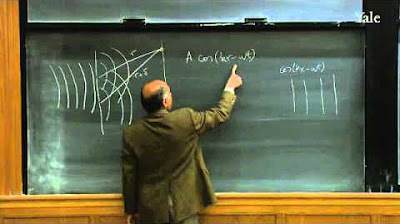Diffraction: Why Does It Happen? (Physics Explained for Beginners)
TLDRThe video script offers an engaging exploration into the phenomenon of wave diffraction, particularly focusing on the diffraction of light waves. It begins by defining diffraction as the bending of waves as they pass through a slit or around an object, using the example of a plane wave of light encountering a material with a gap. The presenter introduces Huygens' principle, which conceptualizes every point on a wavefront as a source of secondary waves that propagate spherically. These secondary waves interfere with each other, contributing to the formation of the resultant wave. The script then delves into the concept of wave interference, explaining how the resultant wave is formed by the superposition of two or more waves. The video also discusses the limitations of Huygens' principle, such as the incorrect prediction of backward wave propagation, and how Fresnel's modifications, including the obliquity factor and phase adjustments, improved the model to align with real-world observations. The presenter concludes by inviting viewers to engage with the content, seek clarification on complex topics, and subscribe for more physics-related content.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Diffraction is the bending of waves as they pass through a slit or around an object, and it's a fundamental behavior of waves alongside reflection and refraction.
- 📊 Huygens' principle suggests that every point on a wavefront acts as a source of secondary waves, which move away in all directions and interfere with each other to form the new wave shape.
- 🌀 When secondary waves from different points on the wavefront interfere, they can create a larger peak (constructive interference) or cancel each other out (destructive interference), leading to the observed wave pattern.
- 📉 The original Huygens' principle does not account for backward wave propagation, which is not observed in nature. This led to the development of the Fresnel modification to Huygens' principle.
- 🔄 Fresnel introduced the obliquity factor to adjust the amplitude of the secondary waves in different directions, which helps the model align with experimental observations.
- 🔀 Fresnel also modified the phases of the secondary waves, allowing the model to better predict real-world wave behavior.
- 📝 The modified model, known as the Huygens-Fresnel principle, is a more accurate description of how waves propagate and bend during diffraction.
- 🎓 Understanding diffraction is not limited to university-level physics; it can be grasped with a basic understanding of high school mathematics and physics.
- 📚 The concept of wave interference is crucial to understanding diffraction, as it explains how the resultant wave is formed when multiple waves overlap.
- 👀 The video provides a visual way to understand why waves diffract and how scientific models like Huygens' principle and the Huygens-Fresnel principle help visualize this phenomenon.
- 🎼 The presenter has started a second YouTube channel named 'path G's Shenanigans' where they post music recordings, covers, discussions, and reviews.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic discussed in the video is diffraction, specifically the diffraction of waves, and how it can be visualized and understood through Huygens' principle and the Huygens-Fresnel principle.
What is a plane wave?
-A plane wave is a type of wave, such as a light wave, that appears as a two-dimensional flat surface when viewed from above. It oscillates up and down and each straight line in the diagram represents a peak of the wave.
What is diffraction?
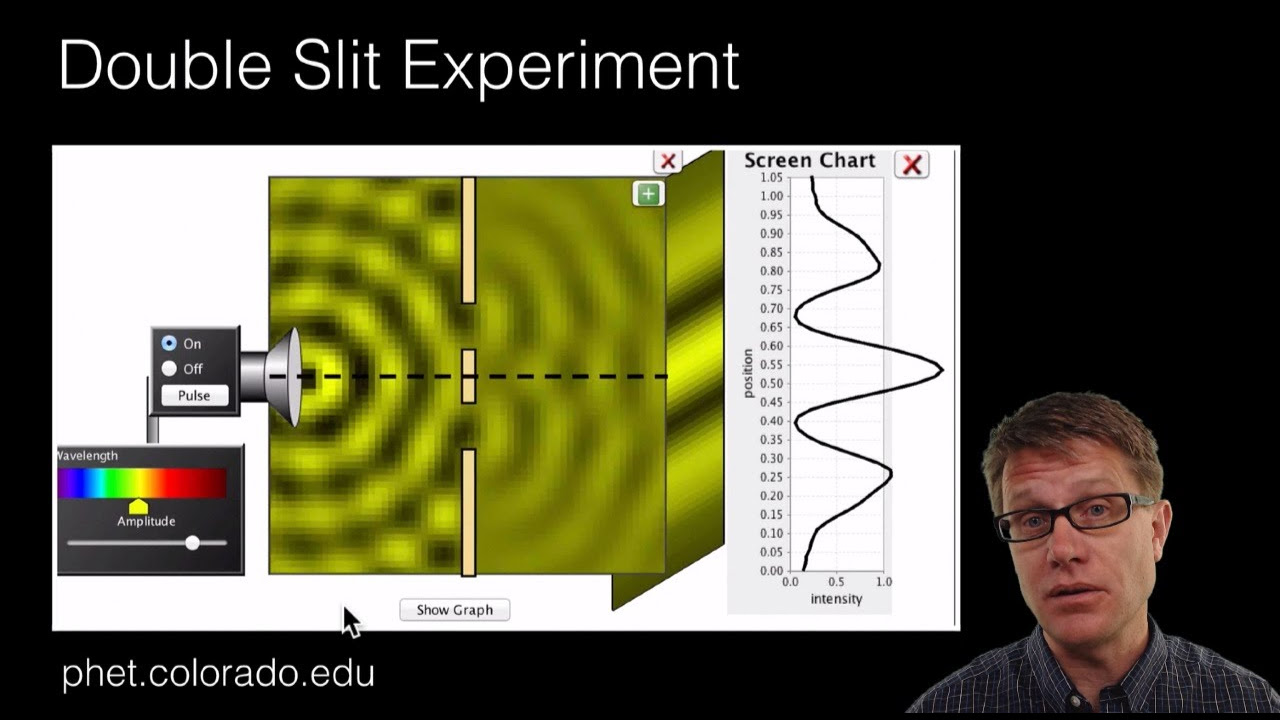
-Diffraction is the bending of a wave as it passes through a slit or around an object. It is a phenomenon where the wave changes direction and can be observed when light waves, for example, pass through a narrow opening.
Who proposed the concept of wavelets to explain wave behavior?
-Christian Huygens, a Dutch physicist, proposed the concept of wavelets, suggesting that every point along a wavefront behaves like a source of waves, emitting secondary waves in all directions.
What is wave interference?
-Wave interference occurs when two or more waves of the same kind meet and combine to form a resultant wave. The displacements of the original waves are added together at every point to determine the amplitude of the resultant wave.
How does the Huygens-Fresnel principle improve upon Huygens' original model?
-The Huygens-Fresnel principle improves upon Huygens' original model by introducing the obliquity factor, which accounts for the varying strengths of secondary waves in different directions, and by adjusting the phases of the secondary waves to better match real-life wave behavior.
Why might the original Huygens' principle not accurately represent real-world wave behavior?
-The original Huygens' principle might not accurately represent real-world wave behavior because it suggests that waves propagate both forward and backward, which is not observed experimentally. Waves are seen to propagate only forward.
What does the obliquity factor represent in the context of the Huygens-Fresnel principle?
-The obliquity factor represents the varying amplitudes of the secondary waves emitted by each point along the wavefront in different directions. It corrects the model to show that waves have different strengths when propagating in various directions.
What is the significance of the video creator starting a second YouTube channel?
-The significance is that the video creator is expanding their content to include music, specifically metal fusion and progressive rock genres. This provides an additional platform for them to share their musical work and engage with a different audience.
How often does the video creator aim to upload new content?
-The video creator aims to upload new content every two weeks on Tuesday evenings at 4 p.m. UK time.
What type of content will be featured on the video creator's second YouTube channel?
-The second YouTube channel, named 'path G's shenanigans', will primarily feature music that the video creator has recorded, including original compositions and covers, as well as discussions and reviews of music.
Outlines
🌟 Introduction to Diffraction and Huygens' Principle
The paragraph introduces the topic of diffraction, particularly the diffraction of waves, and sets the stage for a discussion on why diffraction occurs. It mentions the current coronavirus outbreak and the importance of safety, then transitions into a more advanced concept. The speaker, Path, explains the basic idea of diffraction as the bending of waves when they pass through a slit or around an object. The concept of a plane wave is introduced, and the paragraph ends with an introduction to Huygens' principle, which is a model that helps visualize how each point on a wavefront acts as a source of secondary waves, leading to the phenomenon of diffraction.
📊 Wave Interference and the Resultant Wave
This paragraph delves into the concept of wave interference, which is crucial for understanding diffraction. It describes how two waves of the same kind with the same amplitude and wavelength can combine to form a resultant wave. The process of combining these waves at various points in time is explained, showing how they can either cancel each other out or reinforce each other, leading to a larger peak or trough in the resultant wave. The paragraph emphasizes that what is observed is not the individual waves but the resultant wave, which is formed by the interference of the secondary waves emitted by each point along the wavefront.
🔍 Application of Huygens' Principle to Slit Diffraction
The application of Huygens' principle to the scenario of a wave passing through a slit is explored in this paragraph. It explains how the spherical waves emitted by each point along the wavefront interfere with each other to form a straight line of peaks, which is the observed wave. However, the paragraph also points out the limitations of Huygens' original model, which incorrectly suggests that waves would also propagate backward. To address this, the paragraph introduces Fresnel's modifications to the model, including the obliquity factor and changes to the phases of the secondary waves, resulting in the Huygens-Fresnel principle that more accurately predicts real-life wave behavior.
🎶 Conclusion and Additional Content Announcement
The speaker concludes the discussion on diffraction, Huygens' wavelets, and the Huygens-Fresnel principle, emphasizing the complexity of the topic. They invite feedback and corrections from the audience and announce the launch of a second YouTube channel named 'Path G's Shenanigans,' which will focus on music content, including original recordings, covers, and music discussions. The speaker encourages viewers to subscribe to the new channel if interested in the music genre mentioned. They also ask for likes and comments on the video, request suggestions for future physics topics, and remind viewers to subscribe to the channel for regular updates.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Diffraction
💡Huygens' Wavelets
💡Wavefront
💡Plane Wave
💡Wave Interference
💡Obliquity Factor
💡Fresnel
💡Huygens-Fresnel Principle
💡Wave Propagation
💡Amplitude
💡Wavelength
Highlights
The video discusses diffraction, a wave behavior similar to reflection or refraction, and aims to explain why it occurs.
Diffraction is the bending of a wave as it passes through a slit or around an object, a key concept in wave physics.
Huygens' principle is introduced as a model to visualize how every point on a wavefront acts as a source of secondary waves.
Secondary waves from different points on the wavefront interfere with each other, leading to the formation of a new wave pattern.
Wave interference is explained as the process where two waves combine to form a resultant wave by adding their displacements together.
The resultant wave is observed as a straight line when multiple peaks overlap, illustrating the propagation of waves.
Huygens' principle predicts the bending of waves when passing through a slit, aligning with experimental observations.
Fresnel made modifications to Huygens' principle by introducing the obliquity factor to account for varying wave amplitudes in different directions.
Fresnel also adjusted the phases of the secondary waves to ensure the model's predictions matched real-life wave behavior.
The Huygens-Fresnel principle is a more accurate model for predicting wave behavior than the original Huygens' principle alone.
The video aims to help viewers visualize wave propagation and understand why waves bend when passing through slits.
The presenter invites viewers to provide feedback for clarification and to report any mistakes in the explanation.
A new YouTube channel named 'Path G's Shenanigans' is announced, focusing on music content.
The presenter encourages viewers to subscribe to the new channel if they are interested in metal fusion and progressive genres.
The video concludes with an invitation for viewers to subscribe to the channel, engage with the content, and provide suggestions for future topics.
The presenter mentions a consistent upload schedule, aiming to post every two weeks on Tuesday evenings at 4 p.m. UK time.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: