Calculate Work to Pump Water Out of Rectangular Tank
TLDRThis instructional video demonstrates the process of calculating the work required to pump half the water out of an aquarium. The tank is 2 meters long, 1 meter wide, and 1 meter deep. The video guides viewers through setting up the problem by drawing the tank and establishing the x and y axes, then explains the integral formula for work, considering water density, distance, and area of each layer. Using a density of 9800 kg/m³ for the calculation, the video concludes with the integral evaluation, resulting in 2450 Joules as the work needed to move half the water.
Takeaways
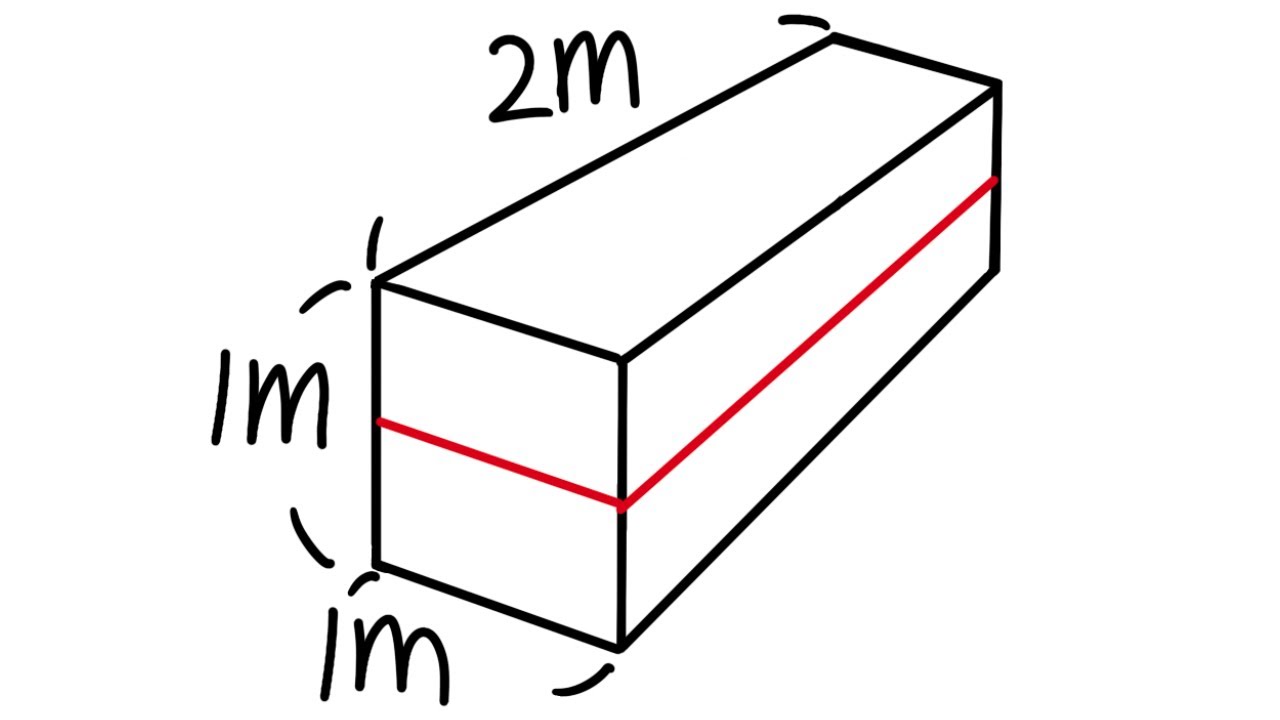
- 📏 The problem involves calculating the work required to pump half the water out of an aquarium with dimensions 2 meters long, 1 meter wide, and 1 meter deep.
- 📐 The aquarium is visualized with an x and y-axis, with the y-axis pointing downwards and the y direction being positive.
- 💧 The task is to pump water from 0 to 1/2 of the tank's depth, representing half of the water.
- 🔄 The process involves imagining multiple layers of water and calculating the work to lift each layer to the top.
- 📚 The formula for work (W) is given as the integral of the product of density, distance (y), area, and dy from the bottom to the top of the water layers.
- 🔢 The density of water is 9800 kg/m^3 for SI units, which results in work being measured in joules.
- 🏢 For imperial units, the density would be 62.5 lb/ft^3, and work would be measured in foot-pounds.
- 📏 The distance each layer of water is pulled is simply y, and the area of each water layer is constant at 2 m^2 (length times width).
- ∫ The integral to solve is 19,600 times the integral of y with respect to y from 0 to 1/2.
- 📉 The anti-derivative of y with respect to y is y^2/2, and the work is calculated by evaluating this from 1/2 to 0.
- 📝 The final calculation simplifies to 19,600 times (1/2)^3, which equals 2450 joules, representing the work needed to pump half the water out of the aquarium.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is to demonstrate how to calculate the work required to pump half of the water out of an aquarium.
What are the dimensions of the aquarium mentioned in the video?
-The aquarium is described as being 2 meters long, 1 meter wide, and 1 meter deep.
What is the significance of the x and y axis in the context of the problem?
-The x and y axis are used to represent the spatial dimensions of the aquarium and to define the range of water levels from which water needs to be pumped out (from 0 to 1/2 meter).
How much water does the problem ask to pump out of the aquarium?
-The problem asks to calculate the work needed to pump out half of the water in the aquarium.
What is the formula for work in this context?
-The formula for work in this context is W = ∫(density * distance * area * dy) from the bottom to the top of the water layer.
What is the density of water used in the formula if the problem is in meters?
-If the problem is in meters, the density of water used in the formula is 9800 kg/m³.
What is the area of the layer of water being pumped out?
-The area of the layer of water being pumped out is the base area of the aquarium, which is 2 meters by 1 meter, equaling 2 square meters.
How is the integral calculated in the formula for work?
-The integral is calculated by integrating the product of the density, distance (y), and area of the water layer from 0 to 1/2 meter.
What is the final result of the work required to pump out half of the water?
-The final result of the work required is 2450 Joules.
Why is the unit of the work calculated in Joules?
-The unit of the work is Joules because the length is given in meters, which is a standard unit for calculating work in the metric system.
What happens if the problem was given in feet instead of meters?
-If the problem was given in feet, the work would be calculated in foot-pounds and the density of water would be a different value, 62.5 lb/ft³.
Outlines
📏 Calculating Work to Pump Water from an Aquarium
This paragraph explains the process of calculating the work required to pump half of the water out of an aquarium. The aquarium is described as being 2 meters long, 1 meter wide, and 1 meter deep, filled with water. The problem involves visualizing the tank, setting up the x and y axes, and understanding that the work involves pumping water from the bottom half of the tank. The work formula is introduced, which includes the integral of the product of density, distance, area, and a differential element dy, from the bottom to the top of the water layer. The density is given as 9800 kg/m³ for metric units, and the area of the water layer is calculated as 2 square meters. The integral is then simplified and evaluated to find the total work needed.
🔢 Final Calculation of Work in Joules
The second paragraph focuses on the final steps of the calculation. It starts by simplifying the integral expression to a constant times the integral of y with respect to y, from 0 to 1/2. The anti-derivative of y is then found, and the limits of integration are applied to evaluate the integral. The calculation results in a work value of 2450 joules, which is the amount of work needed to pump out half of the water from the aquarium, given that the measurements are in meters and thus the work is measured in joules.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Work
💡Aquarium
💡Density
💡Integral
💡Area
💡Volume
💡Layer
💡Distance
💡Joules
💡Anti-derivative
💡Power
Highlights
Introduction to calculating work needed to pump water out of an aquarium.
Aquarium dimensions provided: 2m long, 1m wide, 1m deep.
Problem is to find work to pump out half the water.
Step-by-step approach to solving the problem.
Drawing the aquarium and setting up the x and y axes.
Explanation of the y direction being positive and tank depth.
Pumping water from 0 to 1/2 of the tank depth.
Visualizing multiple layers of water to be pumped.
Distance each layer is pulled is denoted as y.
Work formula introduced: W = integral of density * distance * area * dy.
Explanation of the limits of integration (0 to 1/2).
Density value depends on units (meters or feet).
Distance pulled is simply y.
Area of water layer is base times height (2m * 1m = 2m²).
Simplifying the integral by moving constants outside.
Evaluating the integral to find the work done.
Final calculation and result: 2450 Joules.
Explanation of the answer and unit (Joules) based on given dimensions.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video
calculating work, pumping water out of a rectangular tank, calculus 2 tutorial
Calculate Work to Pump Liquid Out of Tanks - Calculus 2
calculating work by using integral, pumping water out of a tank, calculus 2 tutorial
Pumping water out of a spherical tank, calculating work, calculus 2 tutorial
Pumping water out of a bucket, calculating work, calculus 2 tutorial
Calculating Work, pumping water out of a tank, calculus 2 tutorial, application of integration
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: