Perfecting the Periodic Table
TLDRThe video script discusses the history and significance of the periodic table, highlighting its evolution from early ideas by scientists like Lavoisier, Dalton, Dobereiner, and Newlands to Mendeleev's groundbreaking organization by atomic properties and his prophetic placement of elements. It emphasizes Mendeleev's pivotal role in its development and the subsequent refinement by Moseley based on atomic number rather than atomic weight. The periodic table's current form, detailing each element's name, symbol, atomic number, and mass, reflects the cumulative efforts of these chemists and paves the way for future discoveries and potential redesigns.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Gold's distinct characteristics make it easily recognizable among other elements.
- 📈 The periodic table organizes all known elements based on their properties and similarities.
- 🔍 Historically, various scientists like Lavoisier, Dalton, Dobereiner, and Newlands contributed to the development of the periodic table.
- 📚 John Newlands proposed organizing elements by atomic mass and discovered the law of octaves, which organized elements into groups of 8 with similar properties at regular intervals.
- 🧠 Dmitri Mendeleev's critical analysis of the existing periodic table led to his own rearrangement of elements based on their properties, resulting in a more accurate classification system.
- 💤 Mendeleev's periodic table design, which included gaps for future discoveries, was widely accepted due to its predictive accuracy.
- 🏆 Mendeleev is known as 'the father of the periodic table' for his groundbreaking work in organizing and predicting the properties of elements.
- 🔬 Henry Moseley's discovery of isotopes further refined the periodic table's organization, emphasizing atomic number over atomic mass.
- 📊 Today's periodic table is an updated version of Mendeleev's design, with each element's name, symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass displayed in a grid format.
- 🔄 Elements are arranged in increasing atomic number and organized into groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) based on their chemical reactivity and electron configurations.
- 🔍 The periodic table's evolution and current design reflect the collective genius of many chemists and the ongoing journey of element discovery and classification.
Q & A
What is the significance of the periodic table in chemistry?
-The periodic table is a systematic arrangement of all known chemical elements based on their properties and atomic structure. It helps chemists understand the relationships between elements and predict the properties of new or undiscovered elements.
How did the concept of the periodic table evolve over time?
-The concept of the periodic table evolved through the contributions of several scientists, including Lavoisier, Dalton, Dobereiner, and Newlands. However, it was Dmitri Mendeleev who made the most significant breakthrough by arranging elements based on their atomic mass and reactivity, leaving gaps for future discoveries.
What was John Newlands' contribution to the periodic table?
-John Newlands proposed the law of octaves, organizing elements based on their atomic mass into groups of eight with similar properties at regular intervals. Although his method had limitations, it was an early step towards the modern periodic table.
How did Dmitri Mendeleev improve upon the existing periodic tables of his time?
-Mendeleev rearranged the elements based on their chemical properties rather than just their atomic mass. He also left gaps for elements not yet discovered, which allowed for the periodic table to expand as new elements were found.
What was the role of isotopes in refining the periodic table?
-The discovery of isotopes showed that the classification of elements could not be based solely on atomic mass. This realization led to the understanding that the periodic table should be organized by atomic number, which is the number of protons in an element's nucleus.
Who was Henry Moseley, and how did his work contribute to the periodic table?
-Henry Moseley was a young scientist who deduced that the periodic table should be arranged based on atomic number rather than atomic weight. His work provided a more accurate method for organizing elements and understanding their properties.
What information is provided for each element in the modern periodic table?
-Each element in the modern periodic table is given a square that includes its name, chemical symbol, atomic number (the number of protons), and atomic mass (the combined number of protons and neutrons based on isotopic abundance).
How are elements organized within the periodic table?
-Elements are organized into groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) based on their atomic number and the similarities in their chemical properties, which are due to having the same number of electrons in their outer shell.
How many elements have been discovered to date?
-As of the knowledge cutoff date, 118 elements have been discovered, with some being synthesized, such as Moscovium (element 115).
What is the current status of the periodic table in terms of new element discoveries?
-Scientists are currently exploring the discovery of element 119 and beyond. The periodic table continues to be updated as new elements are synthesized or discovered, and there are ongoing discussions about potential redesigns to accommodate these new findings.
Why should we appreciate the periodic table and its history?
-We should appreciate the periodic table and its history because it represents the collective efforts of many great chemists and their contributions to our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of the universe. It is a testament to human curiosity and the pursuit of knowledge.
Outlines
🌟 Introduction to the Periodic Table and its History
This paragraph introduces the Periodic Table, a fundamental tool in chemistry that organizes all known elements based on their properties and atomic structure. It highlights the widespread recognition of gold as a distinct element and sets the stage for discussing the history and development of the Periodic Table. The paragraph discusses the efforts of early scientists like Lavoisier, Dalton, Dobereiner, and Newlands, who attempted to classify elements. It then focuses on John Newlands' law of octaves, which grouped elements based on atomic mass, and the limitations of this approach. The narrative progresses to Dmitri Mendeleev, who is credited with creating the modern Periodic Table by rearranging elements based on their properties and leaving gaps for future discoveries. The paragraph also touches on the discovery of isotopes and Henry Moseley's contribution to classifying elements by atomic number rather than atomic mass, leading to the updated Periodic Table we use today.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Periodic Table
💡Elements
💡John Newlands
💡Dmitri Mendeleev
💡Atomic Mass
💡Isotopes
💡Henry Moseley
💡Atomic Number
💡Groups and Periods
💡Electron Configuration
💡Element Synthesis
💡Redesigning the Periodic Table
Highlights
The periodic table arranges all known elements based on their properties and similarities.
Many chemists since the 1800s have attempted to find the best way to organize the elements.
John Newlands proposed organizing elements by atomic mass and discovered the law of octaves.
Dmitri Mendeleev rearranged elements into groups with similar properties, leaving gaps for future discoveries.
Mendeleev earned the nickname 'the father of the periodic table' for his contributions.
The discovery of isotopes showed that elements could not be classified solely based on atomic masses.
Henry Moseley deduced that the periodic table should be arranged based on atomic number rather than atomic weight.
Today's periodic table is an updated version of Mendeleev's design, listing each element's name, chemical symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass.
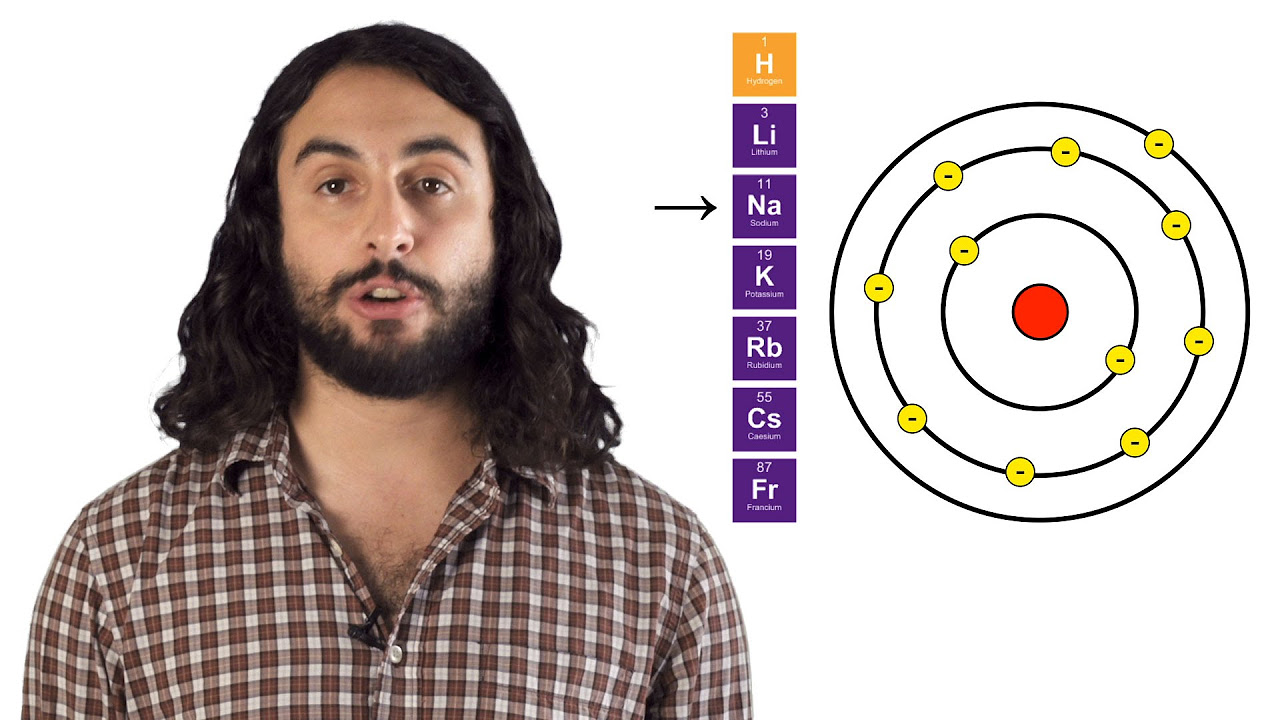
Elements in the same group react similarly due to having the same number of electrons in the outer shell.
Mendeleev's predictions about the periodic table were remarkably accurate despite not knowing about electron arrangements.
There are 118 elements discovered, some of which are synthesized, like Moscovium (element 115).
The discovery of new elements, such as element 119, continues to be an area of interest and research.
The periodic table has gone through several revisions based on the work of great chemists.
Moscovium is produced by bombarding atoms of americium with ions of calcium in a cyclotron.
The periodic table's design and structure are a testament to the genius of Mendeleev and other chemists.
Elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number and organized into groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows).
The modern periodic table accounts for isotopes' abundance in determining an element's atomic mass.
The periodic table is a culmination of the efforts of many scientists and is a valuable resource for understanding elemental properties and reactions.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Modern Periodic Table

Periodic Table Explained: Name Origin

Lesson 11 - Overview Of The Periodic Table of Elements

5 Periodic Tables We Don't Use and Why
The Periodic Table: Atomic Radius, Ionization Energy, and Electronegativity

Atomic Number & Mass Number | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: