States of Matter (Phases of Matter): Solids, Liquids, and Gases
TLDRThe video script explores the three main phases of matter: solids, liquids, and gases. It explains that matter is anything with mass and volume, occupying space. Solids have a fixed shape and volume with closely packed, vibrating particles. Liquids take the shape of their container but maintain a definite volume, with particles that move past each other. Gases, both visible and invisible, have no fixed shape or volume, compress easily, and their particles are far apart and in rapid motion. This introduction to states of matter highlights the unique characteristics and behaviors of each phase.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Matter is defined as anything that occupies space and has mass, which includes solids, liquids, and gases.
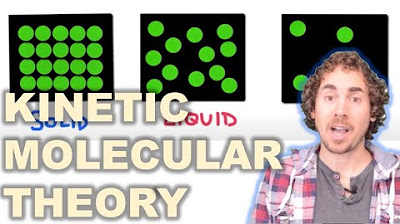
- 📏 Solids are characterized by having a definite shape and volume, with particles that are closely packed and vibrate in place but do not move around.
- 🛡️ Solids are incompressible due to the lack of space between particles, making it difficult to reduce their volume.
- 💧 Liquids have an indefinite shape as they take the form of their container, but maintain a definite volume, with particles that are close together and move around, allowing them to flow.
- 🌊 Liquids are also incompressible because there is minimal space between particles, preventing them from being squeezed together more closely.
- 🌬️ Gases have both an indefinite shape and volume, filling any container they are in and expanding or contracting to fit the available space.
- 🚀 Gas particles are far apart and in constant rapid motion, which allows gases to be easily compressed or expanded.
- 🔍 Zooming into the microscopic view of matter reveals that the behavior of particles in each phase is responsible for their macroscopic characteristics.
- 🔥 The unique properties of each phase of matter are determined by the amount of space between particles and their ability to move or stay fixed in place.
- 📚 Understanding the phases of matter and their characteristics is fundamental to many areas of science, including chemistry and physics.
- 🌐 The study of matter and its phases is applicable to everyday life, from the materials we use to the air we breathe.
Q & A
What is the scientific term for 'stuff' that takes up space and has mass?
-The scientific term for 'stuff' that takes up space and has mass is 'matter'.
What are the three common phases of matter?
-The three common phases of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
What are the defining characteristics of a solid?
-A solid has a definite shape and a definite volume, and it is incompressible.
How do the particles in a solid behave microscopically?
-The particles in a solid are closely packed together, vibrating in place but not moving around to new locations.
What is the reason behind the definite shape of a solid?
-The definite shape of a solid is due to the particles being fixed in one position and not moving to new locations.
What are the characteristics of a liquid in terms of shape and volume?
-A liquid has an indefinite shape, taking the shape of its container, but it has a definite volume that does not change when the shape changes.
Why are liquids considered incompressible?
-Liquids are considered incompressible because there is not much space between the particles, making it difficult to squeeze them together any closer.
How do the particles in a gas phase differ from those in solids and liquids?
-The particles in a gas phase are far apart and in constant rapid motion, allowing the gas to expand or contract to fit its container and making it compressible.
What happens to the volume of a gas when the top of a container is removed?
-When the top of a container is removed, the gas expands to fill the larger volume of the now open container.
How does the compressibility of gases relate to the spacing between their particles?
-Gases are compressible because the particles are far apart from each other, allowing for easy squeezing into a smaller volume due to the extra space between them.
In summary, how do the characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases relate to the behavior of their particles?
-Solids have closely packed, non-moving particles, making them hard and incompressible with a definite shape and volume. Liquids have closely packed particles that move around but not far apart, resulting in an indefinite shape but a definite volume and low compressibility. Gases have widely spaced, rapidly moving particles, leading to no definite shape or volume and high compressibility.
Outlines
🔬 Introduction to the Phases of Matter
This paragraph introduces the concept of matter and its different phases, also known as states. It explains that matter is anything that occupies space and has mass, and categorizes it into three main phases: solid, liquid, and gas. The paragraph also mentions the existence of other phases like plasma but focuses on the primary three. It sets the stage for a more in-depth exploration of each phase's characteristics from both macroscopic and microscopic perspectives.
🏗️ Characteristics and Behavior of Solids
This paragraph delves into the properties of solids, highlighting their definite shape and volume, and their incompressibility. It uses examples like a metal cube, a rock, and a gold bar to illustrate these characteristics. Microscopically, the paragraph describes solids as being composed of closely packed particles that vibrate in place but do not move around. This fixed nature of particles is what gives solids their rigidity and resistance to shape change and compression.
💧 Understanding Liquids and Their Properties
The paragraph discusses the properties of liquids, which have an indefinite shape but a definite volume. It explains that liquids take the shape of their container but maintain a constant volume, regardless of container shape. Liquids are also incompressible, as demonstrated by the inability to reduce their volume in a sealed syringe. Microscopically, the particles in a liquid are close together but are free to move around, allowing liquids to flow and change shape. This movement is what makes liquids take the shape of their container and resist compression.
🌬️ Gases: The Invisible and Compressible Phase
This paragraph focuses on gases, which have both indefinite shape and volume. Gases expand or contract to fit their containers, making them highly adaptable to available space. Unlike solids and liquids, gases are compressible, as shown by the ability to reduce their volume in a syringe. Microscopically, gas particles are far apart and in constant rapid motion, allowing for easy expansion and compression. The large distances between particles in gases explain their compressibility and the fact that they can fill any container, regardless of shape or size.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡Matter
💡Phases of Matter
💡Solid
💡Liquid
💡Gas
💡Definite Shape
💡Definite Volume
💡Incompressibility
💡Microscopic View
💡Compression
Highlights
Matter is defined as anything that takes up space and has mass, which includes solids, liquids, and gases.
Solids have a definite shape and volume, and are characterized by their incompressibility.
The microscopic structure of solids involves closely packed particles that vibrate in place but do not move around.
Liquids, on the other hand, have an indefinite shape but a definite volume, taking the shape of their container.
Liquid particles are closely packed but can move around, allowing liquids to flow and change shape.
Despite their fluidity, liquids are also incompressible due to the minimal space between particles.
Gases exhibit indefinite shapes and volumes, expanding or contracting to fit their containers.
Gas particles are far apart and in constant rapid motion, which contributes to their compressibility.
The three main phases of matter—solids, liquids, and gases—differ significantly in their particle arrangement and behavior.
Understanding the phases of matter is crucial for scientific and technical applications, from everyday objects to advanced materials.
The concept of compressibility versus incompressibility is key to distinguishing between the phases of matter.
The video provides a detailed comparison of the macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases.
The definiteness of shape and volume is a fundamental concept in the classification of the phases of matter.
The movement and spacing of particles within a phase play a critical role in determining the phase's properties.
The video offers a comprehensive educational overview suitable for a wide range of audiences interested in the properties of matter.
The scientific explanation of the phases of matter helps to clarify common misconceptions and deepen understanding.
The relationship between the macroscopic properties of matter and the microscopic behavior of its particles is a central theme of the video.
Transcripts
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: