easy understanding.
Distance (D) is equal to speed multiplied by time, speed is equal to distance divided by time, and time is equal to distance divided by speed.
A table format is used to organize and understand the information better.
Lucy's speed is given as 80 km/h, and Dave's speed is 100 km/h.
Dave leaves one hour after Lucy, which affects the calculation of their respective times.
To find out how far from Nagre Dave overtakes Lucy, we need to equate the distances they have covered.
The distance covered by Lucy is 80T, and by Dave is 100(t-1), where T is the time in hours.
By setting up an equation with the distances, we can solve for the time when Dave overtakes Lucy.
Solving the equation 100(t-1) = 80T gives us the time T when the overtaking occurs.
After solving the equation, it is determined that Dave overtakes Lucy after 5 hours.
The distance from Nagre where Dave overtakes Lucy is calculated by multiplying the time (5 hours) with Lucy's speed (80 km/h).
Dave overtakes Lucy after 400 kilometers from Nagre.
The steps to solve such problems include understanding the relation between distance, speed, and time, translating data into a table, forming an equation, and solving it.
The method simplifies the process of solving complex distance, speed, and time problems.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: