Revenue Streams: Crash Course Entrepreneurship #13
TLDRThis video explains business and entrepreneurship concepts related to money and revenue. It starts by defining key financial terms like revenue, expenses, profit, and breaks down different revenue stream models like product sales, subscriptions, licensing, advertising etc. It stresses the importance of picking revenue streams suited to your business and customer needs. The video advises on pricing considerations as well, emphasizing competitive analysis and customer feedback to arrive at optimal pricing. The main goal is demystifying finance jargon for entrepreneurs to set them up for success.
Takeaways
- 😀 Revenue is the amount of money received from customers
- 💰 Profit is revenue minus expenses
- 📊 Three key financial concepts for a business are revenue, expenses, and profit
- 🌊 Revenue streams feed into total revenue like small streams into a river
- 🛍️ Common revenue streams include product sales, usage fees, renting/leasing, licensing, subscriptions, brokerage fees, and advertising
- 🎯 Successful businesses focus on revenue streams related to their key activities and partners
- 💵 Set prices based on costs and competition to make a profit
- 🔎 Evaluate pricing strategies like margin expanders, disruptors, revenue drivers and pricing pioneers
- 👂 Listen to customer feedback on prices along with watching the competition
- 💡 Don't be intimidated by the vocabulary, pick revenue streams that suit your business and customers
Q & A
What are some key terms related to money that business people need to understand?
-Some key financial terms discussed are revenue, expenses, profit, operating costs, asset sale, usage fee, renting/leasing, licensing, subscription fee, brokerage fee, and advertising.
How is revenue calculated?
-Revenue is calculated by multiplying the number of products or services sold by the price per item.
What is the difference between revenue and profit?
-Revenue is the total money brought in from sales. Profit is revenue minus expenses - the money left over after covering operating costs.
What are some examples of different revenue streams discussed?
-Examples include product sales, usage fees, renting/leasing, licensing, subscriptions, brokerage fees, and advertising.
How did GoldieBlox expand their revenue streams?
-GoldieBlox started with core product sales, then expanded into book publishing, partnering with Girl Scouts for special kits, and earning YouTube ad revenue.
What pricing strategies were mentioned for setting prices?
-Strategies included margin expander, pricing disruptor, revenue driver, and pricing pioneer.
What does it mean to be a pricing disruptor?
-A pricing disruptor throws out previous pricing models to differentiate themselves and address customer complaints.
What does McKinsey say is important when re-evaluating prices?
-McKinsey stresses the importance of listening to customer feedback on what they like/need and paying attention to the competition and your own costs.
What recurring message is there about revenue streams?
-The key point made is to pick revenue streams natural for your business and customers. You can start small and expand/pivot over time.
How can an entrepreneur avoid getting intimidated by financial terminology?
-The script advises entrepreneurs not to be intimidated by the vocab. Most financial concepts are simple, and resources like Investopedia can help decode terms.
Outlines
😀 Understanding Money Flows in Business
This paragraph introduces some key financial terms used in business like revenue, expenses, profit, and assets. It explains the differences between them and why it's important for entrepreneurs to understand these concepts. The main point is that making money requires knowing the financial ins and outs of your business.
😊 Exploring Different Revenue Streams
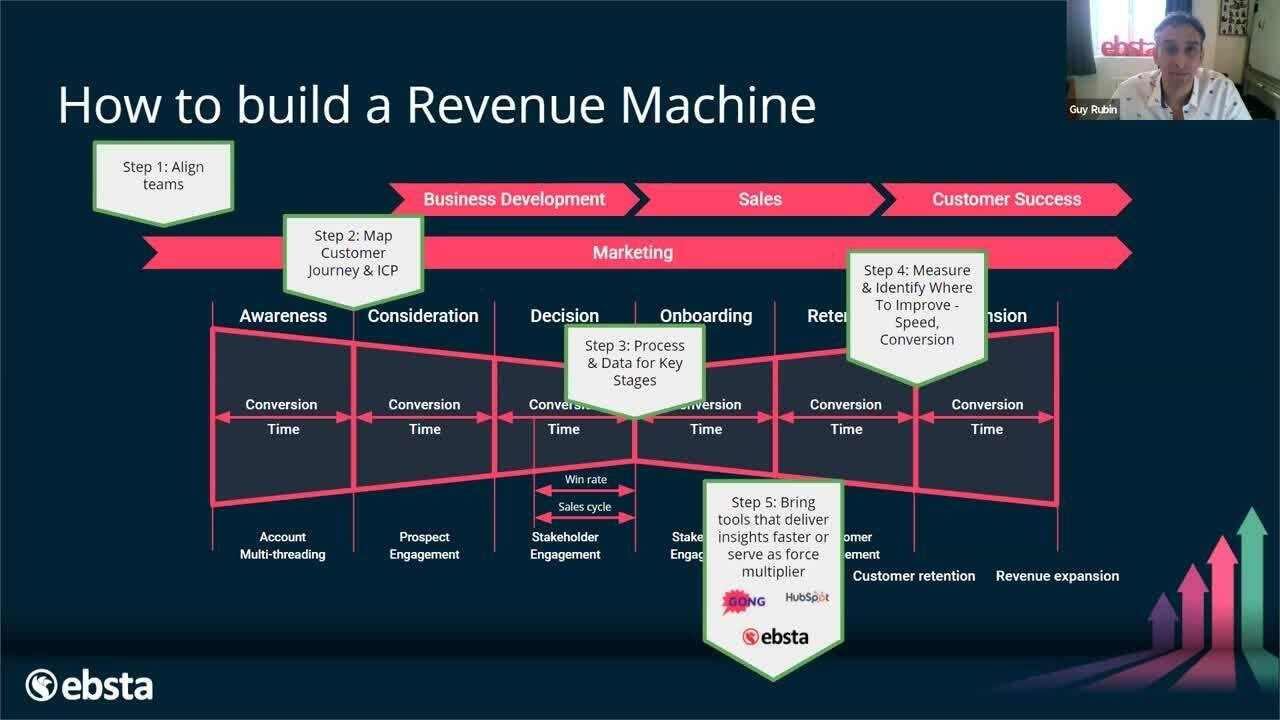
This paragraph discusses the different ways a business can generate revenue through things like product sales, subscriptions, licensing, advertising etc. It uses the example of GoldieBlox to show how a company can leverage multiple revenue streams based on their key activities and partners.
😃 Pricing Strategies and Importance of Customers
This closing paragraph talks about different pricing strategies like bundling products or using disruptive models. It emphasizes understanding costs and competition when setting prices, but also listening to customer feedback. The main point is that pricing should align with your business model and what customers want.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Revenue
💡Expenses
💡Profit
💡Revenue Streams
💡Product Sale
💡Usage Fee
💡Renting/Leasing
💡Licensing
💡Subscription
💡Advertising
Highlights
Money can be an awkward subject, but to make a living and be taken seriously, entrepreneurs need to know the money side of business.
Revenue is the amount of money a customer hands over when they buy a product or service.
Expenses are the costs of operating a business, like employee salaries, supplies, and equipment.
Profit is revenue minus expenses - the money you make if revenue exceeds expenses.
There are many options for revenue streams based on what you sell and how you sell it.
A product sale transfers ownership rights - the customer gets a product, you get money.
With a usage fee, customers pay based on how much they use something you own.
Renting grants someone rights to use something you own for a fixed period, for recurring fees.
Licensing is renting ideas - giving permission to use protected IP for a fee.
A subscription fee sells continuous access to a service for a regular fee.
A brokerage fee is charged for arranging a deal between other parties.
Advertising promotes other brands' products for a fee.
Focus first on revenue streams related to your key activities, then diversify.
Re-evaluate pricing by listening to customers and watching the competition.
Don't be intimidated by the vocab - pick revenue streams that fit your business.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: