01 - Velocity And Acceleration In 1-D (Physics Tutor)
TLDRThe video script is a transcript of a physics tutorial focusing on fundamental concepts such as one-dimensional motion, displacement, velocity, and acceleration. The instructor emphasizes the importance of understanding word problems in physics and provides a straightforward approach to solving them. The script covers the definition of displacement as the change in position, the concept of velocity as speed with a direction, and the calculation of average velocity over time. It also delves into the calculation of average acceleration, using a creative example of a person being shot out of a cannon to illustrate the concept. The instructor uses this example to show how to determine the time taken for an object to travel a certain distance when the final velocity is known, and then calculates the average acceleration experienced. The summary concludes with a comparison of the calculated acceleration to the acceleration due to gravity, highlighting the extreme forces involved in such a scenario.
Takeaways
- 📚 Start with Basics: The course begins with fundamental concepts of physics, emphasizing one-dimensional motion as the initial topic.
- 🚀 Practical Approach: Instead of lengthy lectures, the teaching method involves working through example problems to understand physics concepts.
- 🤔 Word Problems: The tutor highlights that physics is challenging because it involves word problems, which require understanding the context and applying math to solve.
- 📈 Displacement: Defined as the change in position, measured from the initial to the final position, with the formula ΔX = X_final - X_initial.
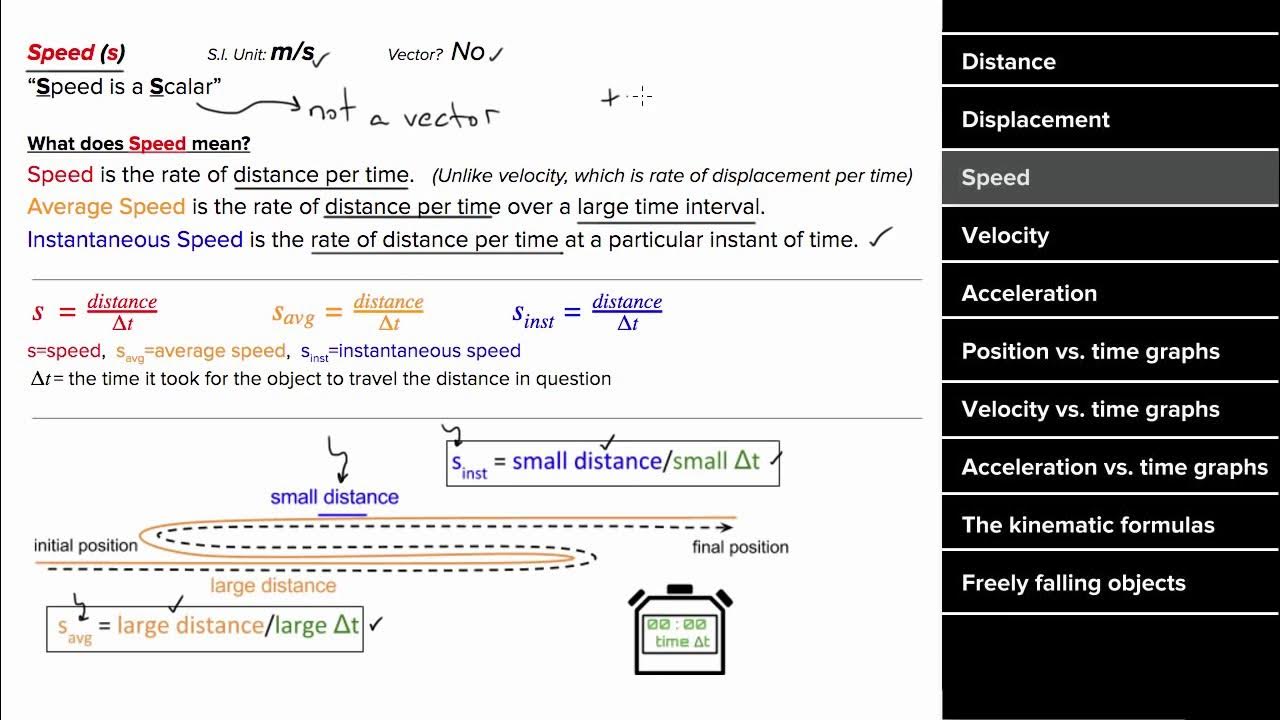
- 🏎️ Velocity: Describes the speed and direction of an object's motion, with units of meters per second (m/s) in physics.
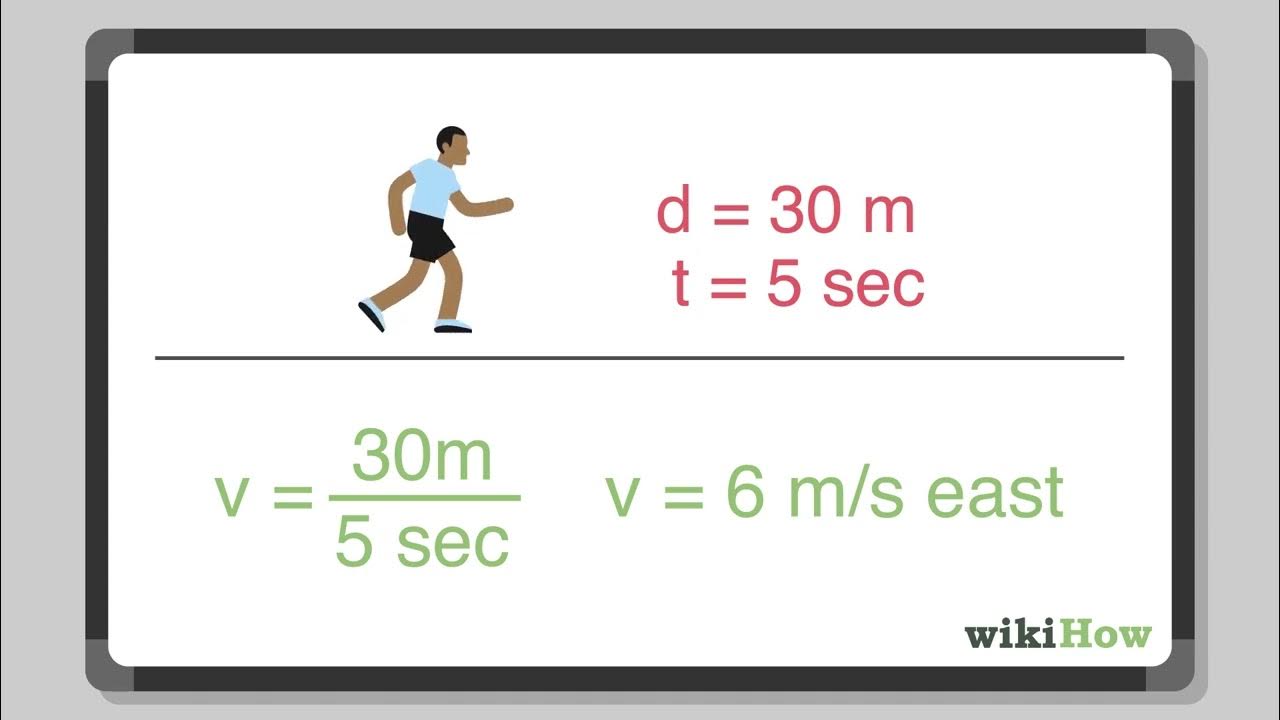
- 🌟 Average Velocity: Calculated as the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken, with the formula v̄ = ΔX / ΔT.
- ⏳ Time and Distance Conversion: The importance of converting units of time (seconds, minutes, hours) and distance (yards, feet, miles) to maintain consistency in calculations.
- 📉 Deceleration Example: An example of calculating average velocity when an object is slowing down is provided, illustrating the concept of changing velocity over time.
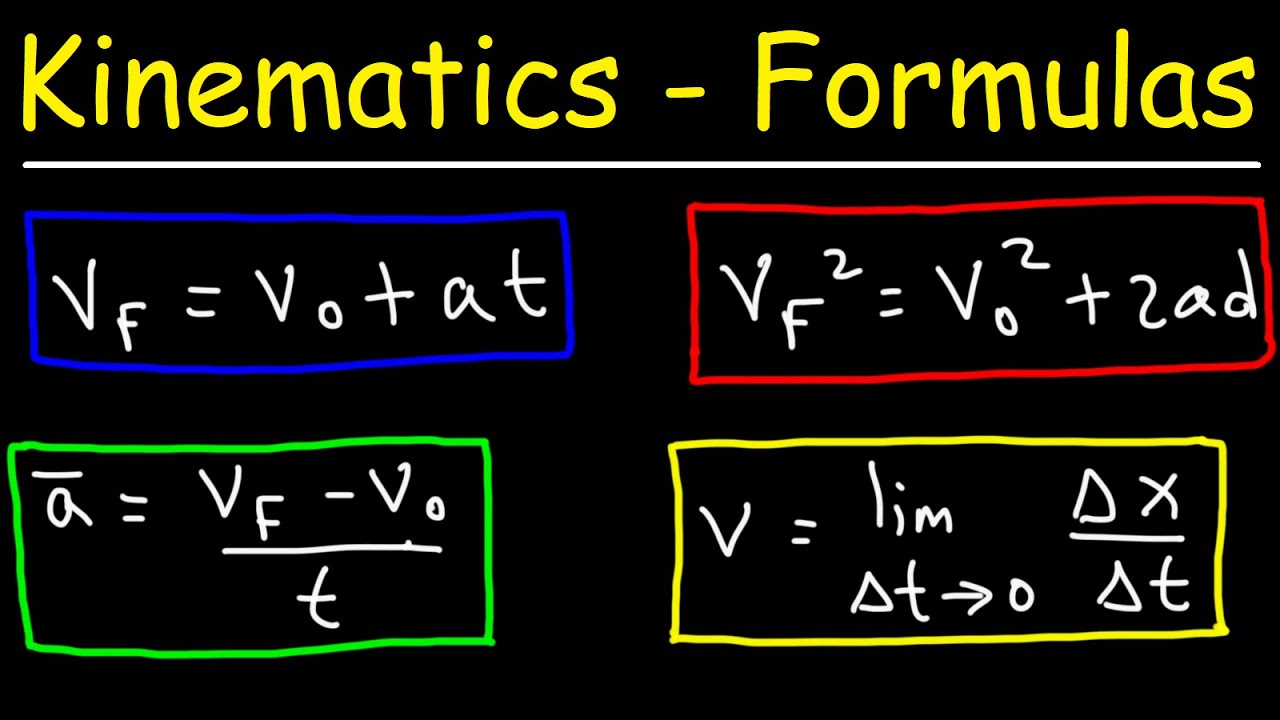
- 🚀 Acceleration: Defined as the rate of change of velocity with time, with units of meters per second squared (m/s²).
- 🧮 Unit Conversion: A detailed example of converting yards to miles and seconds to hours is given to demonstrate unit conversion in physics problems.
- 🎯 Applying Concepts: The script concludes with a problem-solving approach, showing how to apply the concepts of velocity, acceleration, and unit conversion to a hypothetical scenario of a person being shot out of a cannon.
Q & A
What is the main approach of the physics tutor in this DVD course?
-The main approach of the physics tutor is to teach physics through working example problems rather than through boring lectures and complex derivations.
Why does the tutor find physics challenging to teach?
-The tutor finds physics challenging to teach because it often involves word problems, which most people struggle with, and the steps to solve physics problems are not always clear.
What is the first topic typically covered in a physics course?
-The first topic typically covered in a physics course is one-dimensional motion.
What does the term 'displacement' mean in physics?
-In physics, 'displacement' refers to the change in position of an object and is defined as the final position minus the initial position (ΔX = X_final - X_initial).
How is velocity different from speed?
-Velocity is similar to speed, but while speed only indicates how fast an object is moving, velocity also includes the direction of the movement.
What is the unit of displacement in physics?
-The unit of displacement in physics is typically meters.
How is average velocity calculated?
-Average velocity is calculated by dividing the total displacement (ΔX) by the total time (ΔT) taken for the movement.
What is the formula to calculate the speed or velocity of an object?
-The formula to calculate speed or velocity is distance over time (v = Δx / Δt).
How is unit conversion done in physics?
-Unit conversion in physics is done by using conversion factors and canceling out the units you don't want in the final answer, ensuring that the units are consistent throughout the calculation.
What is the concept of average acceleration?
-Average acceleration is the change in velocity divided by the change in time (a = Δv / Δt) and describes the rate at which an object's velocity changes over time.
Why is it important to draw a picture when solving a physics problem?
-Drawing a picture is important because it helps visualize the problem, making it easier to understand the situation and find the solution.
How can you find the time it takes for an object to travel a certain distance if you know the average velocity?
-You can find the time it takes by using the formula time (t) equals distance (d) divided by velocity (v), rearranged as t = d / v.
Outlines
📚 Introduction to Physics and Problem-Solving
The video begins with an introduction to a physics tutorial course, emphasizing a practical approach to learning physics through example problems rather than lengthy lectures and complex derivations. The instructor shares their experience in teaching various subjects, including algebra, calculus, trigonometry, and physics, and acknowledges that physics is notably challenging due to the nature of word problems. The course promises a straightforward lecture followed by problem-solving techniques, and reassures students that it's normal not to know how to start a physics problem. The goal is to build understanding by progressing through the course, starting with one-dimensional motion.
📏 Understanding Displacement and Velocity
The second paragraph delves into the concept of displacement in physics, which is the change in position of an object. Using an example with a ruler and a bug, the instructor clarifies how displacement is calculated as the final position minus the initial position, represented as ΔX. The paragraph also introduces velocity as a measure of how fast an object is moving and differentiates it from speed by emphasizing that velocity includes direction. The units for displacement and velocity are discussed, with meters being the standard unit for distance in physics and meters per second for velocity.
🚀 Average Velocity and its Calculation
The third paragraph explains the concept of average velocity, which is the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken. The instructor uses a graph to illustrate how velocity can change over time, emphasizing that average velocity smooths out these changes to provide an overall speed for the entire journey. The formula for average velocity (ΔX/Δt) is provided, and the units of average velocity are shown to be meters per second, consistent with the units of distance and time.
⏱️ Unit Conversions and Marathon Speed Calculation
The fourth paragraph presents a problem involving unit conversions and the calculation of speed. Given a marathon record time and distance, the task is to find the speed in miles per hour. The instructor demonstrates how to convert yards to miles and minutes and seconds to hours, emphasizing the importance of consistent units for calculations. By converting the distance to miles and the time to hours, the average speed of the marathon runner is calculated using the formula for velocity, resulting in a speed of 12.2 miles per hour.
🔄 Conversion Factors and Acceleration Calculation
The fifth paragraph focuses on converting units, specifically yards to miles and seconds to hours, using conversion factors. The instructor provides a step-by-step method for converting 385 yards to miles and 21 seconds to hours, highlighting the process of canceling out units to reach the desired unit of measurement. The paragraph reinforces the concept that physics problems often involve converting between different units to find a solution.
🚀 Calculating Speed and Acceleration
The sixth paragraph involves a thought experiment of shooting a person out of a cannon to the moon. The problem requires calculating the average acceleration experienced by the person. The instructor uses the formula for average acceleration (ΔV/Δt), where ΔV is the change in velocity and Δt is the change in time. By assuming uniform acceleration, the average velocity is calculated as the average of the initial and final velocities. The time taken to travel the length of the cannon is found using the average velocity and the distance of the cannon. Finally, the average acceleration is calculated, resulting in an acceleration significantly greater than the acceleration due to gravity, emphasizing the extreme nature of the hypothetical scenario.
⚖️ Comparing Acceleration to Gravity
The seventh paragraph concludes the thought experiment by comparing the calculated acceleration from the cannon to the acceleration due to gravity. The instructor converts the acceleration from kilometers per second squared to meters per second squared to facilitate comparison. The result is a significant acceleration that underscores the impracticality and danger of such an experiment, highlighting the vast difference between the calculated acceleration and the gentle pull of Earth's gravity.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡One-dimensional motion
💡Displacement
💡Velocity
💡Average velocity
💡Unit conversion
💡Acceleration
💡Average acceleration
💡Units of measurement
💡Physics problems
💡Conceptual understanding
💡Cannon problem
Highlights
The course aims to teach fundamental concepts of physics through working example problems rather than lengthy lectures.
Physics is considered a challenging subject to teach due to students' difficulties with word problems.
The course emphasizes learning physics by working through problems, starting with basic lectures and progressing to problem-solving.
Units in physics, such as meters for distance, are introduced and used throughout the course.
Displacement is defined as the change in position and is calculated as the final position minus the initial position.
Velocity is described as speed with a specified direction, and its unit is meters per second.
Average velocity is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken.
An example problem demonstrates converting units, such as yards to miles and seconds to hours, to calculate average velocity.
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity over time and is measured in meters per second squared.
The concept of average acceleration is introduced, which is the change in velocity divided by the change in time.
A problem involving a person being shot out of a cannon at a high velocity is used to illustrate the calculation of average acceleration.
The importance of drawing a picture to visualize the problem is emphasized for better understanding and solution.
The method of converting units is highlighted as a crucial skill for solving physics problems.
The concept of average velocity is used to calculate the time it takes for the person to travel through the cannon.
The final calculated acceleration of the person shot from the cannon is compared to the acceleration due to gravity to emphasize its magnitude.
The course concludes by reinforcing the idea that physics problems require careful consideration and consistent unit conversion for accurate solutions.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: