Types of Chemical Reactions
TLDRThis video script delves into the identification of various chemical reaction types, including combustion, synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement reactions. It explains each reaction's characteristics, provides examples, and discusses their applications. The script also touches on redox reactions and the importance of recognizing reaction types for understanding chemical processes.
Takeaways
- 🔥 Combustion reactions involve the burning of a substance, typically releasing heat energy and producing carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
- 🌿 Synthesis reactions, also known as combination reactions, involve combining two or more substances to form a single product, often resulting in a more complex compound.
- 📈 Decomposition reactions are the opposite of synthesis reactions, breaking down a single compound into two or more simpler substances.
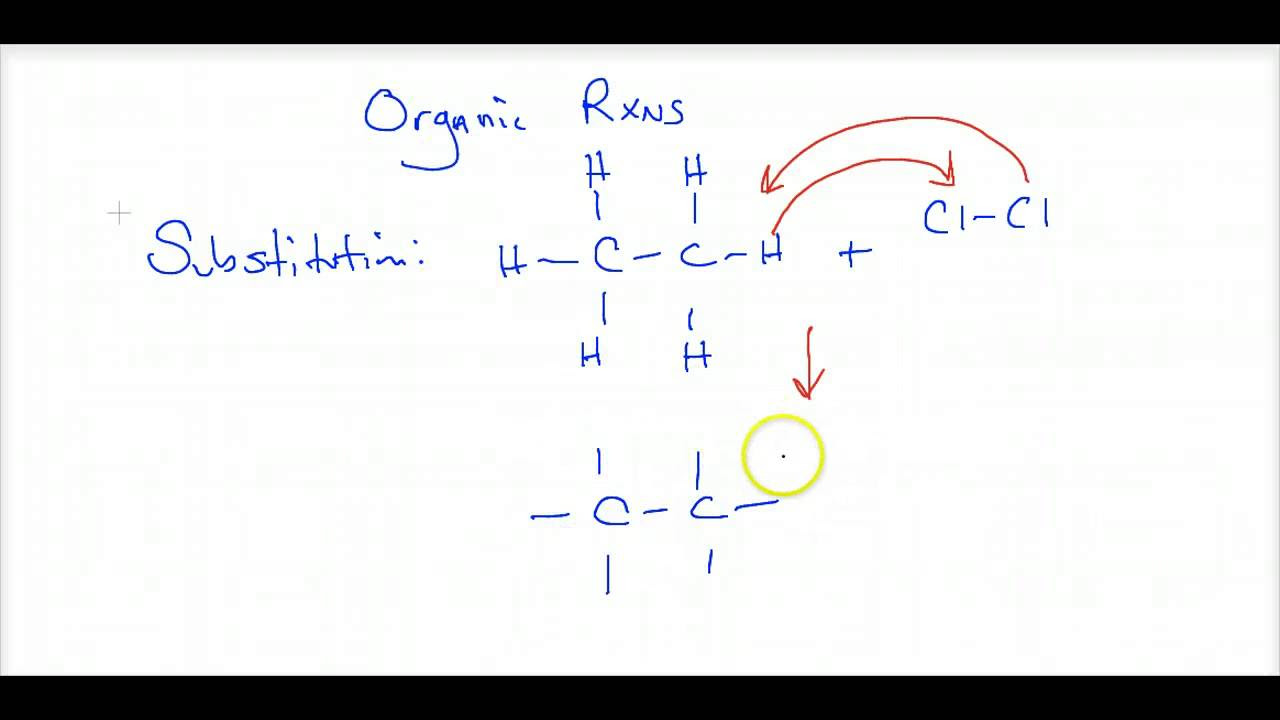
- 🔄 Single replacement reactions occur when an element reacts with a compound, displacing another element within that compound.
- 🔄 Double replacement reactions involve two compounds exchanging components to form two new compounds.
- 💧 Precipitation reactions are a type of double replacement reaction where a solid product forms when two aqueous solutions are mixed.
- 🌬️ Gas evolution reactions occur when two aqueous solutions react to produce a gaseous product.
- 🧪 Acid-base neutralization reactions result in the formation of water and a salt when an acid and a base are mixed.
- 🔥 Combustion reactions are redox reactions, characterized by the transfer of electrons, with oxygen typically being reduced and the hydrocarbon being oxidized.
- 📊 Understanding the products and reactants of a reaction is crucial for classifying it correctly, as different types of reactions have distinct characteristics and outcomes.
Q & A
What is a combustion reaction?
-A combustion reaction is a type of chemical reaction where a substance typically burns, releasing a significant amount of heat energy. It usually involves a hydrocarbon reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, both of which are in gaseous form due to the high temperatures generated during the reaction.
How can you identify a synthesis reaction?
-A synthesis reaction, also known as a combination reaction, is identified by the combination of two or more smaller substances to form a larger, more complex product. It often involves an element reacting with another element or two compounds combining to form a larger compound.
What is the main characteristic of a decomposition reaction?
-A decomposition reaction is characterized by the breakdown of a larger or more complex substance into two or more smaller components. It is essentially the reverse process of a synthesis reaction.
What happens in a single replacement reaction?
-In a single replacement reaction, a pure element reacts with a compound, resulting in the displacement of one of the elements in the compound. The intruding element forms a new compound with one part of the original compound, while the displaced element is released as a pure substance.
How does a double replacement reaction differ from a single replacement reaction?
-A double replacement reaction involves two compounds exchanging components to form two new compounds, whereas a single replacement reaction involves a pure element and a compound where the element displaces another in the compound.
What are the three types of double replacement reactions mentioned in the script?
-The three types of double replacement reactions are precipitation reactions, which result in a solid product when two aqueous solutions are mixed; acid-base neutralization reactions, where an acid and a base react to form salt and water; and gas evolution reactions, where mixing two aqueous solutions produces a gaseous product.
Why are all combustion reactions considered redox reactions?
-All combustion reactions are redox reactions because they involve a transfer of electrons. Oxidation, the loss of electrons, occurs when the hydrocarbon is converted into carbon dioxide and water, while reduction, the gain of electrons, happens when oxygen goes from its elemental form to being part of the oxygen molecules in carbon dioxide and water.
What is the role of heat in a decomposition reaction involving a metal carbonate like magnesium carbonate?
-Heat acts as a trigger for the decomposition of metal carbonates like magnesium carbonate. When heat is applied, it causes the volatile component, such as CO2, to escape into the air, leaving behind the metal oxide.
How does the reaction between sodium bicarbonate and hydrochloric acid classify?
-The reaction between sodium bicarbonate and hydrochloric acid can be classified in multiple ways. Initially, it is a double replacement reaction where sodium pairs up with chlorine to form sodium chloride, and hydrogen pairs up with bicarbonate to form carbonic acid. Subsequently, carbonic acid decomposes into water and carbon dioxide, making it a decomposition reaction. Overall, it is often considered a gas evolution reaction because it produces CO2 gas when two aqueous solutions are mixed.
What is the general equation for a synthesis reaction?
-The general equation for a synthesis or combination reaction is A + B → AB, where A and B are two or more reactants that combine to form a single product, AB.
What is the general equation for a single replacement reaction?
-The general equation for a single replacement or displacement reaction is A + BC → AC + B, where A is a pure element that reacts with a compound BC, displacing B and forming a new compound AC.
Outlines
🔥 Introduction to Chemical Reactions
The video begins with an introduction to different types of chemical reactions, focusing on combustion reactions first. Combustion reactions involve burning, releasing heat energy, and producing carbon dioxide (CO2) and water. Examples include the reaction of octane (found in gasoline) and ethanol (found in alcoholic products) with oxygen. These reactions are useful for generating heat and are characterized by the production of gases and vapors.
🤝 Synthesis and Combination Reactions
The second paragraph discusses synthesis or combination reactions, where two smaller substances combine to form a larger one. This can involve elements or compounds. Examples given include the reaction of magnesium with oxygen to form magnesium oxide, and the reaction of magnesium oxide with carbon dioxide to form magnesium carbonate. The key feature is the creation of a more complex substance from simpler ones.
⤴️ Decomposition Reactions
Decomposition reactions are the reverse of synthesis reactions, breaking down larger or complex substances into smaller components. The paragraph provides examples such as heating metal carbonates to produce metal oxides and CO2, and the electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen and oxygen gases. The general equation for a decomposition reaction is a b → a + b.
🔄 Single Replacement Reactions
Single replacement or displacement reactions involve a pure element reacting with a compound, resulting in the element taking the place of another element in the compound. Examples include zinc displacing copper in a copper chloride solution and bromine displacing iodide in a sodium iodide solution. The general equation for this type of reaction is a + bc → ac + b.
🔀 Double Replacement Reactions
Double replacement or displacement reactions occur when two compounds exchange components to form two new compounds. The paragraph explains this with examples such as silver nitrate reacting with sodium chloride to form silver chloride (a solid) and sodium nitrate (an aqueous solution). The video also introduces different types of double replacement reactions, including precipitation reactions, acid-base neutralization reactions, and gas evolution reactions.
📝 Quiz on Reaction Types
The paragraph presents a quiz to classify different reactions based on the types discussed earlier. Reactions involving decomposition, single replacement, synthesis, double replacement, and other types are analyzed. The quiz reinforces the understanding of reaction classification, emphasizing the characteristics of each reaction type and their identification through the products and reactants involved.
🔄 Redox Reactions and Their Characteristics
This paragraph delves into oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions, explaining that single replacement and combustion reactions are always redox reactions, while double replacement reactions are never redox reactions. It also discusses the characteristics of redox reactions, such as the presence of pure elements and compounds, and the transfer of electrons. The paragraph further clarifies the conditions under which decomposition and synthesis reactions are considered redox reactions.
🌟 Summary of Chemical Reactions
The final paragraph summarizes the main types of chemical reactions covered in the video. It reiterates the definitions and examples of decomposition, synthesis, single replacement, double replacement, and combustion reactions. It also mentions the three types of double replacement reactions: precipitation, acid-base neutralization, and gas evolution reactions, providing a concise review for the viewer.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Combustion Reaction
💡Synthesis Reaction
💡Decomposition Reaction
💡Single Replacement Reaction
💡Double Replacement Reaction
💡Redox Reaction
💡Precipitation Reaction
💡Acid-Base Neutralization Reaction
💡Gas Evolution Reaction
💡Thermal Decomposition
Highlights
Combustion reactions involve burning and release a lot of heat energy, typically producing carbon dioxide and water.
In a combustion reaction, hydrocarbons react with oxygen, generating heat and gas molecules that can be used for mechanical work, such as driving a car.
Synthesis reactions, also known as combination reactions, involve combining two or more substances to form a single product.
Decomposition reactions are the reverse of synthesis reactions, breaking down a single compound into two or more simpler substances.
Single replacement reactions involve an element displacing another element in a compound, resulting in a new element and a new compound.
Double replacement reactions occur when two compounds exchange components to form two new compounds.
Precipitation reactions are a type of double replacement reaction where a solid product forms when two aqueous solutions are mixed.
Acid-base neutralization reactions are a specific type of double replacement reaction that produces salt and water when an acid and a base are mixed.
Gas evolution reactions occur when two aqueous solutions are mixed and a gas is produced.
All single replacement and combustion reactions are redox reactions, involving the transfer of electrons.
Decomposition reactions that break down a compound into pure elements are redox reactions, while those that form smaller compounds from a larger one are not.
Synthesis reactions involving two pure elements combining to form a compound are redox reactions, but those forming larger compounds from smaller ones are not.
Combustion reactions are characterized by the presence of CO2 and water as products and are exothermic, releasing energy.
The reaction of magnesium with oxygen, producing magnesium nitride, is a synthesis reaction and also an oxidation-reduction reaction.
The reaction of pentane with oxygen, producing CO2 and water, is a combustion reaction and also a redox reaction.
The reaction of sodium bicarbonate with hydrochloric acid is complex, involving double replacement, decomposition, and gas evolution reactions.
Understanding the different types of chemical reactions is crucial for identifying and predicting the outcomes of various chemical processes.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

4.2 Types of Chemical Reactions | High School Chemistry
Crash Course Regents Chemistry 12 - Reaction Review

Chemical Reactions

Classifying Types of Chemical Reactions With Practice Problems | Study Chemistry With Us

Classifying Types of Chemical Reactions Practice Problems

Chemical Reactions - Combination, Decomposition, Combustion, Single & Double Displacement Chemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: