02 - Learn Unit Conversions, Metric System & Scientific Notation in Chemistry & Physics
TLDRIn this informative video, Jason introduces viewers to the fundamentals of unit conversions and the SI system, emphasizing the importance of mastering these skills for success in chemistry and other scientific fields. He explains the metric prefixes, their corresponding values, and demonstrates a straightforward method for converting units that involves canceling out common units. Additionally, Jason covers scientific notation, a valuable tool for expressing both large and small numbers succinctly, and provides examples to illustrate the process. The video serves as a solid foundation for those new to these concepts and encourages further exploration through supplementary resources.
Takeaways
- 📐 The importance of mastering unit conversions in chemistry and other scientific fields was emphasized, as it is crucial for accurate calculations and problem-solving.
- 🔢 The SI system of units was introduced as the standard system used in chemistry, physics, and other branches of science, which includes units such as meters, kilograms, seconds, and Kelvin for length, mass, time, and temperature, respectively.
- 🌡️ The Kelvin scale was explained as the absolute temperature scale where zero Kelvin represents the cessation of all atomic motion, although mostly Celsius will be used in practice.
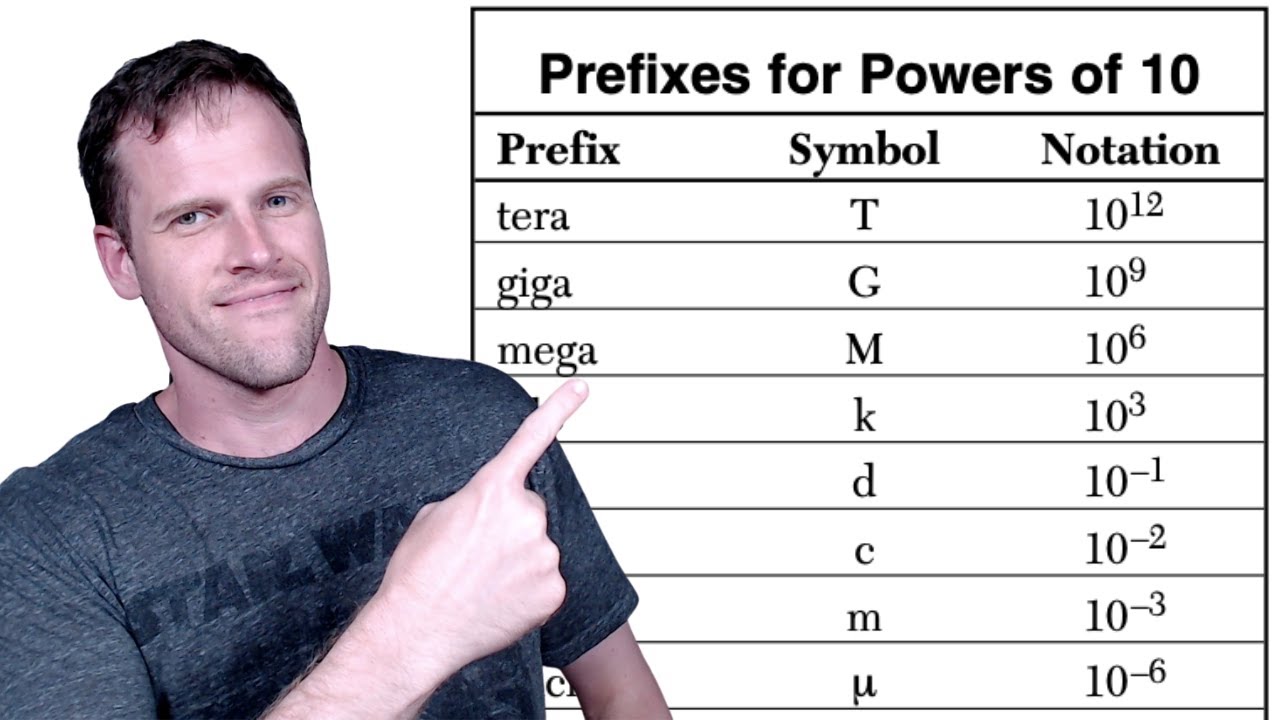
- 📈 The concept of metric prefixes was detailed, showing how they are used to create different orders of magnitude for the base units, with examples like kilo (1000), milli (0.001), and micro (0.000001).
- 🔄 A systematic method for unit conversion was taught, involving setting up a conversion factor and canceling out units to arrive at the desired unit, which simplifies the process and reduces the chance of errors.
- 🤓 The use of scientific notation was introduced as a way to handle very large or very small numbers, with examples provided on how to convert numbers into this format and the significance of the exponent in determining the placement of the decimal point.
- 📚 The script mentioned a comprehensive resource for further learning on unit conversions, a four-hour tutorial DVD, which can be accessed on the website for additional practice and understanding.
- 🎓 The importance of practice in unit conversions and scientific notation was stressed, as repetition is key to mastering these essential skills for success in chemistry and science studies.
- 🚀 The power of the metric system's base 10 structure was highlighted, making it easier to remember and apply conversion factors, and how it contrasts with the less uniform English system of units.
- 📈 The script provided practical examples of unit conversions, such as converting meters to kilometers and centimeters to millimeters, demonstrating the application of the taught method and the importance of getting the correct unit at the end.
- 🌟 The significance of understanding the metric system and scientific notation was reiterated as fundamental to progressing in chemistry and other scientific disciplines, with the potential to save time and effort in problem-solving.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of this chemistry tutorial section?
-The primary focus of this section is on understanding units and unit conversions in the context of chemistry, particularly within the SI system of units.
Why is the SI system of units important in chemistry and other scientific fields?
-The SI system of units is important because it provides a standardized system for measuring and communicating scientific data, facilitating calculations and comparisons across different studies and disciplines.
What are the base units used in the SI system for length, mass, time, and temperature?
-The base units in the SI system are the meter for length, kilogram for mass, second for time, and Kelvin for temperature.
What is the significance of metric prefixes in the metric system?
-Metric prefixes are significant because they allow for easy scaling of units by powers of ten, making calculations and conversions more straightforward and intuitive within the metric system.
How does the tutorial suggest one should approach unit conversions?
-The tutorial suggests approaching unit conversions by setting up a conversion factor as a fraction, canceling out the units that are not needed, and multiplying or dividing by the appropriate power of ten to achieve the desired unit.
What is the method for converting a larger unit to a smaller unit using the metric system?
-To convert a larger unit to a smaller unit, you multiply the value by the conversion factor that corresponds to the metric prefix (e.g., 1 kilometer is 1000 meters, so you multiply by 1000 to convert kilometers to meters).
What is scientific notation, and why is it used?
-Scientific notation is a way of expressing very large or very small numbers by moving the decimal point to the right or left and multiplying by a power of ten. It simplifies the writing and manipulation of numbers in scientific calculations.
How can you convert a number given in scientific notation back to its standard form?
-To convert a number from scientific notation to its standard form, you move the decimal point to the right for positive exponents or to the left for negative exponents the number of places indicated by the exponent, and then add the appropriate number of zeros.
What is the recommended approach for learning and mastering unit conversions and scientific notation?
-The recommended approach is to practice regularly with various problems, watch the entire tutorial series in order, and utilize additional resources like the unit conversion tutor for more detailed explanations and practice.
Why is it important to master unit conversions in chemistry?
-Mastering unit conversions is crucial in chemistry because it allows for accurate calculations involving reactions, molecular quantities, and other chemical processes, which are essential for understanding and solving chemical problems.
What are some examples of metric prefixes and their corresponding powers of ten?
-Examples include kilo (10^3), which means 1000, milli (10^-3), which means 0.001, micro (10^-6), which means 0.000001, and pico (10^-12), which means 0.000000000001.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Units and Unit Conversions
This paragraph introduces the importance of understanding units and unit conversions in the study of chemistry. It emphasizes the SI system of units as the standard for scientific measurements and highlights the significance of mastering unit conversions for problem-solving in chemistry and related fields. The speaker also mentions a comprehensive resource for learning unit conversions, suggesting that it can greatly aid in grasping scientific concepts and calculations.
📏 Base Units and Metric Prefixes
In this paragraph, the speaker explains the base units of the SI system, including the meter for length, kilogram for mass, second for time, and Kelvin for temperature. It also delves into the concept of metric prefixes, which are essential for expressing larger or smaller units of measure. The explanation includes examples of how prefixes like kilo, deci, centi, milli, micro, and nano relate to the base unit of meter, demonstrating how they represent powers of ten.
🔄 Understanding Unit Conversion
The speaker provides a detailed method for converting units within the metric system. By using a step-by-step approach, the paragraph explains how to set up unit conversions in a way that allows for easy calculation without memorizing numerous conversion factors. The method involves writing down the known quantity, the desired unit, and the conversion factor, then performing the calculation in a manner that cancels out unwanted units, leaving the desired unit as the result.
📊 Scientific Notation for Large and Small Numbers
This paragraph introduces scientific notation as a method for writing very large or very small numbers in a more concise form. The explanation covers how to shift the decimal point according to the exponent and how to convert numbers between scientific notation and standard form. The speaker emphasizes the practicality of scientific notation for representing large quantities, such as distances in the universe, and very small measurements, like molecular sizes.
🎓 Encouragement for Sequential Learning
The speaker concludes the script by encouraging a systematic approach to learning chemistry. He advises watching the educational content in order and practicing unit conversions to build a strong foundation. The speaker also promotes a resource for further practice and assures that following this structured learning path will prevent confusion and enhance understanding of complex topics in chemistry.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡SI system of units
💡Unit conversions
💡Metric prefixes
💡Scientific notation
💡Base units
💡Conversion factors
💡Chemistry
💡Temperature scales
💡Atomic motion
💡Unit Conversion Tutor
Highlights
The importance of understanding the SI system of units and its application in chemistry, physics, and other scientific fields.
The base units in the SI system: meter for length, kilogram for mass, second for time, and Kelvin for temperature.
The concept of metric prefixes and their relationship to the base units, making calculations and conversions easier.
The method for unit conversion that involves setting up a ratio with units that cancel each other out, leading to the desired unit.
The use of scientific notation for simplifying the representation of very large or very small numbers.
The explanation of how to convert units using the metric system, with examples such as converting meters to kilometers and centimeters to meters.
The demonstration of converting a length measurement from centimeters to millimeters using the method of connecting the dots with known conversion factors.
The clarification that the unit conversion method can be applied to any unit of measurement, not just within the metric system.
The emphasis on the practicality of unit conversion techniques in solving chemistry problems and the recommendation to practice these methods.
The introduction to scientific notation, including how to convert a normal number into scientific notation and vice versa.
The explanation of how to handle large exponents in scientific notation, moving the decimal point to the right for positive exponents and to the left for negative exponents.
The importance of mastering unit conversion and scientific notation for success in chemistry and other scientific studies.
The availability of additional resources, such as the unit conversion tutor DVD, for those who need more practice and detailed information on these topics.
The structured approach to learning chemistry, starting with the fundamentals like units and unit conversions, before moving on to more complex topics like chemical reactions.
The encouragement for learners to follow the course material in order and to practice problems to gain a solid understanding of the concepts.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

2.4 Units and Conversions | High School Chemistry
Converting units of measurement with scientific notation (3 examples)

Chemistry Reference table C
How to Convert Units in Chemistry

prefixes in measurement explained and how to use them

Converting Metric Units Of Measure For Dosage Calculation | @LevelUpRN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: