Applied Chemistry_Atomic Charecteristics_ Lecture 06 for Polytechnic 1st Semester
TLDRThe video script discusses atomic structure and characteristics, focusing on the importance of understanding atomic numbers, mass numbers, and the role of electrons, protons, and neutrons. It delves into isotopes, the concept of isobars, and the significance of electron shells in determining an atom's properties. The video also touches on the concept of nuclear charge and the impact of electron configuration on an element's behavior, introducing the idea of chemical bonding in simple terms.
Takeaways
- 📚 The importance of understanding atomic structure and its fundamental particles such as electrons, protons, and neutrons.
- 🔬 The role of atomic number in defining the identity of an element and its position in the periodic table.
- 🔄 The concept of isotopes and how they relate to the atomic mass number and the number of neutrons in an element's nucleus.
- 🔧 The impact of the number of electrons and their arrangement on an element's chemical properties and reactivity.
- 🔌 The significance of electron configuration in determining an element's behavior, including its electrical conductivity and chemical bonding.
- 🌐 The periodic table's organization based on atomic numbers and the grouping of elements with similar properties.
- 🔎 The use of isotopes in various applications, such as tracing chemical processes or dating geological samples.
- 🚀 The potential conversion of elements under certain conditions, like the conversion of one hydrogen isotope to another.
- 📈 The relationship between the number of protons and the electrical charge of an element, and how it affects its interactions with other elements.
- 🌟 The identification of elements with the highest number of isotopes and their significance in scientific research.
- 🎓 The educational value of studying atomic structure and isotopes for students of chemistry and related fields.
Q & A
What is the significance of understanding atomic structure in chemistry?
-Understanding atomic structure is crucial in chemistry as it forms the foundation for comprehending chemical reactions, bonding, and the properties of elements. It helps in predicting how substances will interact and the resulting products of these interactions.
What is an atomic number and how is it related to an element's identity?
-The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It uniquely identifies an element, determining its position in the periodic table and its chemical properties, as the atomic number increases by one for each subsequent element.
What are the fundamental particles that make up an atom?
-An atom is made up of three fundamental particles: protons, which carry a positive charge and are located in the nucleus; neutrons, which have no charge and are also found in the nucleus; and electrons, which carry a negative charge and orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells.
How do isotopes differ from one another?
-Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number. All isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons, and thus the same atomic number, but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses.
What is the role of electrons in chemical bonding?
-Electrons play a critical role in chemical bonding. They are involved in forming chemical bonds by being shared, transferred, or exchanged between atoms. The arrangement of electrons in an atom's outermost shell determines its reactivity and the type of bonds it can form with other atoms.
What is the difference between atomic mass and atomic number?
-The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which defines the element. The atomic mass, on the other hand, is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. While the atomic number is always a whole number and determines the element's identity, the atomic mass can be a whole or decimal number due to the presence of neutrons.
How do atomic structures affect the properties of elements?
-The atomic structure, particularly the arrangement of electrons, greatly influences an element's properties. For example, the number of valence electrons (electrons in the outermost shell) determines an element's chemical reactivity, while the overall atomic structure can affect physical properties such as melting point, boiling point, and density.
What is the concept of electronegativity and how does it relate to atomic structure?
-Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. It is influenced by the atomic structure, specifically the number of protons and the distance of the valence electrons from the nucleus. Elements with higher electronegativity have a greater tendency to attract electrons during chemical bonding.
How do atomic structures contribute to the formation of periodic properties in the elements?
-The periodic properties of the elements are a direct result of the periodic arrangement of atomic structures. As the atomic number increases, the pattern of electron configuration repeats in a predictable manner, leading to the periodicity in the properties of elements such as reactivity, atomic radius, and electronegativity.
What is the significance of understanding the different types of atomic spectra?
-Understanding atomic spectra is important as it allows scientists to identify elements and analyze their properties. When an atom absorbs or emits energy, it does so at specific wavelengths unique to each element. By studying these emission or absorption spectra, one can determine the composition of substances and gain insights into the structure and behavior of atoms.
Outlines
📘 Introduction to Atomic Structure and Characteristics
The paragraph introduces the concept of atomic structure, specifically focusing on the characterization of atoms. It discusses the fundamental particles that make up an atom, such as electrons, protons, and neutrons. The importance of understanding the atomic number, which is crucial for identifying an element and its properties, is emphasized. Additionally, the paragraph touches on the concept of isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, and their significance in various applications.
🥩 Atomic Mass and Isotopes
This section delves into the concept of atomic mass, explaining how it is determined by the number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus. The discussion includes the atomic mass unit (amu) and how it relates to the mass of an atom. The paragraph also explores isotopes, which are variants of an element with different atomic masses due to varying numbers of neutrons. The significance of understanding isotopes in fields like chemistry and physics is highlighted, along with a brief explanation of how isotopes can be represented and identified.
🔬 Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration
The focus of this paragraph is on the electron configuration of atoms, which is the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. It explains how electrons are distributed across different energy levels and orbitals within those levels. The concept of atomic number influencing the number of protons, which in turn affects the electron configuration, is discussed. The paragraph also touches on the importance of understanding electron configurations for predicting an element's chemical properties and reactivity.
🌿 Isotopes and Chemical Properties
This section discusses the impact of isotopes on the chemical properties of elements. It explains that while isotopes have the same chemical properties due to having the same number of protons and electrons, they can differ in physical properties such as mass and stability. The paragraph also introduces the concept of radioactive isotopes and their applications in various fields, including medicine and archaeology. The importance of distinguishing between isotopes for both scientific and practical purposes is emphasized.
🔧 Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
The paragraph examines the role of atomic structure in chemical bonding. It explains how the arrangement of electrons in an atom's electron cloud influences its ability to form bonds with other atoms. The concept of valence electrons, which are the outermost electrons involved in chemical bonding, is introduced. The paragraph also discusses how the number of valence electrons determines an element's position in the periodic table and its general reactivity and bonding tendencies.
🔄 Isotopes and Nuclear Reactions
This section explores the behavior of isotopes in nuclear reactions, such as fission and fusion. It explains how the different masses of isotopes can affect the outcomes of these reactions. The paragraph also touches on the practical applications of nuclear reactions, including the generation of energy and the production of new elements. The importance of understanding isotope behavior in these reactions for both scientific research and technological development is highlighted.
🎓 Conclusion and Future Learning
The paragraph concludes the discussion on atomic structure and isotopes, summarizing the key points covered in the previous sections. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these concepts for further studies in chemistry and related fields. The paragraph also encourages continued learning and exploration of topics such as chemical bonding and nuclear reactions, setting the stage for future lessons and deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Atomic Structure
💡Isotopes
💡Electron Configuration
💡Atomic Number
💡Nuclear Reactions
💡Chemical Bonding
💡Periodic Table
💡Quantum Numbers
💡Ionization Energy
💡Electron Affinity
Highlights
The introduction of the concept of atomic structure and its fundamental particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons.
Explaining the atomic number and its significance in defining the characteristics of an element.
The discussion on isotopes and how they vary in the number of neutrons while sharing the same atomic number.
The importance of understanding the mass number in relation to the number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
The concept of electron configuration and its role in determining an element's chemical properties.
The explanation of how an atom can convert into another element through changes in its electron and proton numbers.
The introduction of the term 'isobar' and its relevance in the context of atomic structure.
The discussion on the different types of atomic spaces and their significance in the arrangement of electrons.
The concept of 'neutron number' and how it differs from the proton number in an atom.
Exploring the idea of 'nuclear charge' and its impact on the stability and properties of an atom.
The explanation of the term 'isotopes of hydrogen' and the different names associated with its isotopes.
The importance of understanding the maximum number of isotopes an element can have and its significance.
The concept of 'electronvolts' and its role in measuring the energy of electrons.
The discussion on the different types of chemical bonds and their formation based on electron configurations.
The introduction of the concept of 'electronic isolation' and its implications in atomic structure.
The explanation of the term 'specific number of electrons' and its relevance in the study of atomic structure.
The concept of 'defence number' and its role in determining the stability of an atom.
The discussion on the differences and similarities between the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom.
The conclusion of the lecture with a reminder to subscribe and share the channel for more educational content.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
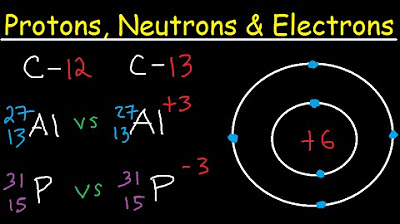
Protons Neutrons Electrons Isotopes - Average Mass Number & Atomic Structure - Atoms vs Ions

Atomic Structure full topic

GCSE Chemistry - Elements, Isotopes & Relative Atomic Mass #2
Protons, Neutrons and Electrons Explained - what's the difference?
What is an Atom? - Structure of an Atom - Atom video for kids

The Basic Structure of the Atom | Chemistry and Our Universe: How it All Works
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: