Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures Examples, Classification of Matter, Chemistry
TLDRThis video script clearly differentiates between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition that appears as one clear solution, such as saltwater and air. In contrast, heterogeneous mixtures consist of visibly distinct parts, like oil and water or sand and water. The key to identifying these mixtures lies in observing whether there's one clear solution or multiple distinguishable parts. The video uses relatable examples to elucidate the concept, enhancing understanding and retention of the topic.
Takeaways
- 🌟 A homogeneous mixture has indistinguishable parts, appearing as one clear solution.
- 🔍 In a heterogeneous mixture, multiple distinguishable parts are visible.
- 💧 Saltwater is an example of a homogeneous mixture, showing only one uniform part.
- 🥄 Oil and water form a heterogeneous mixture due to their immiscibility and distinct layers.
- 🏅 Brass is a homogeneous mixture, being an alloy of zinc and copper with uniformly distributed atoms.
- 🏖️ Sand and water constitute a heterogeneous mixture, as the sand settles at the bottom and is visibly separate from the water.
- 🌬️ Air is a homogeneous mixture, with its components like nitrogen, oxygen, and argon uniformly distributed and not visibly distinguishable.
- 🍹 Rubbing alcohol in a bottle appears as one clear solution, making it a homogeneous mixture.
- 🥗 A tossed salad with ranch dressing is heterogeneous as the ranch (dressing) and salad (ingredients) are visibly distinct parts.
- 🔎 The key to identifying a mixture as homogeneous or heterogeneous lies in the visibility of its components and their uniformity.
- 📚 Understanding these concepts can help in classifying and analyzing different types of mixtures in various contexts.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between a homogeneous and a heterogeneous mixture?
-A homogeneous mixture has uniformly distributed components that are not visibly distinguishable, while a heterogeneous mixture has components that are visibly distinct and can be differentiated by their appearance or position.
How can you identify a homogeneous mixture?
-A mixture is identified as homogeneous if it appears as a single, clear solution without any distinguishable parts or phases.
What is an example of a heterogeneous mixture?
-Oil and water is an example of a heterogeneous mixture because the two substances do not mix and can be seen as two distinct layers with the denser water at the bottom and the lighter oil on top.
How does the density of substances affect their mixture?
-Density affects the分层 of substances in a mixture. In the case of oil and water, water being denser will form the lower layer while the less dense oil will form the upper layer.
What is an alloy and how does it relate to homogeneous mixtures?
-An alloy is a solid solution of one metal dissolved in another, like zinc and copper forming brass. Alloys are examples of homogeneous mixtures because their composition is uniform throughout the material.
How does sand and water differ from salt and water in terms of mixture classification?
-Salt and water form a homogeneous mixture as salt dissolves and doesn't create distinguishable parts. In contrast, sand and water form a heterogeneous mixture because sand doesn't dissolve well and remains as a distinguishable part, settling at the bottom.
What are the main components of air and how are they distributed?
-Air contains nitrogen gas, oxygen gas, argon gas, water vapor, and carbon dioxide. These gases are uniformly distributed throughout the air, making it a homogeneous mixture.
How can you tell if a mixture of rubbing alcohol and water is homogeneous?
-A mixture of rubbing alcohol and water is homogeneous if it appears as one clear solution without any visible separation of the alcohol and water components.
What makes a tossed salad with ranch dressing heterogeneous?
-A tossed salad with ranch dressing is considered heterogeneous because you can visibly distinguish the ranch dressing and the individual salad components, such as lettuce and other vegetables.
How does the concept of distinguishability relate to the classification of mixtures?
-The ability to distinguish components within a mixture is a key factor in classifying it as either homogeneous or heterogeneous. Visible parts indicate a heterogeneous mixture, while a single, clear solution indicates a homogeneous mixture.
What can you learn about a mixture by observing its composition and appearance?
-By observing whether the components of a mixture are uniformly distributed or visibly distinct, you can determine if it is a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture, which provides insights into its properties and potential applications.
Outlines
🌟 Understanding Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures
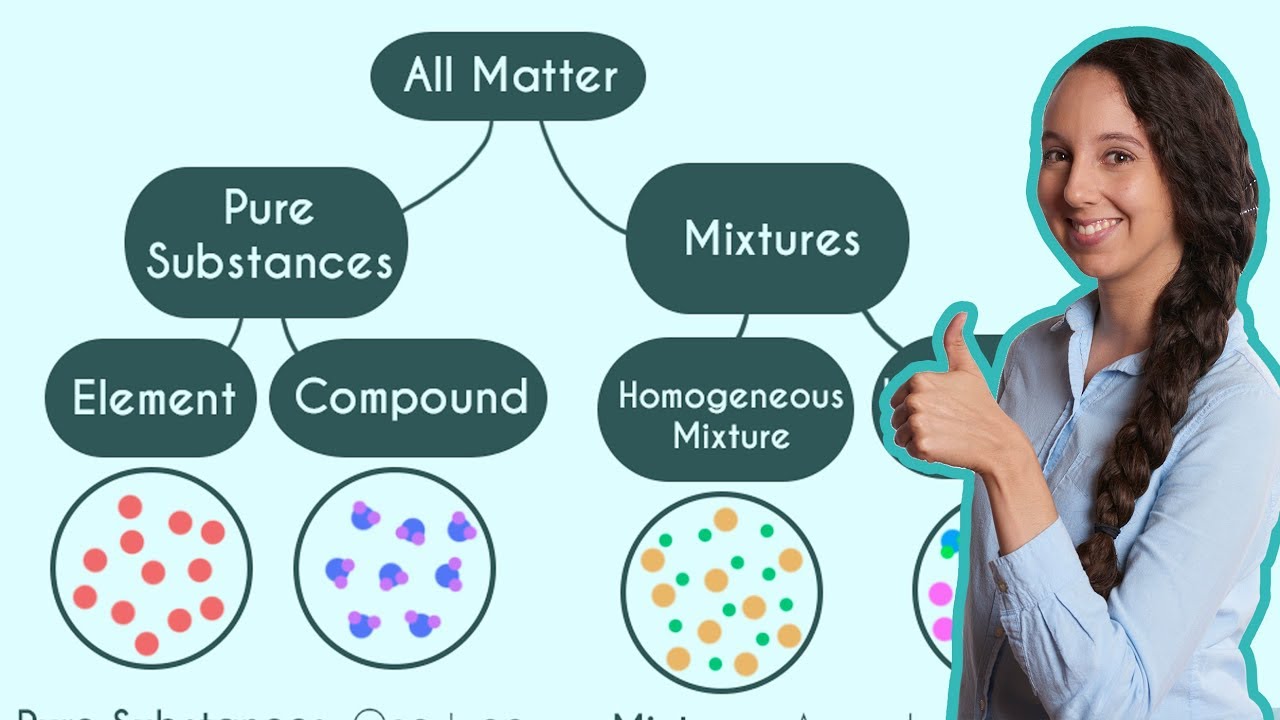
This paragraph introduces the main topic of the video: the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. It explains that a homogeneous mixture consists of parts that are uniformly distributed and not visibly distinguishable, like saltwater, which appears as a single clear solution. In contrast, a heterogeneous mixture has multiple parts that are distinguishable, such as oil and water, where oil floats on top of the water due to differences in density. The paragraph also provides examples of both types of mixtures, including brass (a homogeneous alloy of zinc and copper) and sand in water (a heterogeneous mixture where sand settles at the bottom), to illustrate the concepts discussed.
🔍 Further Examples and Conclusion
The second paragraph continues the discussion on mixtures by providing additional examples and a summary of the key points. It reiterates that sand and water form a heterogeneous mixture because the sand is visibly distinct from the water. The paragraph then addresses air as a homogeneous mixture, as its components—nitrogen, oxygen, argon, water vapor, and carbon dioxide—are uniformly distributed and not visibly separated. Lastly, it examines the mixture of rubbing alcohol and ranch dressing, concluding that while the former is homogeneous, the latter is heterogeneous due to the visible distinction of its components. The paragraph concludes by encouraging viewers to apply their newfound knowledge to identify mixture types.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡homogeneous mixture
💡heterogeneous mixture
💡composition
💡alloy
💡visible parts
💡density
💡dissolving
💡rubb and alcohol
💡tossed salad with ranch
💡clear solution
💡mixture
Highlights
The main topic of the video is the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
A homogeneous mixture has visibly indistinguishable parts, appearing as one clear solution.
In a heterogeneous mixture, multiple distinguishable parts are visible.
Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition throughout.
Heterogeneous mixtures have compositions that can vary by position.
Saltwater is an example of a homogeneous mixture, appearing as one clear solution.
Oil and water form a heterogeneous mixture due to their immiscibility and visible separation.
Brass is a homogeneous mixture, being an alloy of zinc and copper with atoms uniformly distributed.
Sand and water create a heterogeneous mixture, as the sand settles at the bottom and is visibly distinct from the water.
Air is a homogeneous mixture, with its components uniformly distributed and not visibly distinguishable.
Rubbing alcohol appears as one clear solution, making it a homogeneous mixture.
A tossed salad with ranch dressing is a heterogeneous mixture due to the distinguishable parts.
The key to identifying a mixture's type is observing whether it consists of one clear solution or distinguishable parts.
The video aims to help viewers understand and determine whether a mixture is homogeneous or heterogeneous.
The distinction between mixtures is based on the visibility and uniformity of their components.
The practical applications of understanding mixtures include chemistry, material science, and everyday observations.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixture | Chemistry

What is Mixture in Chemistry?

Types of Matter - Elements, Compounds, Mixtures, and Pure Substances

Heterogenous vs Homogenous (Definitions, Examples, & Practice)
Pure Substances and Mixtures! (Classification of Matter)

What are Homogeneous & Heterogeneous Mixtures in Chemistry?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: