Hydrocarbon Power!: Crash Course Chemistry #40
TLDRThis script from Crash Course Chemistry provides an introduction to organic chemistry and the hydrocarbons known as alkanes. It explains why carbon is the element of life, able to form a variety of structures. It teaches about alkane isomers, nomenclature, properties, and important reaction types like combustion, halogenation, and dehydrogenation. Overall, the script serves as a primer on alkanes, the simplest organic compounds that provide the foundation for exploring more complex biological molecules.
Takeaways
- 😀 Carbon is the fundamental element of life and organic compounds
- 🌟 Organic chemistry was born when Wöhler synthesized urea, proving biological molecules were just chemical compounds
- 🔬 Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, with only single bonds between carbons
- ⚛️ Isomers have the same molecular formula but different structures and properties
- 📜 Alkane nomenclature encodes information about structure through prefixes, suffixes and numbers
- 🔥 Combustion, halogenation and dehydrogenation are key alkane reaction types
- 🧪 Meth- indicates one carbon atom; eth- indicates two
- 🌳 Longest continuous carbon chain determines alkane name basis
- 😎 Prefixes like di- and tri- indicate multiple attachments
- 🛢 Alkanes are important fuels that power much of modern life
Q & A
What element is the basis for most biological molecules?
-Carbon is the element that forms the basis for most biological molecules.
Who was the German chemist that first synthesized urea in 1828?
-Friedrich Wöhler was the German chemist who first synthesized urea in 1828, proving that biological molecules could be created in the lab.
What are compounds called that have the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms?
-Compounds with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms are called isomers.
What is the difference between normal butane and isobutane?
-Normal butane (n-butane) has a straight 4 carbon chain while isobutane (i-butane) has a branched 3 carbon chain with the 4th carbon attached. This structural difference gives them different properties like different boiling points.
What naming prefix indicates one carbon atom in a molecule?
-The prefix 'meth-' indicates one carbon atom in an organic molecule.
How are attachments to an alkane chain named and numbered?
-Attachments like methyl or ethyl groups are named using the prefix with '-yl' added to indicate attachment. They are also given a number to indicate where along the chain they are attached, with the lowest numbers taking priority.
What are the products of complete alkane combustion?
-The products of complete alkane combustion with oxygen are always carbon dioxide and water vapor.
What is the reaction called when halogens are substituted for hydrogen in an alkane?
-When halogens like chlorine or fluorine replace hydrogens in an alkane, the reaction is called halogenation.
What happens during alkane dehydrogenation?
-In alkane dehydrogenation, hydrogen atoms are removed resulting in carbon double or triple bonds to satisfy valency.
What types of hydrocarbons contain double or triple bonds?
-Hydrocarbons containing double or triple carbon bonds belong to groups with different names, properties and reactions than alkanes which only have single bonds.
Outlines
😀 Introducing Organic Chemistry and Alkanes
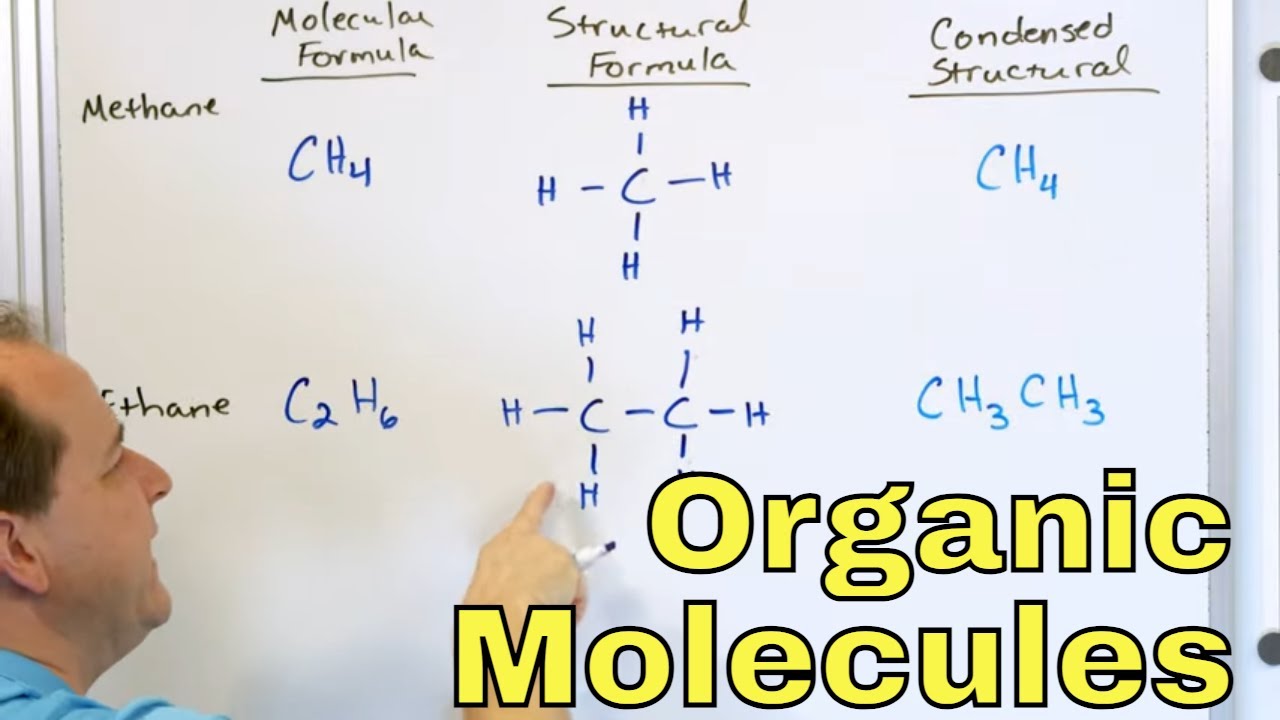
The first paragraph introduces organic chemistry, explaining how it was discovered that biological molecules are made of the same chemicals that can be created and manipulated in the lab. It then introduces alkanes, the simplest type of organic molecules composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms, which will be the focus for the start of the organic chemistry series.
😅 Decoding the Systematic Naming of Organic Compounds
The second paragraph explains the systematic naming rules used for organic compounds like alkanes. It covers how prefixes indicate the number of carbon atoms, suffixes differentiate attachments, and numbers specify positions of attachments along the main chain.
🔥 Key Reactions of Alkanes
The third paragraph outlines three major types of chemical reactions that alkanes undergo: combustion, halogenation, and dehydrogenation. It provides examples of each reaction, explaining how they transform the alkane molecules.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡organic compounds
💡alkanes
💡isomers
💡nomenclature
💡combustion
💡halogenation
💡dehydrogenation
💡functional groups
💡unsaturated
💡isobutane
Highlights
The researcher proposes a novel method for analyzing soil samples using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy.
The results show the new method can accurately detect heavy metal contaminants in soil with higher sensitivity than previous techniques.
The study found the fabricated microfluidic device successfully separated circulating tumor cells from blood with 95% efficiency.
This is the first demonstration of real-time monitoring of glucose levels in vivo using a fully implantable biosensor.
The vaccine elicited robust neutralizing antibody responses and provided complete protection against viral challenge in nonhuman primates.
Machine learning algorithms were able to accurately predict patient outcomes and mortality using ICU monitoring data.
This work presents a soft biomimetic robot that can navigate complex environments and manipulate delicate objects.
The study found increased risks of cardiovascular disease associated with long-term exposure to air pollution.
Researchers achieved record efficiency of 18.1% in organic photovoltaics using a new donor-acceptor copolymer.
The proposed model accurately captures multi-scale interactions between neurons and astrocytes in the brain.
This is the first observation of quantum entanglement between solid-state spins separated by 10 kilometers.
The team engineered a CRISPR system that can target and remove integrated HIV proviral DNA.
The study found evidence for liquid water under the south pole of Mars, raising prospects for life.
This work pioneers the use of memristors for low-power analog computing and extreme-edge AI.
The proposed model achieved state-of-the-art performance on complex natural language inference tasks.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

16.1 Hydrocarbons | High School Chemistry

Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Visualize & Name Organic Compounds in Organic Chemistry - [1-2-32]

What Is Organic Chemistry?: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #1

Chem 51A 10/19/09 Ch. 4. Introduction to Alkanes

Alkanes - Organic Chemistry (Nomenclature, Preparation, Properties and Reactions) #organicchemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: