MJ16 P41 Q1 Gravitational Potential Between 2 Stars | A2 G-fields | Cambridge A Level 9702 Physics
TLDRThe video script delves into the concept of gravitational potential between two stars, emphasizing its negative nature due to the attractive force of gravity. It explains how the potential decreases from infinity, where it is zero, towards the stars, resulting in a negative value. The script uses a graphical representation to illustrate how the gravitational potential varies with distance between the two stars and demonstrates how changes in gravitational potential energy affect kinetic energy. The example of moving an object from one point to another in the gravitational field of two stars is used to calculate changes in kinetic energy and to determine the minimum speed required for an object to travel from one star to the other.
Takeaways
- 🌌 Gravitational potential is a negative quantity because gravity is always attractive, and work is done by the gravitational field to bring an object from infinity to a point within the field.
- 📉 The gravitational potential at infinity is defined as zero, which means that any potential energy value less than zero is negative, indicating the attractive nature of gravity.
- 🔄 When moving an object from one point to another in a gravitational field, the change in kinetic energy is related to the change in gravitational potential energy.
- 🚀 To calculate the change in kinetic energy, multiply the mass of the object by the change in potential (final potential minus initial potential).
- 📊 The provided graph illustrates the combined gravitational potential of two stars, showing how the potential changes with distance from their centers.
- 🔽 The graph's turning point represents the location where the gravitational pull of one star equals that of the other, resulting in no net gravitational force.
- 🎯 To find the minimum speed required for an object to travel from one star to the other, calculate the energy needed to reach the turning point where the second star's gravity takes over.
- 🧮 The mass of the object cancels out in the equation relating kinetic energy change to gravitational potential energy change, simplifying the calculation.
- 🌠 When an object moves from a region of lower gravitational potential to a region of higher gravitational potential, its kinetic energy decreases.
- 🔄 The change in gravitational potential energy is directly related to the work done by gravity, with a decrease in potential energy corresponding to an increase in kinetic energy.
- 📈 Understanding the relationship between gravitational potential and kinetic energy is crucial for grasping concepts in both gravitational fields and electric fields.
Q & A
What is the significance of gravitational potential in the context of two stars?
-Gravitational potential is significant in understanding the energy dynamics between two stars. It represents the work done against gravity to move an object from infinity to a point in the gravitational field. The concept helps in analyzing the energy changes as an object transitions from one gravitational field to another, such as from one star to another.
Why is gravitational potential typically a negative quantity?
-Gravitational potential is a negative quantity because the gravitational field is always attractive. Work is done by the gravitational field to bring a unit mass from infinity to a point within the field, which results in a decrease in gravitational potential energy (GPE). Since GPE at infinity is defined as zero, any decrease from this point results in a negative value.
How does the gravitational potential graph for two stars differ from that of a single star?
-The gravitational potential graph for two stars shows the combined potential of both stars. It reflects the summation of the individual potentials and illustrates how an object would move under the influence of both gravitational fields. The graph can have a mountain-like shape, indicating points of equilibrium where the gravitational pulls of the two stars balance out.
What is the role of gravitational potential in the conservation of energy?
-Gravitational potential plays a crucial role in the conservation of energy, particularly in the transformation between potential and kinetic energy. As an object moves within a gravitational field, the work done against gravity results in a change in gravitational potential energy. This change is mirrored by an opposite change in kinetic energy, conserving the total mechanical energy of the system.
How does the change in gravitational potential affect the kinetic energy of an object?
-A change in gravitational potential directly affects the kinetic energy of an object. When gravitational potential energy decreases, kinetic energy increases, and vice versa. This relationship is a fundamental aspect of the conservation of mechanical energy in a gravitational field.
What is the significance of the turning point in the gravitational potential graph?
-The turning point in the gravitational potential graph represents the location where the gravitational attraction of one star equals that of the other, resulting in a balance of forces. At this point, the object would be in a state of equilibrium and could potentially move towards either star depending on slight perturbations or additional energy inputs.
How can the change in kinetic energy be calculated when a rock moves along the line joining the centers of two stars?
-The change in kinetic energy can be calculated using the change in gravitational potential energy between the initial and final positions of the rock. By taking the difference in potential and multiplying it by the mass of the rock, the change in kinetic energy can be determined, which indicates whether the rock's speed increases or decreases as it moves between two points.
What is the minimum speed required for a rock to travel from one star to another?
-The minimum speed required for a rock to travel from one star to another is the speed needed to reach the turning point in the gravitational potential graph. At this point, the rock has enough energy to be captured by the gravitational field of the second star, which will then provide the necessary force to continue moving towards it.
How does the mass of an object affect the change in gravitational potential energy?
-The mass of an object does not affect the change in gravitational potential energy in terms of the ratio of potential energy change to kinetic energy change. This is because when calculating the change in kinetic energy based on potential energy change, the mass of the object cancels out, leaving a direct relationship between the change in potential energy and the resulting change in kinetic energy.
What is the practical implication of understanding the gravitational potential between two stars?
-Understanding the gravitational potential between two stars has practical implications for space travel and celestial mechanics. It helps in predicting the energy requirements for spacecraft to move between star systems and in understanding the orbital dynamics of celestial bodies influenced by multiple gravitational fields.
Outlines
🌌 Grasping Gravitational Potential Between Stars
This paragraph introduces the concept of gravitational potential between two stars, emphasizing the abstract nature of the topic. It explains that gravitational potential is typically negative, drawing parallels with electric fields and their potential. The explanation begins with a single object's gravitational potential and progresses towards understanding the potential between two stars, setting the stage for a deeper exploration of the topic.
📉 Negative Gravitational Potential Explained
The paragraph delves into why gravitational potential is always negative, using the analogy of work done by gravity. It explains that as gravity attracts a mass from infinity to a point in the gravitational field, work is done by the gravitational field, resulting in a decrease in gravitational potential energy (GPE). The summary highlights the key points that GPE is zero at infinity and that gravity's attractive nature leads to negative GPE values when objects are brought closer together.
🪐 Two Stars and the Gravitational Potential Graph
This section focuses on the graphical representation of gravitational potential between two stars, illustrating how the potential varies with distance. It describes the process of adding the potential graphs of two stars to obtain a combined graph, which helps visualize where mass will move under the influence of both gravitational fields. The explanation clarifies how the graph can predict the motion of an object between the two stars, emphasizing the importance of understanding the graph's shape and implications.
🚀 Calculating Kinetic Energy Changes in a Gravitational Field
The paragraph discusses the calculation of changes in kinetic energy as an object moves within a gravitational field. It uses the example of a 180 kg rock moving along the line joining the centers of two stars, demonstrating how to calculate the change in kinetic energy using the given data and graph. The summary points out that the change in kinetic energy is related to the change in gravitational potential energy, and it provides a step-by-step breakdown of the calculation, highlighting the significance of understanding these energy transformations.
🥇 Achieving the Minimum Speed for Interstellar Travel
This part of the script addresses the concept of minimum speed required for an object to travel from one star to another. It explains that only enough energy is needed to reach a turning point, beyond which the gravitational field of the destination star takes over. The summary details the calculation process for determining this minimum speed, emphasizing the role of gravitational potential in the energy conservation equation and the importance of understanding the interplay between gravitational potential and kinetic energy.
🌠 Wrapping Up the Gravitational Potential Discussion
The final paragraph summarizes the main points discussed in the script, reinforcing the concepts of gravitational potential, kinetic energy, and their relationship. It reflects on the practical applications of understanding these concepts, particularly in the context of space travel and the efficient use of fuel. The summary encourages a deeper understanding of the material and looks forward to future discussions on related topics.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Gravitational Potential
💡Work-Energy Principle
💡Gravitational Field
💡Potential Energy
💡Kinetic Energy
💡Gravitational Potential Graph
💡Turning Point
💡Gravitational Potential Difference
💡Infinite Distance
💡Mass
💡Conservation of Energy
Highlights
Exploration of gravitational potential between two stars, providing a unique insight into celestial mechanics.
Discussion on the abstract concept of potential and its significance in both gravitational and electric fields.
Explanation of why gravitational potential is considered a negative quantity, demystifying the concept with relatable examples.
Illustration of the gravitational potential graph, offering a visual understanding of the potential changes with distance.
Clarification on the relationship between gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy, highlighting the conservation of energy principle.
Detailed calculation of the change in kinetic energy as an object moves between two stars, providing a practical application of theoretical concepts.
Use of the gravitational potential graph to determine the turning point where the gravitational influence of one star is balanced with another.
Explanation of how an object's minimum speed can be determined to reach a final position in the gravitational field of two stars.
Discussion on the role of gravity in the solar system's formation and how it affects the potential energy of celestial bodies.
Comparison of gravitational potential to a trolley moving up and down a track, simplifying the concept with an everyday analogy.
Emphasis on the importance of understanding gravitational potential as it relates to the attraction and movement of masses in space.
Explanation of how the gravitational potential at infinity is defined as zero and its implications on the potential energy of objects.
Demonstration of how the gravitational potential graph can predict the behavior of an object as it moves between the gravitational fields of two stars.
Clarification on the calculation of the gravitational potential at different points between two stars, using the given data and equations.
Discussion on the significance of the intersection point in the gravitational potential graph, where the gravitational forces of two stars are balanced.
Explanation of the conservation of energy in the context of gravitational potential and kinetic energy, and how it applies to the movement of celestial bodies.
Practical example of calculating the minimum speed required for an object to travel from one star to another, showcasing the application of gravitational potential concepts.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
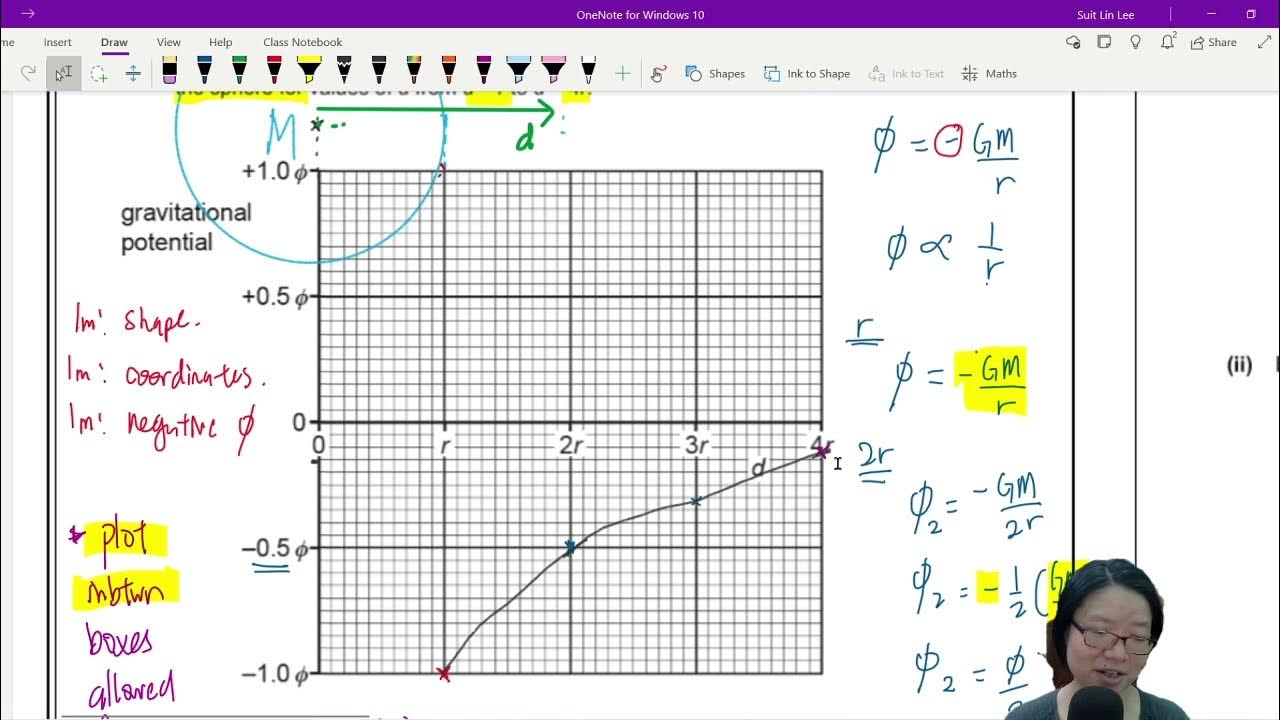
13.3b Ex1 MJ20 P42 Q1 Rock Potential Energy | A2 Gravitational Fields | Cambridge A Level Physics
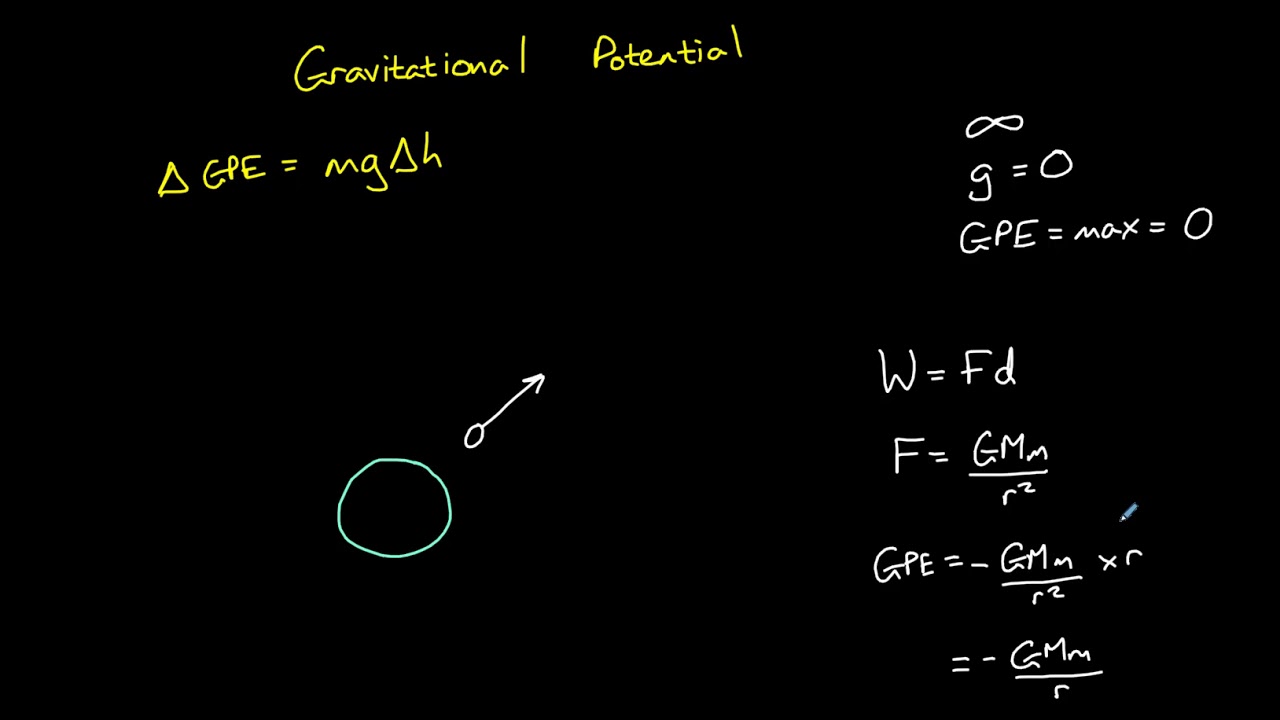
Gravitational Potential and Gravitational Potential Energy

13.3a Gravitational Potential Theory | A2 G-Fields | Cambridge A Level Physics
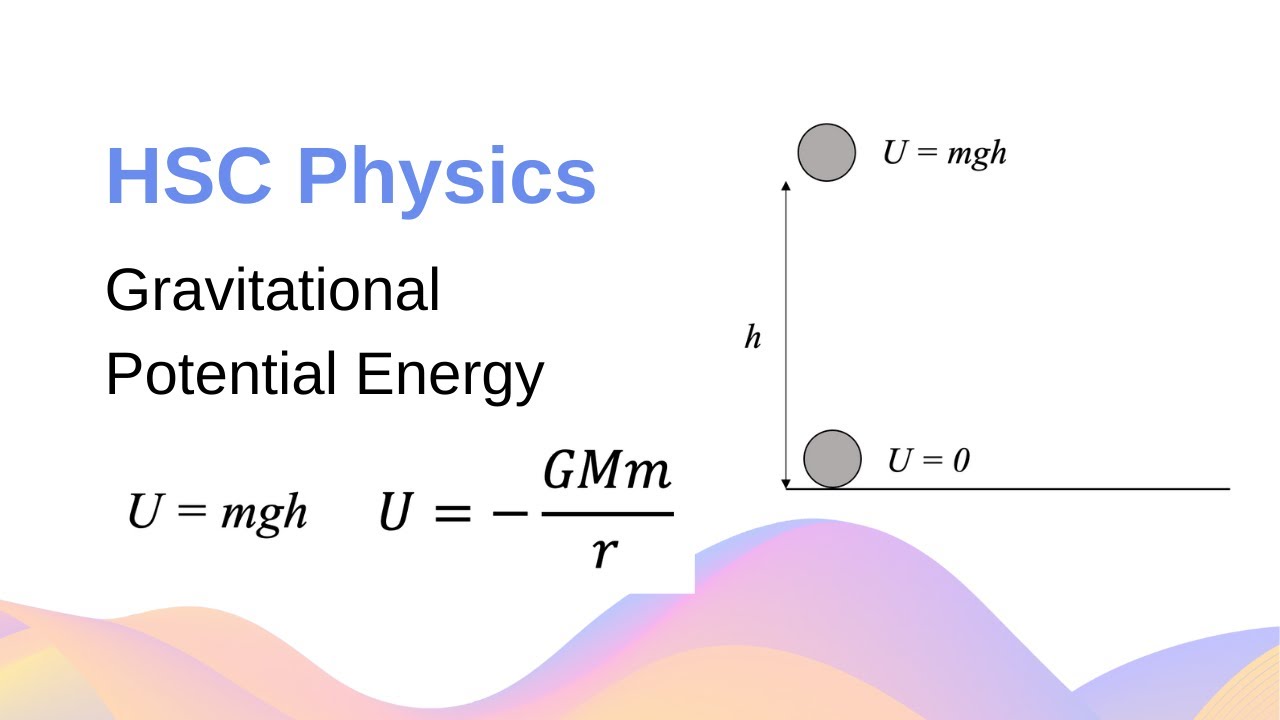
Gravitational Potential Energy & Work Done + Calculation Example // HSC Physics
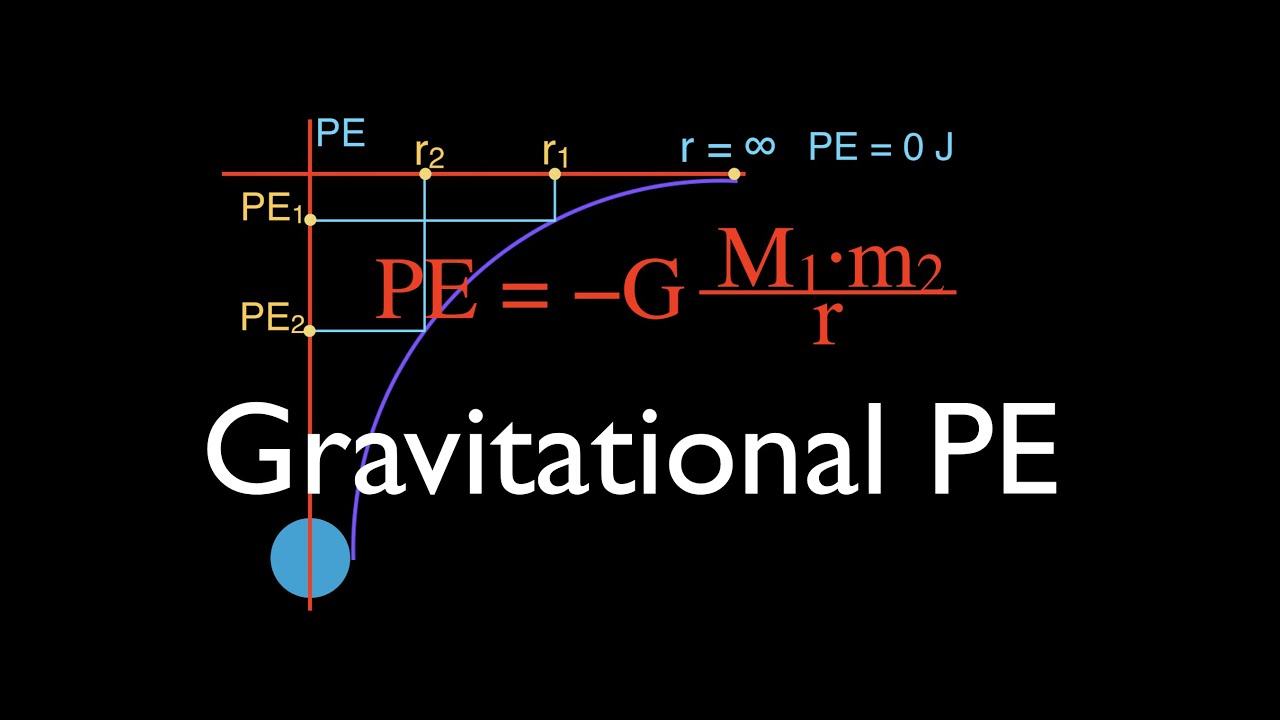
Gravitation (9 of 17) Gravitational PE Far From Earth, the Negative Sign, An Explanation

Kinetic Energy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: