States of Matter - Solids, Liquids, Gases & Plasma - Chemistry
TLDRThe video script delves into the fundamental states of matter—solids, liquids, and gases—each defined by their distinct properties. Solids, with a fixed shape and volume, are rigid and incompressible due to tightly packed atoms. Liquids, while maintaining a definite volume, lack a fixed shape, conforming to the container's form and exhibiting fluidity. Gases, with their low density and high compressibility, are highly fluid and can flow through various spaces. Density is explored as mass per unit volume, with solids generally denser than liquids and gases. The video also explains phase changes, such as melting, vaporization, sublimation, freezing, condensation, and deposition, which are driven by heat absorption or release. An introduction to the fourth state of matter, plasma, is provided, highlighting its ionized nature and ability to conduct electricity, with examples from the sun, neon signs, and lightning. The script concludes by emphasizing the importance of temperature in controlling the state of matter and encourages viewers to subscribe for more educational content.
Takeaways
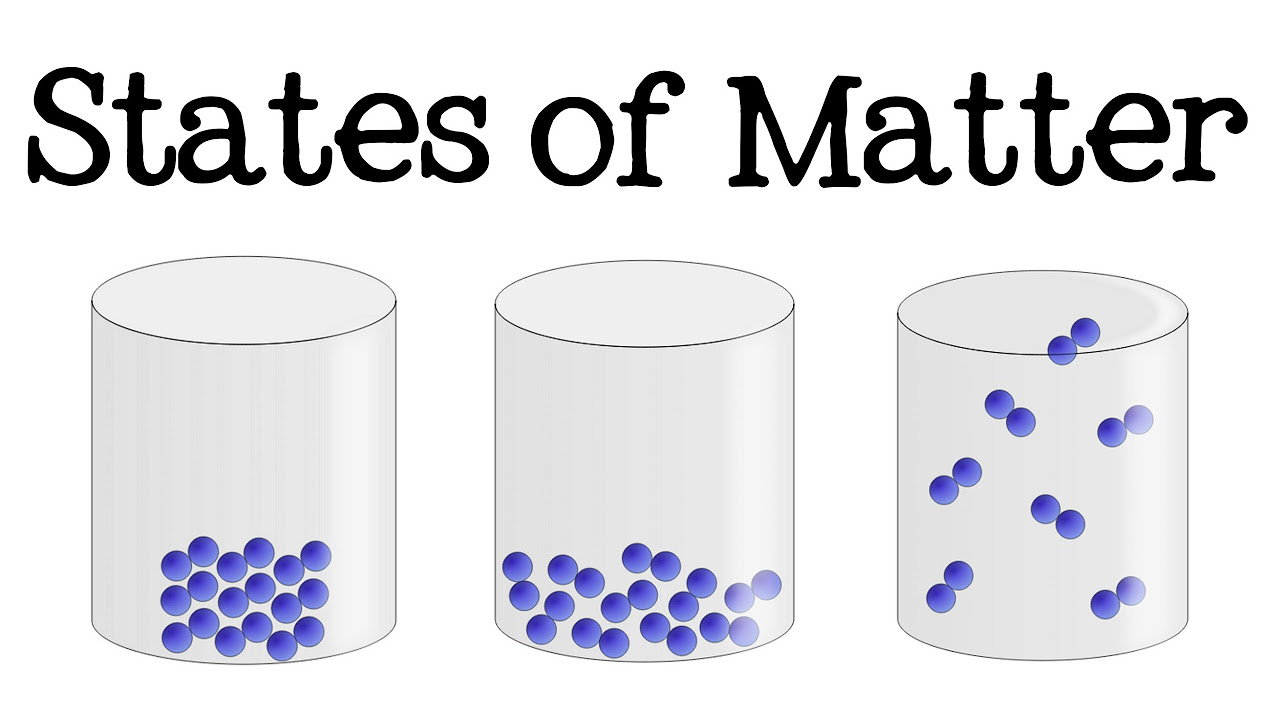
- 🧊 **Solids**: Have a definite shape and volume, are rigid, and their atoms are closely packed with little space between them, making them incompressible.
- 💧 **Liquids**: Have a definite volume but no fixed shape, take the shape of their container, and can flow. Their atoms are close together but not as neatly arranged as in solids.
- 🌫️ **Gases**: Can flow and fill their container, have very low density, and are highly compressible due to the large empty spaces between their particles.
- 🔵 **Density**: Measured as mass divided by volume, with solids generally having higher density than liquids, and liquids having higher density than gases.
- ❄️ **Exception**: Ice (solid water) is less dense than liquid water, which is a rare case where the solid state is less dense than the liquid state.
- 🔥 **Phase Changes**: Include melting (solid to liquid), vaporization (liquid to gas), sublimation (solid to gas), freezing (liquid to solid), condensation (gas to liquid), and deposition (gas to solid).
- 🌡️ **Heat and Phase Changes**: Adding heat generally causes a substance to move from solid to liquid to gas, while removing heat leads to the reverse transitions.
- 🔥 **Endothermic Processes**: Require heat absorption and include melting, vaporization, and sublimation.
- 🏮 **Exothermic Processes**: Release heat and include freezing, condensation, and deposition.
- ⚡ **Plasma**: The fourth state of matter, an ionized gas that conducts electricity and can be created by adding heat or electricity to a gas.
- 🌟 **Ionization and Recombination**: The process of creating plasma by adding heat or electricity (ionization) and the reverse process where ions and electrons recombine to form neutral atoms, often emitting light and heat.
- 📚 **Educational Content**: The video script provides an educational overview of the states of matter, phase changes, and plasma, encouraging viewers to subscribe for more content.
Q & A
What is the basic definition of matter?
-Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It is composed of individual tiny particles known as atoms.
How does the shape and volume of a solid differ from that of a liquid?
-A solid has a definite shape and a fixed volume. In contrast, a liquid has no definite shape but maintains a definite volume, taking the shape of its container.
What property of liquids and gases allows them to be classified as 'fluids'?
-Liquids and gases are classified as 'fluids' because they can flow. This is due to the ability of their particles to move and change position.
How is the density of solids, liquids, and gases generally compared?
-Solids generally have a higher density than liquids, and gases have a very low density. This is because atoms in solids are closely packed, while gases have a lot of empty space between their particles.
Why is the density of liquid water higher than that of ice?
-The density of liquid water is higher than ice because of the molecular arrangement. Ice has more open structure leading to lower density, whereas liquid water's molecules are closer together, resulting in a higher density.
What is the term used to describe the process of a solid turning into a liquid?
-The process of a solid turning into a liquid is known as melting.
How does the process of vaporization differ from sublimation?
-Vaporization is the process where a liquid turns into a gas upon heating, while sublimation is the process where a solid turns directly into a gas without passing through the liquid phase, as seen with dry ice.
What are the three endothermic processes associated with phase changes?
-The three endothermic processes are melting (solid to liquid), vaporization (liquid to gas), and sublimation (solid to gas). These processes require the absorption of heat.
What is plasma and how is it different from a gas?
-Plasma is a fourth state of matter that is an ionized gas. It is created by adding heat to a gas until the atoms lose their electrons, forming ions and free electrons. Unlike a neutral gas, plasma can conduct electricity.
How do neon signs generate light?
-Neon signs generate light through the process of ionization. Electricity is used to separate electrons from gas particles, creating plasma. When the ions and electrons recombine, they emit light and heat energy.
What is the process called when a gas is heated to the point that it becomes a plasma?
-The process of a gas turning into a plasma upon heating is known as ionization.
How can the state of matter be controlled?
-The state of matter can be controlled by either increasing or decreasing the temperature. Adding heat can cause a phase change from solid to liquid or liquid to gas, while removing heat can cause a phase change from gas to liquid or liquid to solid.
Outlines
🧊 Understanding States of Matter
This paragraph introduces the three common states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases. Matter is defined as anything with mass that takes up space and is made up of tiny particles called atoms. Solids have a fixed shape and volume, while liquids have no fixed shape but maintain a definite volume. Gases are capable of flowing and do not have a fixed shape or volume. The concept of density is also introduced, with solids having a high density, liquids also having a relatively high density (though usually less than solids), and gases having a very low density. An exception to the general rule is noted, where liquid water has a higher density than its solid form, ice.
🌡️ Phase Changes and Compressibility
The paragraph delves into phase changes, which are processes that convert one state of matter into another. For instance, adding heat to a solid (like ice) causes it to melt into a liquid (water), and further heating turns the liquid into a gas (steam). Conversely, removing heat can cause a gas to condense into a liquid or a liquid to solidify. The paragraph also explains that solids and liquids are slightly compressible due to their close atomic packing, whereas gases are highly compressible because of the significant empty space between particles. Terms like melting, vaporization, sublimation, freezing, condensation, and deposition are defined in relation to phase changes. Additionally, the concept of a fourth state of matter, plasma, is briefly mentioned, which is created by adding heat to a gas until it becomes ionized.
🌟 The Fourth State of Matter: Plasma
This paragraph focuses on the properties and formation of plasma, the fourth state of matter. Plasma is an ionized gas that can conduct electricity, unlike a neutral gas. It is created through ionization, where gas particles are heated to such an extent that electrons are stripped away from atoms, resulting in positively charged ions and free electrons. Plasma is found in various natural and man-made phenomena, such as the sun, neon signs, and lightning. The paragraph also explains that when ions and electrons recombine, they emit light and heat, which is the principle behind the glowing effect in neon signs. The process of recombination, where ionized gas particles and electrons combine to form neutral atoms, is also discussed.
Mindmap
Keywords
💡States of Matter
💡Solid
💡Liquid
💡Gas
💡Density
💡Phase Changes
💡Melting
💡Vaporization
💡Sublimation
💡Plasma
💡Ionization
Highlights
Matter is defined as anything with mass that takes up space, composed of tiny particles known as atoms.
Matter can be classified into three states: solids, liquids, and gases.
Solids have a definite shape and volume, such as a rock.
Liquids have no definite shape but maintain a definite volume, taking the shape of their container.
Gases can flow through pipes and are highly compressible due to the large empty spaces between particles.
Density is calculated as mass divided by volume and varies among solids, liquids, and gases.
Solids generally have a higher density than liquids, with exceptions like water and ice.
Gases have a very low density, making them highly compressible compared to solids and liquids.
Phase changes involve converting one state of matter into another, such as melting, vaporization, and sublimation.
Melting is the process of converting a solid into a liquid by adding heat.
Vaporization occurs when a liquid is heated and turns into a gas.
Sublimation is the direct transition from a solid to a gas, exemplified by dry ice.
Endothermic processes require heat absorption, such as melting, vaporization, and sublimation.
Exothermic processes release heat, including freezing, condensation, and deposition.
Plasma is a fourth state of matter, an ionized gas that conducts electricity.
Ionization is the process of turning a gas into a plasma by adding heat or electricity.
Recombination is the reverse process of ionization, where ions and electrons recombine to form neutral atoms.
Neon signs and lightning are examples of plasma in action, where recombination emits light and heat.
The video provides a comprehensive overview of the properties and behaviors of the four states of matter.
Transcripts
Browse More Related Video

Phases of Matter and Phase Change Diagrams

States of Matter (Phases of Matter): Solids, Liquids, and Gases

What are States of Matter in Chemistry? - Solid - Liquid - Gas - Plasma - [1-1-2]

States of Matter : Solid Liquid Gas
3 States of Matter for Kids (Solid, Liquid, Gas): Science for Children - FreeSchool

Intro to fluids and pressure
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
Thanks for rating: