population sample parameter statistic | Gourav Manjrekar
TLDRThe video script discusses the concepts of population and sample in statistics, emphasizing the importance of understanding the position of population and the meaning of parameters. It explains how a population can be studied through samples, and introduces the different types of populations, such as finite and infinite. The script also delves into the methodology of sampling, including random and stratified sampling, and the significance of representative samples. The video aims to clarify these statistical concepts to help viewers grasp the basics of population and sample analysis.
Takeaways
- 📊 Population and sample are fundamental concepts in statistics, with population referring to the entire group under study and sample being a subset of the population.
- 🔍 The term 'parameter' is used to describe specific characteristics or attributes of a population, while 'statistics' refers to the calculated values from a sample.
- 🎯 When studying a specific group, the group itself is referred to as the population, and the individuals within it are called elements.
- 📈 Population can be of two types: finite population, which is a countable set, and infinite population, where the number of elements is uncountable.
- 🔢 Infinite population can be exemplified by the number of students or the height of students in a university, where the number is theoretically endless.
- 🔎 The process of selecting a sample from a population is called sampling, and the representativeness of the sample is crucial for accurate statistical analysis.
- 🔄 The concept of 'similar property' is important in population studies, where all items or elements within the population should share similar properties.
- 📐 The term 'sample size' refers to the number of individuals or elements within the sample, which should be representative of the population for valid statistical inferences.
- 🔽 The process of 'down sampling' involves selecting a subset of elements from a population, while 'up sampling' refers to the opposite, increasing the sample size.
- 🔄 Random sampling is a method used to ensure that every element in the population has an equal chance of being selected in the sample, thus maintaining representativeness.
- 📝 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding population and sample concepts, as well as the methods of sampling, in order to conduct effective statistical analysis and make accurate inferences.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The main focus of the video is to explain the concepts of population and sample in the context of statistical studies, including the importance of understanding the position of population and the meaning of parameters in specific studies.
What is the difference between a population and a sample in statistics?
-A population in statistics refers to the entire group of individuals or elements that are being studied, while a sample is a subset of the population that is selected for the actual data collection and analysis.
What are the two basic types of populations mentioned in the script?
-The two basic types of populations mentioned are female population and infinite population. The female population refers to the group of all females in a particular context, while the infinite population refers to a theoretical construct where the number of individuals is so large that it can be considered virtually unlimited.
What is the term used to describe a population that includes all elements of a certain type?
-The term used to describe such a population is 'finite population', which encompasses all the elements of interest for a particular study.
How is the term 'sample' defined in the context of the script?
-In the context of the script, a sample refers to a subset of individuals or elements selected from the larger population for the purpose of study. The selection of a sample is meant to represent the larger population in a way that the findings from the sample can be generalized to the entire population.
What is the significance of the term 'representative sample' in statistical studies?
-A 'representative sample' is a subset of the population that accurately reflects the characteristics of the entire population. It is crucial for valid and reliable statistical analysis because it allows researchers to make inferences about the population based on the findings from the sample.
What is the role of parameters in specific studies?
-Parameters in specific studies are numerical values that describe particular characteristics of a population. They are used to quantify attributes such as the mean, variance, or proportion within the population, which can then be used for further statistical analysis and interpretation.
How does the concept of 'random sampling' relate to the selection of a sample?
-Random sampling is a method of selecting a sample from a population in such a way that every possible subset of the same size has an equal chance of being chosen. This method helps to ensure that the sample is representative of the population and reduces the risk of bias in the study results.
What is the importance of understanding the difference between population size and sample size?
-Understanding the difference between population size and sample size is important because it helps researchers determine the appropriate sample size for a study, which can affect the precision and reliability of the results. A larger population may require a larger sample size to ensure that the sample is representative, while a smaller population may allow for a smaller sample size.
What is the significance of the term 'standard deviation of the population'?
-The standard deviation of the population is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values within the population. It is a key parameter in statistical analysis as it provides insight into the spread of the data and is used in the calculation of confidence intervals and margins of error.
How does the concept of 'sample proportion' relate to statistical analysis?
-The sample proportion refers to the proportion of a particular attribute or outcome within the sample. It is used as an estimate of the population proportion and is a fundamental concept in inferential statistics, allowing researchers to make predictions and draw conclusions about the entire population based on the sample data.
What is the role of 'sampling distribution' in statistical studies?
-The sampling distribution is the theoretical distribution of a statistic based on the probabilities of each possible sample outcome, assuming all possible samples of a given size are equally likely. It is crucial in statistical studies as it provides the basis for hypothesis testing and the calculation of confidence intervals.
Outlines
📌 Introduction to Population and Sample
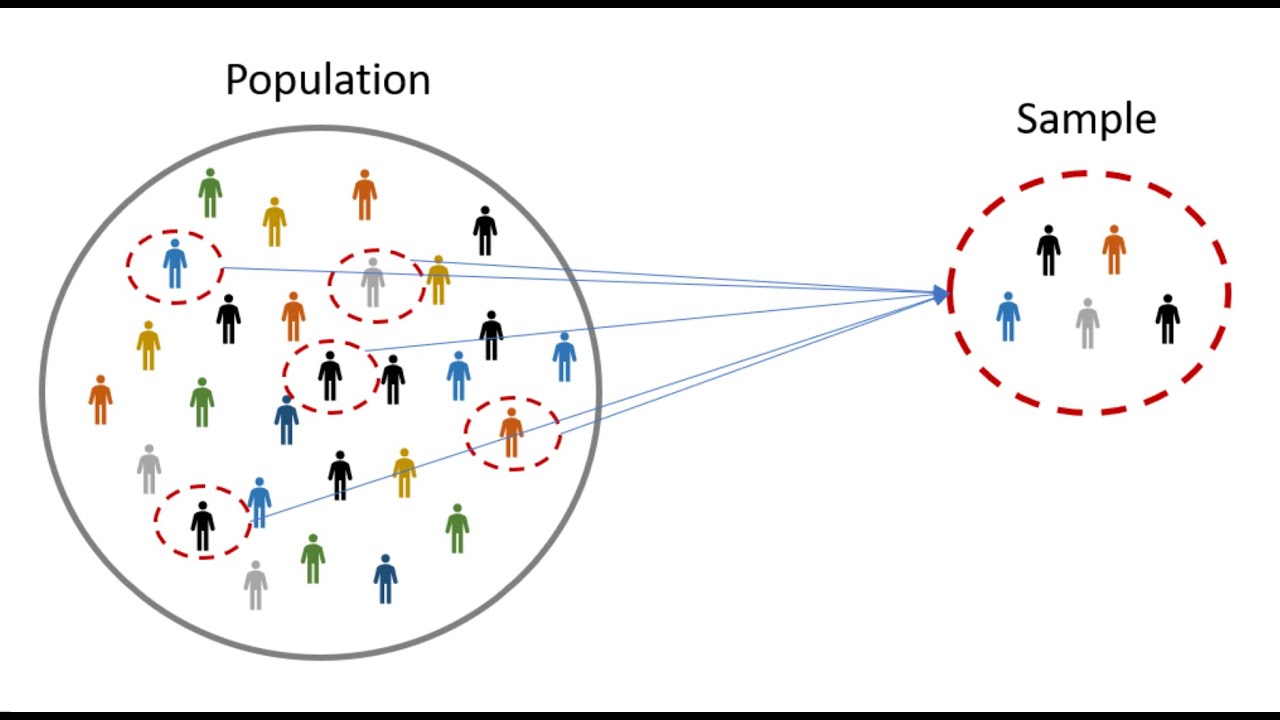
The paragraph introduces the concepts of population and sample in the context of statistical studies. It explains that the population refers to the entire group under study, while a sample is a subset of the population. The discussion includes the importance of understanding the position of the population and the meaning of the term 'population' when studying a specific group. It also touches on the idea of 'similar properties' that should be present in both the population and the sample for accurate representation.
🔍 Selecting a Sample from a Population
This paragraph delves into the process of selecting a sample from a population for statistical analysis. It highlights the challenges of studying an entire population and the practicality of using samples. The text discusses the term 'representative sample' and explains how it is chosen to ensure that the sample's characteristics are reflective of the population. It also introduces the concept of 'random sampling' and its role in ensuring that every element of the population has an equal chance of being included in the sample.
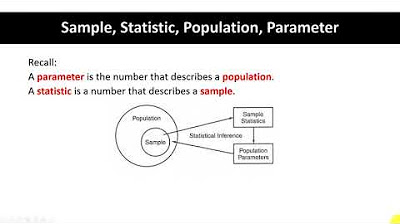
📈 Understanding Population Parameters and Sample Statistics
The paragraph focuses on the difference between population parameters and sample statistics. It clarifies that population parameters are fixed, overall characteristics of the population, such as the mean or proportion, while sample statistics are the estimates of these parameters based on the sample data. The text also discusses the concept of 'finite population correction' and its application when the population size is small. Additionally, it touches on the idea of 'infinite population' and how it relates to the selection of samples.
🔢 Types of Sampling Methods
This section discusses various sampling methods, including simple random sampling, systematic sampling, and stratified sampling. It explains how each method works and the situations in which they might be used. The paragraph also addresses the concept of 'sampling error' and 'sampling distribution', emphasizing the importance of understanding these concepts for accurate statistical analysis. The discussion includes examples and comparisons to illustrate the differences between the methods and their outcomes.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Population
💡Sample
💡Parameters
💡Statistical Constants
💡Sample Size
💡Random Sampling
💡Population Parameters
💡Sample Statistics
💡Assembly
💡Distribution
Highlights
Exploring the concepts of population and sample, understanding their definitions and applications in statistical studies.
Discussing the importance of population position and sample position in the context of specific studies.
Defining population as the entire group of individuals or elements under study.
Describing the process of selecting a sample from a population and the significance of representative sampling.
Explaining the difference between finite and infinite populations in statistical studies.
Clarifying the meaning of 'parameter' in the context of population studies.
Discussing the concept of 'similar property' in the context of population and sample studies.
Exploring the idea of 'final population' in the context of group studies and its implications.
Describing the process of selecting a sample and its impact on the understanding of the population.
Discussing the role of 'sample function' in statistical studies and its importance.
Explaining the concept of 'infant population' and its relevance in specific studies.
Discussing the process of selecting a sample and defining it as a 'representative sample'.
Describing the method of random sampling and its role in obtaining a representative sample.
Exploring the concept of 'assembly' in the context of population and sample studies.
Discussing the impact of sample size on the accuracy and reliability of statistical studies.
Clarifying the difference between 'female population' and 'sample size' in the context of statistical analysis.
Explaining the concept of 'sample proportion' and its significance in understanding the population.
Discussing the process of random sampling and its importance in achieving a representative sample.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Population vs Sample
Statistics: Populations & Samples and Parameters vs Statistics
Introduction to sampling distributions | Sampling distributions | AP Statistics | Khan Academy

01 - Sampling Distributions - Learn Statistical Sampling (Statistics Course)
Sample, Statistic, Population, Parameter Part 1

Sampling 03: Stratified Random Sampling
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: